Vitamin E for skin is an antioxidant that helps defend your skin against damage from sunlight, smoke, and pollution. It stays in the oily parts of your skin cells and protects those fats from breaking down. You get it from food and skincare. You can also use it in a safe product on your face or body.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhen you use it the right way, it helps your barrier hold water, eases dryness, and supports a smoother look. It does not replace sunscreen or medical care. It works best as part of a simple daily routine that you can follow.
What Is Vitamin E?
Overview of vitamin E and its natural forms
Vitamin E is a group of fat-soluble antioxidants. The most well-known forms are tocopherols and tocotrienols. Alpha-tocopherol is the main form in human skin. These molecules sit in cell membranes. They guard fats from damage. They also support the skin’s own repair systems.
Vitamin E comes in two main types on labels. The natural form is d-alpha-tocopherol. The synthetic mix is dl-alpha-tocopherol. Your body keeps its natural form a little better. Both can work in skincare. The dose, the formula, and the partner ingredients matter more than the label alone.
How it protects skin from oxidative stress
Free radicals form every day in the skin. Sunlight, smoke, and pollution raise them fast. These unstable bits attack cell fats and proteins. Vitamin E donates an electron. That act stops the chain reaction. It helps limit lipid peroxidation. It keeps cell membranes more stable. It also supports the skin’s enzymes that calm stress after UV.
Fat-soluble vitamin found in oils, nuts, and seeds
Vitamin E dissolves in fat. That means it likes oils more than water. Nature packs it in nuts, seeds, and plant oils. Sunflower oil, almond, hazelnut, and wheat germ are rich in vitamin E. Avocado and spinach also help. A simple diet with nuts and seeds covers the daily needs for most people.
What Does Vitamin E Do for Your Skin?
Neutralizes free radicals that damage skin cells
UV light sparks free radicals. Smoke and city air do the same. Vitamin E neutralizes them in the lipid layer. This lowers stress markers in the skin. It may ease redness after the sun. It helps skin look calmer and less dull.
Strengthens skin barrier and locks in moisture
The outer layer of skin holds fats and proteins in neat layers. Vitamin E sits in those fats. It slows water loss. It helps skin feel soft and springy. A strong barrier means less tightness and flaking. That is why many moisturizers include it.
Reduces signs of premature aging and dullness
Oxidative stress speeds lines and spots. Vitamin E lowers that stress. It supports a smoother look. It helps improve glow by keeping the lipid layer intact. Skin reflects light better when the surface is even and moist.
Supports wound healing and scar recovery
Small studies suggest vitamin E can aid in repair. It helps calm lipid damage around a wound. That may support better texture over time. Results vary. Some people see no change. A few get irritated. Use it as part of a full routine, not the only tool.
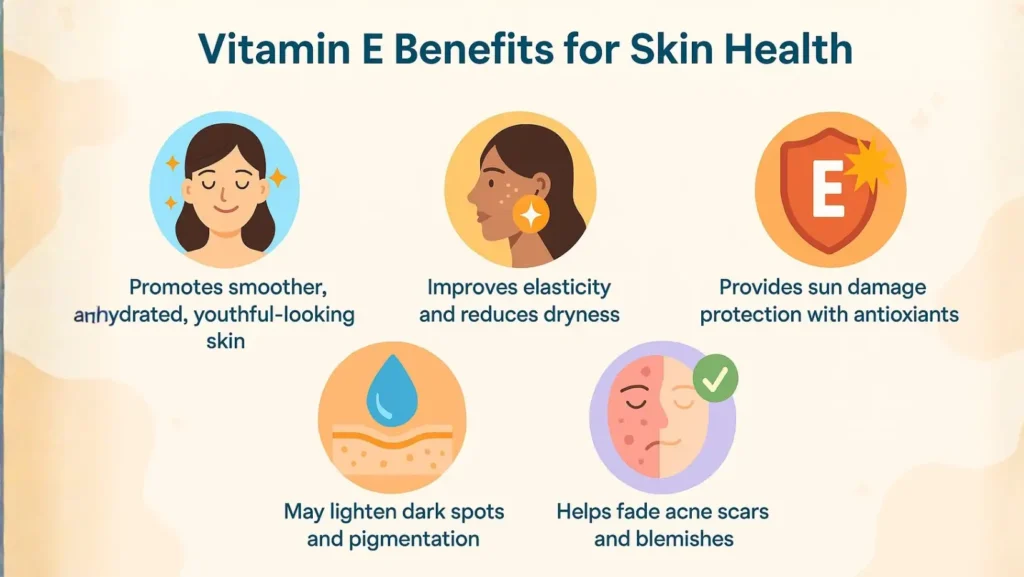
Vitamin E Benefits for Skin Health
Promotes smoother, hydrated, youthful-looking skin
Moist skin looks healthier. Vitamin E helps hold water in the outer layer. It improves slip in formulas. It pairs well with emollients like squalane and ceramides. The result feels soft, not greasy, when the blend is right.
Improves elasticity and reduces dryness
Elasticity depends on proteins and lipids. Oxidative stress can harm both. Vitamin E helps limit that harm. Users often report less flaky skin after regular use. Fine lines from dryness look softer when the barrier holds.
May lighten dark spots and pigmentation
Vitamin E does not bleach skin. It can help reduce new dark spots by lowering oxidative stress from UV. When paired with vitamin C, results improve. Stubborn spots often need sunscreen, vitamin C, and retinoids as well. Think “support,” not “magic fix.”
Helps fade acne scars and blemishes
Post-acne marks fade with time. Vitamin E may speed the process a little by easing oxidative stress and dryness. Some people with acne get clogged pores from heavy oils. Patch test first. Choose non-comedogenic blends.
Provides sun damage protection with antioxidants
Vitamin E is not a sunscreen. It cannot replace SPF. It can help reduce UV-induced free radicals. It also helps calm skin after exposure. For best results, use daily SPF and antioxidants together in the morning.
Vitamin E Oil for Skin: How It Works
Deeply moisturizes and repairs damaged skin
Oil rich in vitamin E coats the skin’s surface. It fills small gaps between cells. That lowers water loss. It also softens rough spots. Over time, the barrier strengthens. Redness from dryness fades. Cracked heels and cuticles respond well to this approach.
Enhances collagen production for firmness
Vitamin E supports an environment that protects collagen from oxidative stress. That helps collagen work better. The vitamin does not make collagen on its own. It helps prevent the breakdown that stress can cause.
Best used at night for maximum absorption
Skin repairs while you sleep. Oil blends absorb well when you apply them to slightly damp skin at night. A few drops are enough for the face. More can feel heavy. Layer water-based serum first, then a cream, then the oil if your skin is very dry.
Combine with vitamin C or aloe vera for brightening
Vitamin C and vitamin E recycle each other in the skin’s antioxidant network. Together they work better. Aloe vera can soothe. A formula with both antioxidant vitamins and soothing bases can improve tone and comfort over weeks.
Vitamin E Capsules for Skin
How vitamin E capsules nourish skin from within
Dietary vitamin E supports cell membranes across the body. That includes skin. A balanced intake helps the skin handle daily oxidative stress. Food sources are best. Supplements help only if your diet lacks them or your doctor advises them.
Safe daily intake and dosage limits
Adults need about 15 mg alpha-tocopherol per day from food and supplements combined. The upper limit is high, at 1000 mg per day from supplements. That high dose is not a target. High doses can raise bleeding risk. Always check with a clinician if you take blood thinners.
Topical use: breaking capsules for direct application
Some people pierce a capsule and spread the oil. This can feel thick and sticky. Capsules are made for swallowing, not for skin. They often contain soybean oil and gelatin. They may not be stable on air exposure. A skincare-grade serum is safer and more pleasant.
Best time to consume for glowing skin results
If a clinician suggests a supplement, take it with a meal that contains fat. Absorption improves with dietary fat. Morning or evening does not matter. Consistency matters more than timing.
Advantages of Vitamin E for Skin Glow
Boosts natural radiance and texture
A moist, smooth surface reflects light better. Vitamin E supports this by sealing in water. It also protects lipids from damage. Over time, tone looks more even. Makeup sits better on calm, soft skin.
Helps skin recover from dryness and pollution
Pollution triggers free radicals on contact. Vitamin E blunts this stress. It helps avoid the rough texture that comes from repeated exposure. A gentle cleanse and a vitamin E cream at night help the skin bounce back.
Protects against UV and environmental stressors
Use sunscreen daily. Add antioxidants like vitamin E and vitamin C. Wear hats and seek shade at midday. These steps work together. Each one lowers cumulative stress and helps the skin stay strong.
How to Use Vitamin E on Skin
Apply vitamin E oil directly to dry or rough areas
Start with clean, damp skin. Warm one or two drops between fingers. Press onto dry spots like cheeks or elbows. Use more on the body than on the face. Stop if you feel stinging or see bumps.
Mix a few drops with moisturizer or serum
Oil blends well with cream. Add one drop to your usual moisturizer. This light mix suits many skin types. It cuts the risk of clogged pores. It also spreads more easily and leaves less shine.
Use as an overnight facial treatment for dull skin
At night, use a gentle cleanser. Apply a hydrating serum. Seal with a vitamin E cream or a light oil blend. Keep a thin layer. Heavy coats can smear on your pillow and irritate your eyes.
Patch test to prevent irritation before full use
Test a small area on the jaw or inner arm. Wait 24 to 48 hours. Check for redness, itching, or small bumps. Skip the product if you react. Try a lighter formula or a lower dose next time.
Best Vitamin E Products and Sources
Vitamin E-rich foods: almonds, sunflower oil, avocados
Snack on almonds or hazelnuts. Add sunflower seeds to salads. Use sunflower or safflower oil in cooking. Avocado on toast helps too. Food gives a full mix of nutrients that support skin beyond vitamin E alone.
Top-rated skincare products with vitamin E
Look for serums or creams that list tocopherol or tocopheryl acetate near the middle of the ingredient list. A mix with vitamin C, ferulic acid, or resveratrol works well in the morning.
For night, pair tocopherol with ceramides and glycerin. Choose fragrance-free if your skin is sensitive. Airless pumps help keep antioxidants stable.
Natural vs. synthetic vitamin E — key differences
Natural vitamin E appears on labels as d-alpha-tocopherol. Synthetic appears as dl-alpha-tocopherol. Natural binds better to your transport proteins. In topical care, both can help when the formula is stable. Judge the full formula, packaging, and your skin’s response, not just one label term.
Vitamin E for Specific Skin Concerns
For dry and flaky skin: Restores the moisture barrier
Dry skin lacks lipids and water. Vitamin E helps rebuild the lipid layer. Use a gentle cleanser, then a rich cream with tocopherol, ceramides, and fatty acids. Apply twice daily. Avoid hot showers and harsh scrubs.
For acne scars: Aids regeneration and tone repair
Marks after acne come from inflammation. Vitamin E can ease that stress. A thin layer in a non-comedogenic base works best. Use sunscreen. Add retinoids at night if your skin tolerates them. Expect a gradual change over the months.
For hyperpigmentation: Helps fade dark patches
Dark patches form from excess melanin and UV stress. Vitamin E helps control oxidative triggers. For faster results, combine with vitamin C and sunscreen. Consider azelaic acid or niacinamide as add-ons. Patience is key.
For aging skin: Reduces wrinkles and fine lines
Fine lines look deeper on dry, stressed skin. Vitamin E supports the lipid layer and protects collagen from free radicals. Pair with retinol or peptides for stronger results. Spread a pea-size amount over the whole face. Do not forget the neck.
Combining Vitamin E with Other Nutrients
Vitamin E + Vitamin C — powerful antioxidant pair
These two antioxidants work in a cycle. Vitamin C can help renew vitamin E after it fights free radicals. Morning use under SPF makes sense. Serums with both show better support against UV-induced stress than either alone.
Vitamin E + Hyaluronic Acid — for deep hydration
Hyaluronic acid draws water into the skin. Vitamin E seals that water in the top layer. Use a HA serum on damp skin. Follow with a vitamin E cream or light oil. This simple stack often cures tightness fast.
Vitamin E + Retinol — anti-aging synergy
Retinol boosts cell turnover and collagen signaling. It can feel harsh at first. Vitamin E helps limit dryness and flaking. Use retinol at night. Buffer with a vitamin E cream after ten minutes. Start twice a week, then increase if your skin is calm.
How to balance for sensitive skin
Keep formulas simple. Avoid strong scents and heavy essential oils. Start with low frequency. One product at a time helps you spot triggers. If you react, stop and reset with a bland moisturizer for a week.
Vitamin E Safety and Side Effects
May cause mild irritation on sensitive skin types
A small number of people react to tocopherol. Signs include redness, itch, or small bumps. Reactions can come from the oil base or the added fragrance, too. Patch testing helps. Less is more at the start.
Avoid excessive oral doses (toxicity risk)
High supplement doses can raise bleeding risk. They may interact with blood thinners and some chemotherapy drugs. Do not exceed the dose your clinician recommends. Food first is the safer plan for most people.
Consult a dermatologist for acne-prone skin use
Some oils clog pores. If you break out, choose a light gel-cream with tocopherol in a low dose. Keep using sunscreen daily. If acne persists, see a dermatologist. You may need retinoids or other proven treatments.
Use only dermatologist-tested topical forms
Pick products tested for skin use and stability. Capsule oil meant for swallowing can oxidize quickly in the air. Skincare-grade oils or creams are safer. Airless pumps and opaque tubes help keep the antioxidant fresh.
When to See a Dermatologist
Persistent irritation after topical application
Stop the product if redness or burning lasts more than two days. Make an appointment. Bring the product list with you. A patch test in a clinic can find the real trigger.
Vitamin E allergies or eczema flare-ups
If eczema worsens, pause vitamin E products. Resume only under guidance. Your clinician may adjust your routine to include bland emollients and short courses of medicated creams.
Advice for mixing vitamin E with prescription creams
If you use tretinoin, benzoyl peroxide, or steroid creams, ask how to layer. Space products to reduce stinging. Often, you will use the prescription at night and vitamin E cream later as a buffer.
FAQs
Is vitamin E good for all skin types?
Most skin types can use it. Dry and mature skin often benefits the most. Oily or acne-prone skin should use light formulas. Patch testing is wise for everyone.
Can I apply vitamin E oil directly to my face?
Yes, in small amounts. Use one or two drops. Apply to damp skin. If you get clogged pores or bumps, switch to a lighter cream with tocopherol.
How often should I use vitamin E on my skin?
Start three nights a week. Move to nightly if your skin stays calm. In the morning, pair a vitamin C serum with SPF. Use vitamin E at night for comfort.
Does vitamin E remove acne scars completely?
No. It can help texture and color over time. Deep scars need extra care, like retinoids, peels, microneedling, or lasers. Talk with a professional about these options.
What’s the difference between vitamin E oil and capsules?
Skincare oil or cream is made for the skin. It often blends with other helpful lipids. Capsules are made for swallowing. They can feel heavy and may oxidize when opened.
Can I use vitamin E daily for glowing skin?
Yes, if your skin tolerates it. Keep the dose small. Pair with sunscreen. Give it six to eight weeks for visible results.
Is vitamin E safe for sensitive or acne-prone skin?
It can be. Choose fragrance-free, non-comedogenic formulas. Patch test before full use. Stop if you see bumps or rash.
How does vitamin E help with pigmentation?
It lowers oxidative triggers that worsen dark spots. It works best with sunscreen and vitamin C. It supports an even tone but does not bleach skin.
Can I mix vitamin E with other skincare ingredients?
Yes. It pairs well with vitamin C, hyaluronic acid, niacinamide, and ceramides. Use care when mixing with strong acids or new retinoids. Add one new product at a time.
Does vitamin E make skin lighter?
No. It helps even tone by reducing stress and dryness. It does not change your natural color.
Should I take vitamin E supplements for better skin?
Food sources are enough for most people. Take a supplement only if your clinician advises it. High doses carry risks.
Can vitamin E help with sunburn recovery?
It can soothe dryness and reduce flaking. Cool compresses and aloe help too. Always protect with SPF to prevent future burns.
Is it safe to use vitamin E around eyes and lips?
Yes, in very small amounts. Avoid direct contact with the eye. Stop if you notice swelling or stinging.
What are natural food sources of vitamin E for skin?
Almonds, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds, avocado, spinach, and plant oils like sunflower and safflower are good sources.

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, Board-Certified Neurologist, providing expert insights and reliable health information.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained neurologist with over a decade of experience. Known for his compassionate care, he specializes in treating neurological conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Dr. Chugh is highly regarded for his patient-centered approach and dedication to providing personalized care.