Diabetes is a long-term condition that affects how your body uses sugar (glucose) for energy. Normally, your body turns food into glucose and uses a hormone called insulin to help glucose enter cells. But in diabetes, the body either doesn’t make enough insulin or cannot use it properly. This leads to high blood sugar levels that can harm your body over time.
What Exactly Happens In Diabetes
How The Body Uses Glucose And Insulin
Every time you eat, your body breaks down food into glucose, which serves as the primary fuel for your cells. The pancreas, located behind the stomach, releases insulin to regulate this process. Insulin acts like a key, allowing glucose to enter your cells and be used for energy.
In a healthy system, insulin keeps blood sugar levels stable. After a meal, glucose levels rise, and insulin moves that glucose into the cells. When glucose levels fall, insulin production decreases. This balance is what helps maintain a Normal Glucose Level After Eating, preventing spikes or crashes in blood sugar.
When Things Go Wrong — The Root Cause Of Diabetes
In diabetes, this process does not work properly. Either the pancreas stops making insulin, or your cells resist insulin’s action. When insulin doesn’t work, glucose stays in the blood instead of going into cells. This leads to high blood sugar, which can damage your nerves, blood vessels, kidneys, and heart over time.
Common Causes Of Diabetes
The causes differ depending on the type, but some factors increase the risk for all.
- Family history, being overweight, lack of physical activity, poor diet, and high stress can all play a role.
- Certain infections and immune reactions can trigger type 1 diabetes, while unhealthy lifestyle habits can lead to type 2.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy may cause gestational diabetes.
Learning what causes diabetes helps you take preventive steps early.
Types Of Diabetes And How They Differ
Type 1 Diabetes – The Autoimmune Attack
Type 1 diabetes happens when your immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-making cells in the pancreas. This means your body can’t produce insulin. Without insulin, blood sugar rises dangerously high.
Type 1 usually appears in children or teens but can also occur in adults. People with this type must take insulin every day to live. Symptoms often appear suddenly, including thirst, frequent urination, and weight loss.
Type 2 Diabetes – The Lifestyle-Linked Type
Type 2 diabetes develops when your body still makes insulin but doesn’t use it properly. Over time, the pancreas can’t keep up, and insulin production drops. It’s more common in adults, but it’s rising among young people due to sedentary lifestyles.
Poor diet, being overweight, and low activity levels are major factors. However, genetics also plays a role. The good news is that early changes in diet and exercise can help control blood sugar and even delay diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes – Diabetes During Pregnancy
Gestational diabetes affects some women during pregnancy. Hormones from the placenta can interfere with insulin, causing blood sugar levels to rise. It usually goes away after childbirth, but it increases the mother’s risk of type 2 diabetes later.
The baby may also be born larger than normal or have low blood sugar after birth. Doctors often test blood sugar during pregnancy to catch this early.
What Is Prediabetes And Why It Matters
Prediabetes means your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough for diabetes. It’s a serious warning sign. If untreated, it often turns into type 2 diabetes.
Knowing what pre-diabetes is pre diabetes can help you act in time. Common signs of prediabetes include fatigue, weight gain, and dark patches on the skin (especially around the neck or armpits). Losing weight, eating healthier, and exercising can often reverse prediabetes naturally.
Recognizing The Warning Signs — Diabetes Symptoms To Watch For
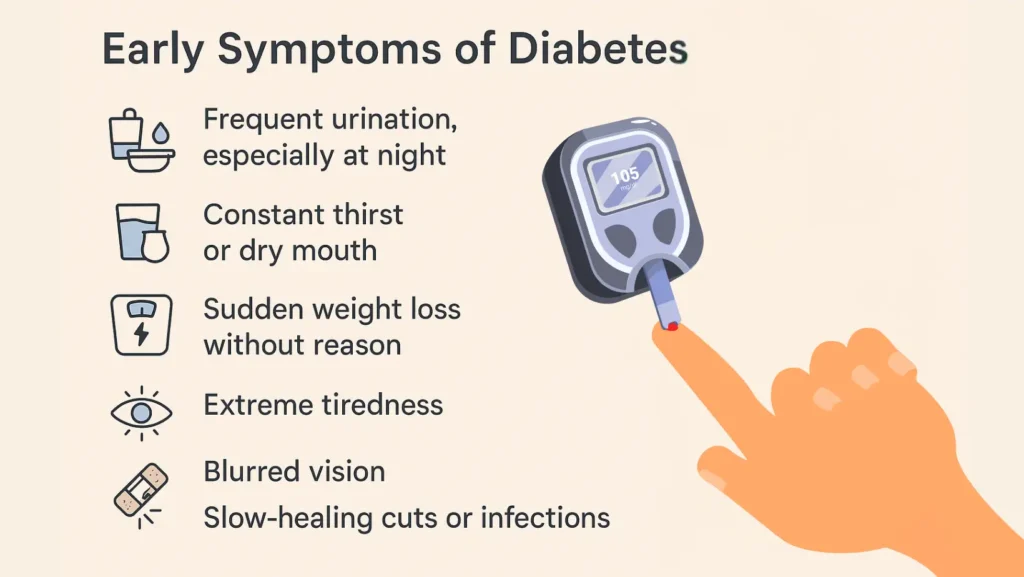
Early Symptoms Of Diabetes
The body gives early warning signs before diabetes becomes severe. Common diabetes symptoms include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Constant thirst or dry mouth
- Sudden weight loss without reason
- Extreme tiredness
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing cuts or infections
Ignoring these signs can allow the disease to progress quietly and cause serious problems.
Signs Of Prediabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore
Prediabetes usually develops quietly, with Prediabetes Symptoms that are mild or easy to overlook. Some people experience increased fatigue, slight weight gain, or darkened skin patches. If you are overweight, older than 40, or have a family history of diabetes, regular blood sugar testing is essential to detect changes early.
When To See A Doctor
If you notice these symptoms or feel unusually tired and thirsty, see a doctor. Early testing can detect problems before they become serious. If you feel dizzy, confused, or faint, seek medical help right away.
How Diabetes Is Diagnosed
Common Tests Used
Doctors use several blood tests to diagnose diabetes. The most common are:
| Test | What It Measures | Normal Range | Diabetes Range |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | Blood sugar after fasting for 8 hours | Below 100 mg/dL | 126 mg/dL or higher |
| A1C Test | Average blood sugar over 2–3 months | Below 5.7% | 6.5% or higher |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test | Blood sugar after a sweet drink | Below 140 mg/dL | 200 mg/dL or higher |
These tests help doctors confirm whether you have diabetes and identify if you have prediabetes or diabetes.
Interpreting Your Results
If your test shows prediabetes, it’s not too late. It’s a signal to make changes. If your results show diabetes, your doctor will guide you through treatment options, diet plans, and follow-ups. Consistent monitoring keeps you healthy.
Managing Diabetes — Treatment, Diet & Daily Routine
Medical Management And Insulin Therapy
Treatment depends on the type. Type 1 always needs insulin. Type 2 may start with diet and exercise, but can later require pills or insulin. Some newer medicines help your body use insulin better and protect the heart and kidneys.
Always follow your doctor’s plan, check your blood sugar regularly, and never skip medicines. If using insulin, learn how to store and inject it properly.
Lifestyle Management
Your lifestyle affects your blood sugar. A balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, Best Snacks for Diabetes and lean protein is vital.
- Avoid sugary drinks and junk food.
- Regular activity helps insulin work better.
- Aim for 30 minutes of movement daily; walking, swimming, or cycling all help.
Maintaining a healthy weight can greatly improve your blood sugar.
Mental Health And Diabetes
Managing diabetes can feel stressful. Worry about sugar levels, meals, and medication can affect your mood. Many people feel anxious or depressed. Remember, it’s okay to ask for help. Talking to a counselor or joining a support group can make a big difference.
Can Diabetes Be Prevented?
Preventive Steps That Actually Work
Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, but type 2 often can. Simple lifestyle changes lower risk:
- Eat more vegetables and fiber
- Reduce sugar and processed food
- Exercise regularly
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid smoking and excess alcohol
- Sleep well
These habits not only prevent diabetes but also protect your heart and brain.
Reversing Prediabetes Naturally
Prediabetes is a critical turning point. Research shows that losing just 5–10% of your body weight and completing at least 150 minutes of weekly exercise can reverse early glucose abnormalities. These strategies are also fundamental in understanding How to Reduce Insulin Resistance, since weight loss, consistent physical activity, and improved diet directly enhance insulin sensitivity. Pair these habits with stress management and monitor your blood sugar every few months to track measurable progress.
Complications Of Uncontrolled Diabetes
Short-Term Complications
Without control, diabetes can cause dangerous short-term problems.
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): This can happen from too much insulin or skipping meals. Symptoms include sweating, shakiness, and confusion.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Mostly in type 1 diabetes, when sugar can’t enter cells, the body breaks down fat for energy, leading to acid buildup. It’s a medical emergency.
Long-Term Complications
High blood sugar for years damages blood vessels and nerves. It can cause:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Kidney damage
- Vision loss (diabetic retinopathy)
- Nerve pain and numbness (neuropathy)
- Foot ulcers and infections
Controlling blood sugar, pressure, and cholesterol can delay or prevent these problems.
Living Well With Diabetes
Mindset And Motivation
A positive mindset changes everything. Diabetes doesn’t have to control your life. Stay consistent with your routine. Learn about your condition. Celebrate small progress, lower sugar levels, better diet, or regular exercise. Every small step counts.
Support And Community
You’re not alone. Many people live full, active lives with diabetes. Support groups and online communities offer advice and motivation. Share experiences, learn new recipes, and stay inspired. Having people who understand you helps you stay strong.
FAQs
What is diabetes in simple terms?
Diabetes is a condition where your body can’t use sugar properly, leading to high blood sugar that can harm your organs over time.
What are the main causes of diabetes?
The main causes include family history, obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise. Learning what causes diabetes helps you prevent it early through healthy choices.
What are the early signs of diabetes?
The common diabetes symptoms are thirst, frequent urination, tiredness, blurred vision, and weight changes. Ignoring these signs can make the condition worse.
How can you prevent diabetes naturally?
You can prevent it by eating whole foods, exercising daily, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight. These habits protect you from future risks.
What is prediabetes, and can it be reversed?
Pre diabetes means your blood sugar is high, but not diabetic yet. With weight loss and daily exercise, you can reverse it and avoid full-blown diabetes.
What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 happens when the body makes no insulin, while Type 2 means insulin is made but not used well. Both need control to stay healthy.
What are the long-term complications of diabetes?
If not managed, diabetes can cause heart, kidney, and nerve problems. It can also damage eyes and feet. Regular monitoring helps prevent these.















Leave a Comment