Yes, acne is hereditary. Genes play a major role in whether you get acne, how severe it becomes, and how long it lasts. You can inherit oilier skin, stronger inflammatory reactions, and greater sensitivity to hormones. This does not mean you have no control. Treatments and daily care still work.
Genetic Causes Of Acne
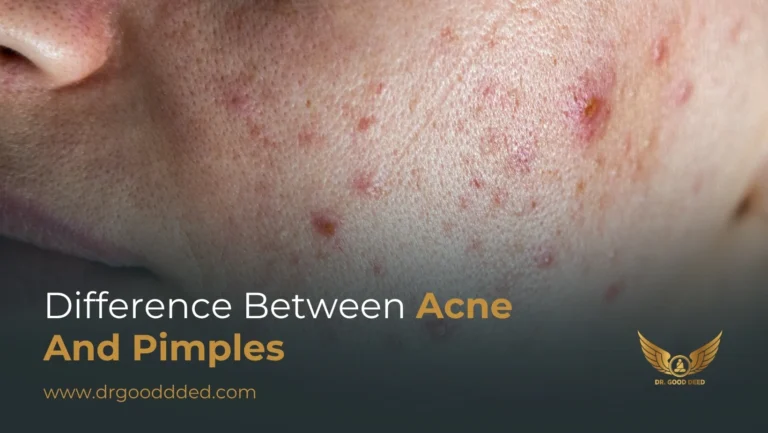
Genes affect many skin parts that cause pimples. They shape oil glands, pore size, and immune reactions. If your family has a pattern of acne, your genes likely raise your risk.
Twin and family studies show a clear genetic link. Identical twins often share acne more than nonidentical twins. One large twin study estimated that genetics explain most of the difference in acne between people. This means genes matter a lot, but the environment also helps decide who actually breaks out.
How Inherited Traits Affect Oil Production And Skin Inflammation
You get oil from sebaceous glands. Some genes make these glands larger or more active. More oil raises the chance that pores will clog. When a pore clogs, bacteria grow. Your immune system fights the bacteria. That fight causes redness and pus. Genes can increase each step of this chain.
For example, some gene variants change how skin cells flake off. Other variants change how strongly your skin reacts to bacteria. Together, these inherited traits can make acne start more easily and heal more slowly.
Evidence From Twin And Family History Studies
Twin studies give strong proof that acne has a genetic basis. Studies of twins show much higher acne match rates in identical twins. A notable study found that about 80 percent of acne risk came from genes in women.
Family studies also show that if parents had acne, children have higher odds of getting it. That higher odds rises with the number of close relatives affected. Still, identical genetics do not guarantee acne. Environment, diet, and hormones also shape outcomes.
Why Genetics Influence Acne Severity And Duration
Genes not only affect the chance of acne. They also affect how bad acne becomes. Some gene variants link to deep inflamed nodules and cysts. Other genes influence how quickly pimples heal.
If your family shows early teen acne that lasts into adulthood, genes likely guide that pattern. Scarring risk also shows family trends. If your relatives scar easily, you may scar more often too. Genetics can raise both the severity and duration of acne.
Is Hormonal Acne Hereditary?
Acne is hereditary when hormones are the key driver. Hormonal acne is linked to how your skin responds to androgens. Androgens are hormones that increase oil production. You can inherit higher sensitivity to these hormones. That sensitivity raises the chance of hormone-driven breakouts, especially around the jaw, chin, and lower face.
How Hormone Sensitivity Is Passed Down Genetically
Your skin has hormone receptors. Genes can make these receptors more active. When receptors are more active, small hormone changes cause big oil boosts. This means normal hormone shifts can trigger acne in people who inherit sensitive receptors. You may notice breakouts at puberty, before periods, or during stress if hormone sensitivity runs in your family. Genetic causes of acne appear when receptors overreact.
PCOS And Inherited Hormonal Disorders Linked To Acne
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, often runs in families. PCOS raises androgen levels in many women. Higher androgens lead to more oil and more acne. If relatives have PCOS and acne, your risk for hormone-driven acne rises.
Doctors check for PCOS when acne shows with irregular periods, excess hair, or weight gain. Treating PCOS can reduce acne by lowering androgen levels.
Signs Your Acne Is Hormone-Driven And Genetic
Look for patterns that suggest inherited hormone influence. These signs include:
- Deep, painful pimples on the jaw and chin.
- Monthly flare-ups are tied to your menstrual cycle.
- Acne that starts at puberty and keeps returning.
- A family history showing similar patterns.
If you see these signs, mention them to your doctor. They may test hormones. Hormonal acne often shows this way.
Family History Acne Causes
Family history is a practical way to estimate your acne risk. It is not exact, but it helps doctors decide on tests and treatments. If your parent or sibling had severe or long-lasting acne, you should seek early care and consider medical advice sooner. Family history of acne causes can point to inherited oil production, hormone sensitivity, and scar tendency.
Risk Of Acne If One Parent Had It Versus Both
If one parent had acne, your risk rises compared to the general population. If both parents had acne, your risk rises further. The pattern is dose-dependent. More affected relatives mean a stronger genetic influence.
Still, lifestyle factors can change the outcome. Use family history only as a guide. Hereditary acne risk increases with the number of affected relatives.
Hereditary Early-Onset And Persistent Acne
Some families show acne early in life. Early onset often predicts longer persistence. If multiple relatives had acne at a young age, expect possible early acne for you. Early care is important. Treating acne early can cut long-term damage and scarring. Hereditary acne risk links to early starts.
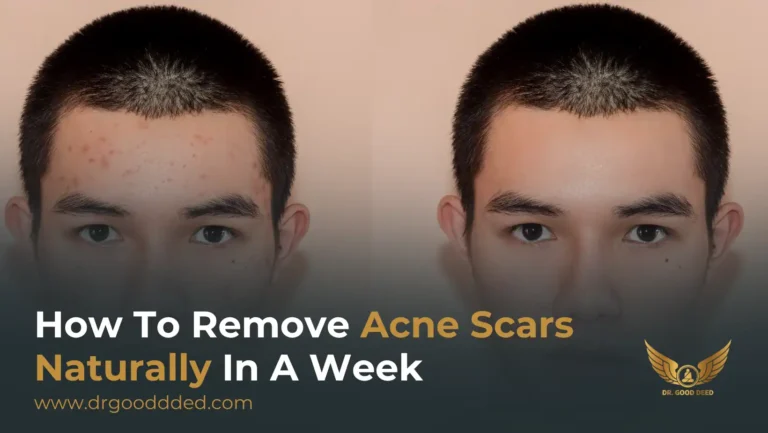
Genetic Likelihood Of Acne Scarring
Scars form when deep lesions damage skin’s structure. Some people scar more easily because of inherited skin repair traits. If close family members have visible acne scars, you may share that tendency.
Early, effective treatment reduces scar risk. If you scar easily, ask a doctor about treatments that protect skin while clearing acne. Hereditary acne includes a risk for scarring in some families.
Genetics And Acne Breakouts
Genetics shape how and when your skin breaks out. If you inherit active oil glands, your skin stays oilier. Oil mixes with dead skin. Pores clog more often. Clogged pores trap bacteria. That causes inflammation and pimples. You may notice flare-ups at predictable times. Puberty and stress are common triggers. Even without obvious triggers, your inherited skin traits keep the risk higher. Hereditary acne often shows through repeat flare patterns you cannot fully control.
You will see patterns if family genes drive your acne. You may break out more on the face, back, or chest. Some people mostly get blackheads. Others get deep cysts. Your genes push the pattern you see. Keep a log to spot repeating triggers. Share this with your doctor for better care. Genetics and acne breakouts come from how your skin, hormones, and immune system work together.
Breakout Patterns In Genetically Prone Individuals
If you are genetically prone, breakouts follow typical rhythms. Puberty triggers many first episodes. Monthly hormone cycles cause flare-ups in those with sensitive hormone receptors. Stress and lack of sleep worsen flares. You may have long, quiet spells with sudden, severe flares. Your family history helps show which pattern fits you. Recognize early signs. Treat early to avoid worse inflammation and scars. Is acne hereditary
Acne On Face/Back/Chest: The Hereditary Connection
Locations matter. Oil gland density changes across body zones. Genetics influences gland density and skin thickness. You may inherit a tendency for chest and back acne. If family members had similar body location patterns, your risk rises in those zones, too. Location guides treatment choice. Topical care works better on the face. Oral or systemic options may fit back and chest acne.
Differences Between Genetic Acne And Lifestyle-Triggered Acne
Lifestyle acne comes from obvious causes. Heavy oil products or tight clothing cause breakouts. Genetic acne occurs despite clean habits. If you clean well and still break out, genes likely matter. Lifestyle changes alone may not stop genetic acne. You still benefit from good habits, but you may need medical treatments too.
Hereditary Acne Risk Factors
Certain inherited traits make acne more likely and more severe. You should know them if your family had heavy acne.
High Androgen Sensitivity And Genetic Predisposition
If your skin overreacts to androgens, oil ramps up quickly. This trait is often inherited. Small hormone shifts then cause big flares. Birth control or hormone blockers work when this trait drives acne. Ask your doctor about hormone testing if you suspect this.
Overactive Sebaceous Glands Inherited From Family
Large or overactive sebaceous glands make the skin oily all the time. You will feel oil on your skin soon after washing. Oily skin blurs makeup and clogs pores. Use oil-lowering products. See a doctor for stronger options when needed.
Cystic Acne Tendencies Passed Through Genes
Cystic acne forms deep, painful lumps. These often run in families. If relatives had cysts, watch for early signs. Cysts cause scarring if untreated. Early medical treatment prevents scarring and reduces pain.
Diagnosis Of Genetic Acne
Doctors use several steps to determine whether acne is inherited. Your answers help more than tests alone.
Using Family History To Assess Hereditary Risk
Tell your doctor who in your family had acne and when it started. Note how severe it was. Mention any scarring or cysts. This history tells the doctor whether genes likely explain your pattern. Honest answers get better plans.
Hormonal And Medical Tests For Inherited Acne
Blood tests can measure hormones. Tests for PCOS include ultrasound and hormone panels. Skin swabs check bacteria only in selected cases. Genetic tests for common acne risk are not routine. Doctors order genetic tests only for rare syndromes. Most care uses family history plus hormone testing.
When Genetic Evaluation Is Recommended
Genetic evaluation may be helpful when acne is linked to other inherited conditions. If many relatives have acne plus other symptoms, your doctor may suggest further genetic work. Otherwise, focus on hormone tests and skin exams first.
Treatment For Hereditary Acne
You can treat inherited acne. You cannot change genes. But you can control oil, bacteria, and inflammation. Treatments vary by age, sex, and severity.
Best Skincare For Genetically Oily Skin
Use a gentle cleanser twice daily. Choose oil-free moisturizers labeled non-comedogenic. Use a topical retinoid at night to prevent clogged pores. Apply a light sunscreen daily. Avoid heavy creams and greasy hair products. Simple daily steps lower flare frequency.
Hormonal Treatments For Inherited Acne
Hormonal options suit many women. Combined birth control pills lower androgen effects. Spironolactone blocks androgen receptors on the skin. Both reduce oil production. These approaches help when tests or family history point to hormone sensitivity. Discuss risks and benefits with your doctor.
Antibiotics, Retinoids, And Isotretinoin Options
Topical antibiotics fight bacteria. Oral antibiotics reduce bacteria and inflammation when severe. Topical retinoids unclog pores. Isotretinoin reduces oil gland size and activity. Use isotretinoin for long-lasting severe acne or scarring risks. Doctors monitor blood tests on systemic drugs. Follow medical advice closely to limit side effects.
Treating Severe Cystic And Scarring Acne
For deep cysts, doctors use steroid injections to reduce pain quickly. Early oral or topical therapy lowers scar risk. Laser therapies and chemical peels treat old scars. Combine approaches for best results. If you scar easily, ask about scar prevention early.
Preventing Genetic Acne Breakouts
You cannot erase genetic risk. You can reduce its impact with steady care.
Daily Skincare Routine For Genetically Prone Skin
A simple routine helps:
- Cleanse gently twice daily.
- Apply topical retinoid nightly.
- Use a light moisturizer.
- Use oil-free makeup.
- Wear sunscreen daily.
Small, consistent steps reduce flare frequency. Keep routines simple and repeat them every day.
Diet And Lifestyle Changes That Help
Some people benefit from low glycemic diets. Reducing high sugar foods can lower flare risk. Dairy may worsen acne for some. Manage stress and get enough sleep. Exercise supports hormone balance. Lifestyle steps do not remove genes. They help your skin react less strongly.
Early Treatment To Prevent Long-Term Scarring
Treating early helps most. If pimples deepen or persist, see a doctor. Early treatment shortens active time. Less time with inflammation lowers scarring. Track outcomes and adjust treatment if needed.
When To See A Dermatologist
You should see a dermatologist when acne causes pain, scarring, or low confidence. Early specialist care can stop many long-term problems.
Warning Signs Of Severe Hereditary Acne
Seek care if you have:
- Deep, painful nodules.
- Rapid scarring.
- Widespread cysts.
- Acne that affects sleep or mood.
These signs need stronger, doctor-supervised care.
When Acne Continues Into Adulthood
If acne persists after your twenties, see a doctor. Adult acne often needs hormonal checks. Long-lasting acne needs a tailored long-term plan.
When OTC Treatments Do Not Work
If over-the-counter options fail after two months, see a doctor. Prescription medicine is often more powerful and targeted. Do not keep switching OTC products. Seek medical advice.
FAQs
Is Acne Directly Inherited From Parents?
Acne is not passed as a single gene. Many genes increase risk. You inherit a mix of traits that raise the likelihood of getting acne. Family patterns matter.
Are Cystic Acne And Nodules Hereditary?
Cystic acne can run in families. If relatives had deep nodules, your risk rises. Early treatment prevents scarring and reduces severity.
Can Lifestyle Changes Reduce Genetic Acne?
Yes. Better skin care, diet changes, sleep, and stress control reduce flare-ups. Lifestyle does not change genes but cuts symptoms and lowers scarring risk.
Is Adult Acne Hereditary?
Adult acne often reflects inherited tendencies. If relatives had long-lasting acne, adult acne is more likely. Hormones and lifestyle also affect outcomes.
Do Acne Scars Run In Families?
The tendency to scar can be inherited. If close family members scar easily, you may too. Early specialist care reduces visible scarring.
Can Genetic Acne Be Prevented?
You cannot stop genes. You can prevent many breakouts with early care and medical treatment. Early, steady action lowers long-term damage.
Is PCOS-Related Acne Hereditary?
PCOS often runs in families. When PCOS raises androgens, acne may follow. Treating PCOS often improves acne by reducing hormone levels.
Does Diet Matter If Acne Is Genetic?
Diet affects many people. Lowering high sugar foods and testing dairy effects can help. Diet is one modifiable factor alongside medical care.
Are Blackheads And Whiteheads Hereditary?
Yes. Pore size and oiliness influence blackheads and whiteheads. These traits often run in families and raise risk for these lesion types.











Leave a Comment