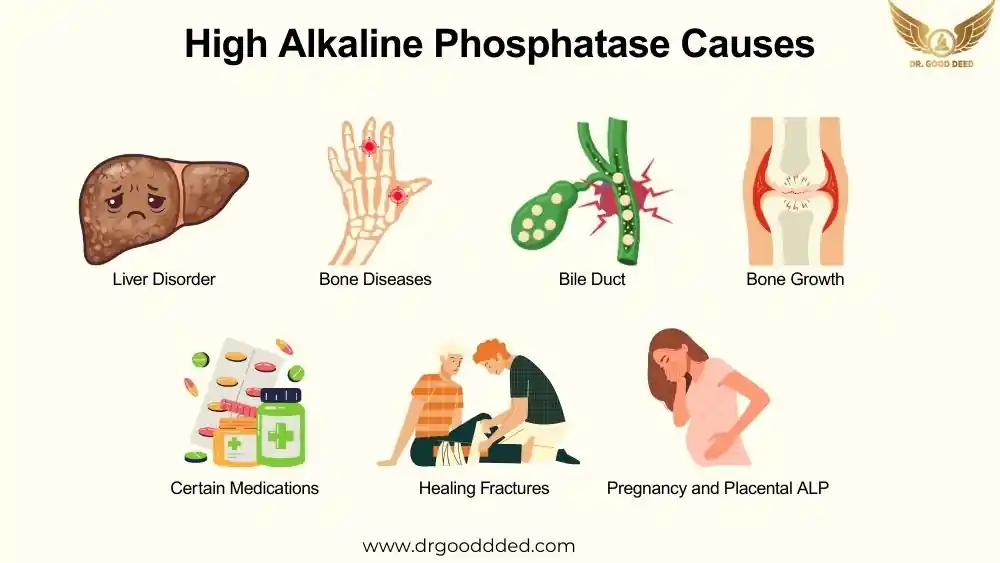
Causes for high alkaline phosphatase usually mean that cells in your liver, bile ducts, or bones are under stress or working faster than normal. This enzyme rises when bile flow slows, liver tissue swells, or bones repair damage or grow rapidly. Common triggers include bile duct blockage, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, bone disorders like Paget disease, vitamin D deficiency, healing fractures, certain medicines, and normal states such as growth or pregnancy.
Temporary illness, recent surgery, and even test conditions can also raise levels for a short time. A high result does not point to one disease, but it signals that your body needs attention and careful follow-up to find the exact cause.
High Alkaline Phosphatase Causes
Alkaline phosphatase, also called ALP, is an enzyme that helps move minerals in your body. The body makes alkaline phosphatase in many tissues, but the liver and bones release the largest amounts into the blood. Each source raises ALP for different reasons. Understanding these causes for high alkaline phosphatase prevents confusion and delays in care.
Liver and Bile Duct Disorders
The liver clears waste and makes bile, a fluid that helps digest fats. Bile flows through small tubes called bile ducts. When these ducts swell, scar, or block, ALP leaks into the blood.
Gallstones are a common trigger. They block bile flow and raise ALP fast. Inflammation of bile ducts, called cholangitis (infection of bile ducts), can raise ALP even before pain begins. Tumors in or near the liver can press on the bile ducts and cause the same effect.
ALP rises more in bile blockage than in direct liver cell damage. That is why doctors compare ALP with other liver enzymes. These conditions remain major causes for high alkaline phosphatase in adults.
Bone Growth and Bone Diseases
Bones constantly break down and rebuild. Alkaline phosphatase plays a key role in this process. When bone activity speeds up, ALP increases.
Children and teens often have higher ALP due to growth, which is normal and expected. In adults, bone diseases raise ALP in a different way. Paget disease causes abnormal bone remodeling, which drives ALP up. Bone cancers or cancer spread to bone can also raise ALP, sometimes sharply.
ALP often rises before bone pain becomes severe. That makes bone-related causes for high alkaline phosphatase important to catch early.
Pregnancy and Placental ALP
During pregnancy, the placenta produces its own alkaline phosphatase. Levels rise most in the third trimester. This rise supports nutrient flow to the baby.
Placental ALP does not harm the mother or baby. Doctors usually ignore mild to moderate ALP rises in pregnancy unless other liver tests are abnormal. Pregnancy remains a natural and temporary entry among causes for high alkaline phosphatase .
Certain Medications
Some drugs raise ALP by stressing the liver or affecting bone turnover. Anti-seizure medicines can increase liver enzyme activity. Long-term steroid use affects bones and may raise ALP. Some antibiotics and hormonal drugs can also cause changes.
Drug-related ALP elevation often improves after stopping the medicine. Doctors usually confirm this by repeating the test after a safe drug pause. Medication effects are well-known causes for high alkaline phosphatase in routine blood work.
Healing Fractures
When a bone breaks, your body enters repair mode. Bone cells work faster to rebuild strength. Alkaline phosphatase rises during this healing phase.
ALP may stay high for several months during fracture recovery. The level slowly drops as healing completes. This rise is harmless and expected. Healing fractures are temporary causes for high alkaline phosphatase and rarely need treatment.
Reasons For High ALP Levels
Not all ALP rises come from disease. Some reflect body states like growth, deficiency, or immune response. These reasons for high ALP levels often confuse people because symptoms may be mild or absent.
Age-Related ALP Elevation
Age strongly affects ALP. Children have higher levels due to bone growth. Teenagers often peak during growth spurts. In older adults, mild increases may appear due to slow bone loss. Age remains one of the most common reasons for high ALP levels .
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D helps bones absorb calcium. When vitamin D is low, bones weaken. The body responds by increasing bone turnover, which raises ALP.
ALP often rises before fractures occur in severe vitamin D deficiency. Correcting the deficiency usually lowers ALP over time. This deficiency is a leading global contributor to high ALP levels .
Chronic Inflammation
Long-term inflammation stresses organs. Autoimmune diseases can inflame the bile ducts or the bones. Conditions like inflammatory bowel disease can affect the liver through immune signals.
Chronic inflammation raises ALP slowly and steadily. This pattern differs from sharp spikes seen in blockages. Inflammation-driven changes explain many unexplained reasons for high ALP levels .
Infections Affecting Liver or Bone
Viral hepatitis infects liver cells and bile ducts. Bone infections damage tissue and trigger repair. Both raise ALP as part of the immune response.
Infections often raise other markers like fever or white blood cell count. Still, ALP may rise first. These infections remain serious reasons for high ALP levels that need medical review.
Genetic Enzyme Variations
Some people inherit naturally higher ALP activity. Their levels stay above average for life without illness. These people have stable ALP levels and normal imaging results. Family history helps confirm this. Genetics explains rare but benign reasons for high ALP levels .
High ALP Causes In Blood Test
Sometimes the issue lies in testing conditions rather than the disease. These high ALP causes in blood test results often correct on repeat testing.
Lab Reference Range Variations
Each lab sets its own normal range based on equipment and population data. A result labeled high in one lab may fall within normal limits elsewhere. Doctors focus on trends rather than single values. Range differences account for many high ALP causes in blood test reports.
Temporary ALP Elevation
Short-term stress can raise ALP. Heavy exercise strains muscles and bones. Mild dehydration can concentrate enzymes in the blood. These elevations fade within days. Temporary spikes are a common high ALP cause in blood test findings.
Fasting vs Non-Fasting Blood Sample
Eating triggers bile release. This can slightly raise ALP. Non-fasting samples may show higher values than fasting ones. For clarity, doctors often repeat ALP tests after fasting. Sample timing explains many high ALP causes in blood test concerns.
Recent Illness or Surgery
After illness or surgery, the body repairs tissue. The liver processes medications and waste. Bones rebuild strength after stress. These processes raise ALP temporarily. Recovery-related changes remain a frequent high ALP cause in blood test results.
Lab Errors and Repeat Testing
Sample handling errors happen. Hemolysis, which means red cells breaking, can affect results. Doctors confirm high ALP with repeat testing before diagnosis. Errors remain a practical part of high ALP causes in blood test evaluation.
High Alkaline Phosphatase Symptoms
High alkaline phosphatase itself does not cause symptoms. What you feel depends on the underlying problem. Many people feel normal at first. Symptoms usually appear when the condition affecting the liver or bones progresses. Recognizing these signs early helps you act before complications start. These are common symptoms of high alkaline phosphatase that doctors take seriously.
Fatigue and Weakness
Ongoing tiredness is one of the earliest signs. Liver stress reduces how well your body turns food into energy. Bone disorders also strain muscles over time. This fatigue does not improve with rest. If blood tests show causes for high alkaline phosphatase along with long-lasting weakness, doctors often look deeper.
Bone Pain or Joint Stiffness
Bone-related conditions cause dull, deep pain. You may feel it in the hips, back, or legs. Joint stiffness often appears in the morning or after rest. ALP rises as bone cells increase repair work. These aches are key symptoms of high alkaline phosphatase linked to bone disease.
Abdominal Pain or Bloating
Liver or bile duct problems cause discomfort on the right side of your upper belly. Bloating happens when bile does not flow properly. Pressure builds inside the liver. This pain may worsen after meals. These digestive changes often appear with causes for high alkaline phosphatase related to bile blockage.
Yellowing of Skin or Eyes
This sign is called jaundice, which means bile pigments build up in the blood. Your skin and the whites of your eyes turn yellow. ALP rises early in bile obstruction, sometimes before jaundice appears. This is one of the most serious symptoms of high alkaline phosphatase .
Itching and Dark Urine
When bile salts stay in the blood, they irritate the skin and cause itching. Urine may turn dark brown or tea-colored. These changes signal impaired bile flow. They often appear together with other symptoms of high alkaline phosphatase and require prompt medical review.
Alkaline Phosphatase High Liver Causes
Liver-related problems account for a large share of abnormal ALP results. Doctors compare ALP with other liver enzymes to find the source. These conditions represent important causes for high alkaline phosphatase tied directly to liver health.
Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease occurs when fat builds up inside liver cells. This slows bile movement and stresses the liver. ALP often rises along with mild increases in other enzymes. Many people have fatty liver without symptoms, making ALP a useful early marker. This condition is one of the fastest-growing causes for high alkaline phosphatase worldwide.
Bile Duct Obstruction
Blocked bile ducts raise ALP more than most liver conditions. Gallstones, scars, or tumors can block bile flow. Pressure forces ALP into the bloodstream. Doctors often see ALP rise before imaging confirms the blockage. This makes obstruction a classic example among causes for high alkaline phosphatase .
Hepatitis
Hepatitis means liver inflammation. Viruses, alcohol, or autoimmune reactions can cause it. ALP rises when bile ducts swell during inflammation. Hepatitis often raises ALT more than ALP, but both can increase together. Hepatitis remains a well-known contributor to high alkaline phosphatase .
Liver Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis develops when long-term damage replaces healthy liver tissue with scar tissue. Scar tissue narrows bile channels. ALP rises as bile flow slows. Cirrhosis-related ALP elevation usually signals advanced disease. It stands among the most serious causes for high alkaline phosphatase .
Liver Tumors or Metastasis
Tumors inside the liver or cancer that spreads from other organs can compress the bile ducts. This causes a steady or rapidly rising ALP. ALP often rises before pain or weight loss appears. Tumors remain a critical causes for high alkaline phosphatase that need urgent evaluation.
When To Worry About High Alkaline Phosphatase
Not every elevated ALP is dangerous. Certain patterns raise concern and demand follow-up. These warning signs help identify risky causes of high alkaline phosphatase .
Persistently High ALP Levels
One abnormal test may mean little. Repeated high results over weeks or months matter more. Persistent elevation suggests ongoing liver or bone stress. Doctors consider this pattern a red flag among causes of high alkaline phosphatase .
ALP With Abnormal Liver Tests
High ALP combined with high bilirubin or GGT points to bile flow problems. Studies show this pattern strongly predicts bile duct disease. Doctors often order imaging right away. This combination highlights serious causes of high alkaline phosphatase .
High ALP With Bone Pain
Bone pain paired with high ALP raises concern for bone disease. Imaging and mineral tests often follow. This pairing helps narrow the causes of high alkaline phosphatase linked to skeletal damage.
Rapidly Rising ALP Levels
Fast increases suggest acute blockage, infection, or aggressive disease. Slow rises suggest chronic conditions. The rate of change helps doctors judge urgency when evaluating causes of high alkaline phosphatase .
When To See A Doctor
Medical review is needed when high ALP lacks a clear explanation, appears with symptoms, or occurs in people with prior liver or bone disease. Early evaluation helps prevent silent progression of serious underlying conditions.
High ALP With Symptoms
Symptoms like pain, itching, jaundice, or fatigue with high ALP need evaluation. Doctors often repeat tests and order scans. Symptomatic cases frequently point to treatable causes for high alkaline phosphatase .
Unexplained ALP Elevation
If ALP rises without a clear reason, doctors investigate liver and bone markers. Imaging may follow. Unexplained results often reveal hidden causes for high alkaline phosphatase .
History of Liver or Bone Disease
Past liver or bone problems increase the risk of recurrence. Doctors monitor ALP trends closely in these people. History shapes how doctors assess causes for high alkaline phosphatase .
High ALP Detected On Routine Blood Test
Routine tests often catch disease early before symptoms start. Early detection improves outcomes. Many serious causes for high alkaline phosphatase are found this way.
FAQs
What Is The Most Common Cause Of High Alkaline Phosphatase?
Liver and bile duct problems are the most common cause in adults, while bone growth explains many cases in children. These remain the leading causes for high alkaline phosphatase across age groups.
Can High ALP Be Temporary?
Yes. Short-term illness, healing bones, medications, or stress can raise ALP briefly. Levels often return to normal within weeks. These short-lived changes are common reasons for high ALP levels .
Does High ALP Always Mean Liver Disease?
No. Bone disorders, pregnancy, and vitamin deficiencies also raise ALP. Doctors use other tests to separate liver causes from non-liver high ALP causes in blood test results.
Can Vitamin Deficiency Cause High ALP?
Yes. Vitamin D deficiency weakens bones and increases bone turnover. ALP rises as bones try to repair damage. This is a well-documented source of reasons for high ALP levels .
Is High Alkaline Phosphatase Dangerous?
High ALP itself is not dangerous. The risk depends on the cause. Some causes are harmless, while others need treatment. Risk assessment focuses on causes for high alkaline phosphatase , not the number alone.
What Foods Affect ALP Levels?
Heavy fatty meals can slightly affect bile flow. Alcohol stresses the liver and may raise ALP over time. Diet can influence high ALP causes in blood test results, but rarely causes large spikes alone.
How Is The Cause Of High ALP Confirmed?
Doctors repeat blood tests, check related enzymes, and may order imaging. This step-by-step process helps pinpoint high ALP causes in blood test findings accurately.
Can High ALP Return To Normal On Its Own?
Yes. If the trigger resolves, such as healing, stopping a drug, or correcting a deficiency, ALP often normalizes. Many reasons for high ALP levels improve without treatment.
What ALP Level Is Considered Very High?
Levels more than three times the upper limit raise concern. Doctors act faster at this range because it often signals serious causes for high alkaline phosphatase .
When Should High ALP Be Treated Urgently?
Urgent care is needed when high ALP appears with jaundice, severe pain, fever, or rapid rises. These signs often point to dangerous causes for high alkaline phosphatase that cannot be ignored.














Leave a Comment