Middle back pain is one of the most commonly overlooked types of back discomfort, even though it can significantly impact your daily life more than you realize. This pain occurs in the thoracic spine (the area between your shoulder blades and the bottom of your rib cage). It can range from a dull ache to a sharp stabbing pain that makes it hard to twist, breathe deeply, or sit for long hours.
What Is Middle Back Pain?
Middle back pain refers to pain felt along the thoracic spine, which sits between your neck (cervical spine) and your lower back (lumbar spine). This region includes 12 vertebrae (T1–T12) connected to your ribs. Because this section supports your upper body and helps with breathing, pain here can disrupt even simple activities like reaching or bending.
People often describe this type of pain as dull, tight, or burning. In some cases, it may radiate to the chest, shoulders, or even the stomach, depending on the cause.
The Thoracic Spine: Where Middle Back Pain Originates
The thoracic spine forms the middle portion of your backbone. It provides stability, protects your heart and lungs, and helps maintain posture. While this region isn’t as flexible as your neck or lower back, it still plays a key role in every movement you make. When the muscles, joints, or discs in this area become strained or inflamed, pain in the middle of the back often appears.
How It Differs From Upper Or Lower Back Pain
Upper middle back pain sits between the areas commonly described as Upper Left Back Pain or Upper Right Back Pain, which occur around the shoulder blades and neck. In contrast, Lower Back Pain affects the region near the waist. Middle back pain falls between these two zones, and because this part of the spine connects directly to the ribs, the discomfort often feels deeper and more pressure-driven than typical lower back pain.
Anatomy Of The Middle Back
The Thoracic Vertebrae (T1–T12)
These twelve bones create a strong, semi-rigid structure that holds your ribs. Each vertebra connects through small joints and discs that absorb shock during movement.
Key Muscles And Ligaments (Rhomboids, Trapezius, Lats)
The main muscles here are the rhomboids (which pull your shoulder blades together), trapezius (upper back and neck support), and latissimus dorsi (side and lower back muscles). When these muscles are tight, weak, or injured, pain builds up quickly.
Nerves, Ribs, And Their Connection To Internal Organs
The thoracic nerves travel from the spine to the ribs and into your chest and abdomen. Because of this, problems in your organs, like your gallbladder or kidneys can sometimes show up as back pain.
Why The Mid-Back Is Less Flexible Yet Susceptible To Pain
This region doesn’t move as freely as the neck or lower back because it’s attached to the ribs. Limited movement means more stress on specific joints or muscles, which can trigger pain.
Common Causes Of Middle Back Pain
Muscular And Postural Causes
- Poor posture or slouching from long desk work can overstretch your back muscles and weaken them.
- Muscle strain or overuse happens when you lift something heavy or twist too quickly.
- Weak core muscles put more pressure on your spine.
- Sedentary habits , such as sitting for hours, stiffen your back and shoulders.
Spinal And Skeletal Causes
- A herniated disc (when a spinal disc bulges or ruptures) can press on nearby nerves.
- Arthritis or spinal degeneration causes stiffness and chronic inflammation.
- Scoliosis (spinal curvature) or deformities affect muscle balance.
- Compression fractures from osteoporosis can cause sudden, sharp pain in older adults.
Referred Or Internal Organ Pain
Sometimes, the middle back of the left side hurts because of issues not directly in the spine. For instance:
- Gallbladder problems may cause pain under the right shoulder blade.
- Stomach ulcers or acid reflux can radiate pain to the mid-back.
- Kidney infections or stones often cause flank pain that spreads to the back.
- Heart or lung issues can mimic spinal pain and need urgent care.
Lifestyle And Environmental Factors
Your daily routine affects your spine more than you think.
- Sleeping on a saggy mattress leads to misalignment.
- Carrying extra weight puts stress on the midsection.
- Poor lifting habits or weak posture increase your risk of injury.
Psychological And Stress-Related Factors
Stress and anxiety often make muscles tighten without you noticing. You might feel tension between your shoulder blades or pain that worsens after emotional stress.
Types Of Middle Back Pain
Sharp Vs. Dull Or Aching Pain
Sharp pain often points to an injury or disc issue. Dull pain usually signals strain or poor posture.
Localized Vs. Radiating Pain
Pain in one spot is usually muscular. If it spreads to your chest or arms, nerves might be involved.
Acute Vs. Chronic Pain
Acute pain lasts a few days or weeks. Chronic pain continues for months and needs ongoing management.
Symptoms That May Accompany Middle Back Pain
- Stiffness or limited movement when twisting or bending.
- Burning or tingling sensations along the spine, suggesting nerve irritation.
- Muscle tightness or spasms , especially after sitting too long.
- Pain when breathing, coughing, or lifting , indicating rib or muscle strain.
- Fatigue or heaviness after long periods of poor posture.
When Middle Back Pain Signals Something Serious
- Chest tightness or shortness of breath might mean a heart issue, so seek emergency care.
- Fever or chills along with back pain could point to infection.
- Numbness or weakness in limbs suggests nerve involvement.
- Weight loss or night sweats without a reason may hint at an underlying illness.
Middle Back Pain In Specific Situations
Middle Back Pain After Eating (Digestive-Linked Pain)
Pain in the middle back after meals can come from your digestive system rather than your spine. Issues like acid reflux, gallbladder trouble, or ulcers can send pain to the back. Heavy, greasy meals or eating too fast can worsen it. Tracking what you eat and when pain appears helps. If it persists, see your doctor.
Middle Back Pain While Breathing or Coughing
If breathing or coughing makes your back ache, it could be from strained muscles or irritated ribs. Sometimes, chest or lung inflammation can cause this too. Rest and gentle heat often help, but if breathing feels tight or painful, get medical advice right away. It’s always better to rule out something serious early.
Middle Back Pain During Pregnancy
Pregnancy often brings middle back pain as your body adjusts to a new center of gravity. Weakened muscles and hormonal changes add extra pressure to your spine. Light stretching, proper posture, and supportive pillows can ease the strain. If the pain feels sharp or constant, talk to your healthcare provider for tailored advice.
Middle Back Pain After Exercise or Injury
Soreness after a workout usually means tired muscles, but sharp or lasting pain might signal a strain or disc issue. Rest, ice, and gentle stretching usually help recovery. Avoid heavy lifting until the pain eases. If numbness or tingling appears, get checked out to prevent long-term problems.
Long-Term Outlook And Recovery
Typical Recovery Time
Mild muscle strain often improves within two to three weeks. Disc problems or fractures may take several months.
Dealing With Chronic Or Recurring Pain
For ongoing pain, physical therapy, posture correction, and core training can reduce symptoms. In severe cases, medical treatments like injections may help.
Importance Of Early Intervention
Act early. Don’t ignore mild pain. Correct posture, stretch regularly, and strengthen your back before pain becomes chronic.
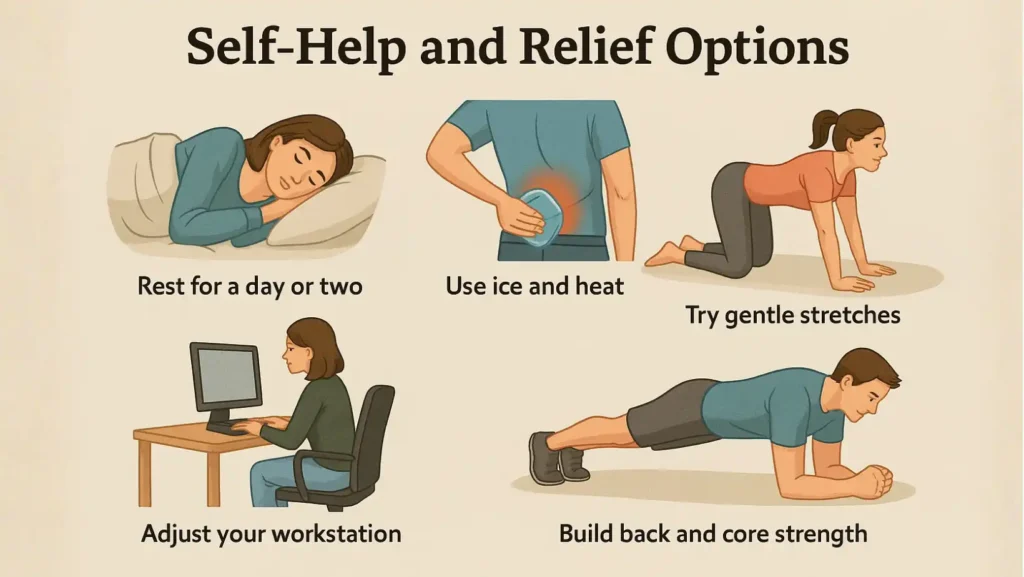
Self-Help And Relief Options
You can learn how to help middle back pain at home using simple habits:
- Rest for a day or two after sudden pain, but don’t stay in bed too long.
- Use ice for 15–20 minutes in the first two days, then apply heat to relax muscles.
- Try gentle stretches like cat-cow pose or wall angels.
- Adjust your workstation. Keep your screen at eye level and chair supportive.
- Build back and core strength through regular exercise.
These steps are the best starting points if you’re wondering how to relieve middle back pain naturally.
FAQs
What Is The Most Common Cause Of Middle Back Pain?
The most common cause of middle back pain is poor posture and muscle strain from sitting too long or using weak core muscles during daily activities.
Can Poor Posture Really Cause Mid-Back Pain?
Yes, poor posture stretches and weakens your mid-back muscles, leading to pain in the middle of your back that worsens with sitting or slouching.
Why Does My Middle Back Hurt When I Breathe Deeply?
Deep breathing moves your ribs, so if your muscles or nerves are irritated, it can cause middle back pain during deep inhalation.
How Can I Tell If My Middle Back Pain Is Muscular Or Spinal?
If it feels sore and improves with rest, it’s likely muscular. If it causes tingling or sharp shooting pain, the spine or nerves may be involved.
Can Gallbladder Or Stomach Issues Cause Pain In The Middle Back?
Yes. Conditions such as gallbladder inflammation or stomach ulcers can trigger upper-middle-back pain, especially after consuming fatty or spicy foods. These symptoms differ from what you typically see in Kidney Pain vs Back Pain, where kidney-related discomfort is deeper, often radiates toward the flank, and may come with nausea, fever, or urinary changes.
What Are The Best Exercises To Help Middle Back Pain?
Try gentle movements like thoracic extensions, shoulder blade squeezes, and wall slides to strengthen and stretch your back muscles safely.
How Do I Sleep Properly To Avoid Mid-Back Discomfort?
Use a medium-firm mattress, keep your spine neutral, and place a pillow under your knees when lying on your back.
When Should I See A Doctor For Middle Back Pain?
Seek help if your middle back pain lasts more than two weeks, gets worse, or comes with fever, chest pain, or numbness.
Can Stress Or Anxiety Cause Pain Between the Shoulder Blades?
Yes, stress triggers tension in the shoulder and upper back muscles, which can lead to tightness and pain on the left side of the middle back.









Leave a Comment