Period blood brown appears when menstrual blood takes longer to leave your uterus. Fresh blood is red because it still carries oxygen. When blood sits inside the uterus or cervix, oxygen levels drop, and the color darkens to brown. This often happens at the start or end of a period, during light flow, or when hormones slow uterine shedding.
Hormonal shifts, delayed ovulation, stress, and birth control can all reduce flow speed. In most cases, brown menstrual blood reflects timing and flow changes, not disease, as long as pain, odor, and bleeding volume stay normal.
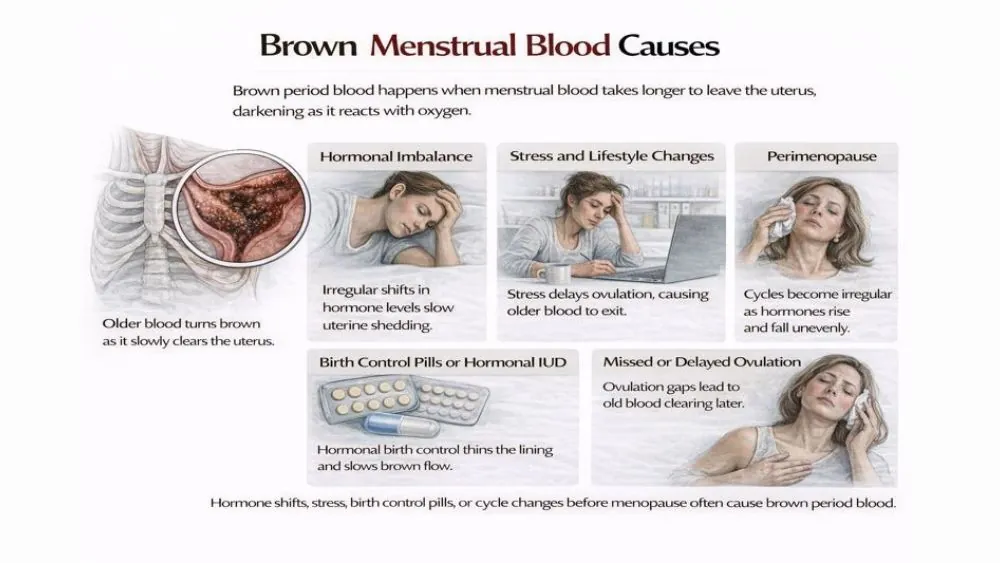
Common Brown Menstrual Blood Causes
When period blood brown appears, it usually reflects slower uterine shedding rather than disease. Blood oxidation increases when flow speed drops, which explains why hormonal shifts and ovulation timing strongly affect color.
Hormonal Imbalance
Hormones control when your uterus sheds its lining. When estrogen or progesterone levels shift, the lining may shed slowly. Slow shedding leads to darker blood. Thyroid problems can cause this shift. PCOS, which means polycystic ovary syndrome, can also affect hormone balance. Skipped ovulation often causes brown bleeding at the start of a cycle. This explains why period blood brown appears without other symptoms.
Stress and Lifestyle Changes
Stress affects your brain first, then your hormones. High stress can delay ovulation. Delayed ovulation means old blood leaves later. Sleep loss, sudden weight loss, or heavy exercise can trigger this change. Chronic stress is linked with irregular cycles. Short episodes of period blood brown after stressful weeks often resolve once stress is lower.
Birth Control Pills or Hormonal IUD
Hormonal birth control thins the uterine lining. A thin lining sheds less blood. Less blood moves more slowly; that blood darkens before it exits. Spotting and brown flow are common during the first three months of pill or hormonal IUD use. You will notice brown blood instead of red period during this adjustment phase.
Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the phase before menopause. Hormones rise and fall unevenly. Ovulation may stop for some months. Cycle changes can start in your late 30s or early 40s. During this time, brown blood in the period becomes more common. Flow may look watery, dark, or mixed with mucus. These changes usually repeat across cycles.
Missed or Delayed Ovulation
Ovulation triggers a full period. When ovulation does not happen, the uterus sheds lining unevenly. Some blood stays behind and exits later, and that blood looks brown. Peer-reviewed gynecology journals confirm that irregular ovulation often causes brown bleeding without disease.
Brown Discharge During Period
Brown discharge during period often forms when menstrual blood mixes with cervical mucus or exits late from the uterus. Studies from gynecology journals confirm this is common during light-flow cycles and does not signal infection without other symptoms.
Light Menstrual Flow
A light flow means blood leaves slowly. Oxygen darkens it before it exits. This explains why period blood often appears brown on lighter days. Light flow alone is not harmful when cycles remain regular.
Residual Blood From Previous Cycle
Not all blood leaves during your last period. Small amounts can stay inside. When your next cycle starts, that old blood exits first. This causes brown discharge during the period on day one. This pattern is common and harmless.
Cervical Mucus Mixed With Blood
Your cervix makes mucus. When mucus mixes with blood, the color looks brown or tan. This often happens near the end of a period. Cervical mucus changes through the cycle. Color changes alone do not signal disease.
How Brown Discharge Differs From Spotting
Spotting happens outside your period days. Brown discharge during the period happens during expected cycle days. Spotting often links to hormones or early pregnancy. Timing helps you judge which one you see.
Brown Period Blood With Cramps
Brown period blood with cramps occurs when uterine contractions push out thicker or older blood. Pain intensity matters more than color, since mild cramps reflect normal muscle action, while worsening pain may indicate tissue-related disorders.
Normal Uterine Contractions
Your uterus contracts to push blood out. Mild cramps help this process. When the flow stays slow, the blood darkens. This causes period blood to be brown with mild cramps. This pattern often appears on day one or the last day.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis means tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. This tissue bleeds but cannot exit easily. That trapped blood irritates nerves. Pain feels deep and sharp. Brown bleeding may appear before or after periods. Pain severity, not color alone, signals concern here.
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis occurs when uterine lining tissue grows into the uterine muscle. This makes the uterus heavy and tender. Periods feel painful and long. Blood may appear dark brown. Adenomyosis often causes worsening cramps over time.
Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids are non-cancerous muscle growths inside the uterus. They block normal blood flow. Blood pools behind them and darkens. This leads to brown period blood with cramps , clots, or long cycles. Fibroid symptoms depend on size and location.
When Cramps With Brown Blood Need Attention
You should pay attention when pain stops daily activity. Pain that spreads to your back or legs matters. Pain that worsens each cycle matters. Severe cramps with brown period blood deserve medical review. Color alone does not decide risk; pain pattern plays a major role.
Pregnancy-Related Causes of Brown Period Blood
Early pregnancy can cause brown bleeding because hormone-driven blood vessels become fragile. Slow cervical bleeding oxidizes quickly, making early pregnancy spotting appear brown instead of bright red.
Implantation Bleeding
Implantation bleeding happens when a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine wall. This can cause light bleeding that looks brown or pink. This occurs about 6 to 12 days after ovulation. The flow stays light and does not last more than two days. You may mistake this for brown blood instead of red period , especially when their cycle is irregular. Implantation bleeding does not cause strong cramps or heavy clots.
Early Pregnancy Spotting
Early pregnancy raises blood flow to the cervix. The cervix becomes sensitive and may bleed after sex or physical activity. That blood often exits slowly, which makes it brown. Light brown spotting without pain is common in early pregnancy. Still, any bleeding during pregnancy should be reported to a doctor.
Miscarriage
A miscarriage can cause brown or red bleeding. Brown blood may appear first, followed by heavier bleeding. Cramping often feels strong and steady. Tissue or clots may pass. Early miscarriage is common, but heavy bleeding and pain always need medical care. Period blood brown alone does not confirm miscarriage, but color combined with pain and volume matters.
Ectopic Pregnancy (Warning Signs)
An ectopic pregnancy grows outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube. This condition is dangerous. Brown bleeding may occur with sharp pelvic pain, shoulder pain, or dizziness. Internal bleeding can happen quickly in an ectopic pregnancy. This is an emergency. Brown period blood is not normal when severe pain or fainting appears.
Infections That Can Cause Brown Period Blood
Certain infections inflame reproductive tissues, causing small amounts of blood to leak and darken before exit. These causes of brown menstrual blood usually involve odor, pain, or discharge changes rather than color alone.
Vaginal Infections
Bacterial vaginosis and yeast infections irritate vaginal tissue. Small amounts of blood mix with discharge and turn brown. A fishy odor, itching, or burning often appears. Untreated infections can worsen symptoms, but usually do not cause heavy bleeding.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause inflammation of the cervix. Inflamed tissue bleeds easily. That blood may appear brown between or during periods. Untreated STIs can cause irregular bleeding and fertility problems. Brown discharge during period with pelvic pain or discharge changes needs testing.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
PID occurs when infection spreads to the uterus or fallopian tubes. Symptoms include fever, pelvic pain, and abnormal bleeding. Brown bleeding may appear due to inflamed tissue shedding slowly. PID is a major cause of preventable infertility when untreated.
Signs of Infection to Watch For
You should watch for strong odor, yellow or green discharge, fever, chills, or pain during sex. These signs, combined with period blood brown signal an infection risk and need medical care.
Other Possible Causes
Structural factors like uterine shape, growths, or retained objects can delay blood flow. When blood pools before exiting, oxidation darkens it, creating brown blood instead of red period, even when hormone levels stay normal.
Retained Menstrual Blood
A tilted uterus or a tight cervix can trap blood. Trapped blood exits later and looks brown. This often causes stop-and-start flow. Uterine position alone does not cause disease.
Cervical or Uterine Polyps
Polyps are soft growths inside the cervix or uterus, and they bleed easily. Blood often appears brown after sex or between periods. Ultrasound or pelvic exam confirms this cause.
Recent Pelvic Exam or Sex
A pelvic exam or sex can irritate the cervix. Small blood vessels may break. That blood exits slowly and turns brown. This explains short episodes of brown blood instead of red period without pain.
Foreign Object (e.g., Tampon Left In)
A retained tampon can cause brown discharge with a strong odor. Fever or pelvic pain may follow. This situation needs immediate removal and medical care.
Symptoms That Matter Along With Brown Period Blood
Doctors assess symptoms over color because pain, fever, or odor reflect inflammation or infection. The normal brown blood during a period depends entirely on what other signs appear alongside it.
Foul Odor
A strong smell often points to infection or trapped blood. Normal menstrual blood should not smell foul.
Fever or Chills
Fever signals infection. Brown bleeding with fever needs urgent care.
Severe Pelvic Pain
Sharp or constant pain is not normal. Severe pain with brown period blood with cramps needs evaluation.
Heavy Bleeding or Clots
Soaking pads every hour or passing large clots is abnormal, regardless of color.
When to See a Doctor for Brown Period Blood
Persistent changes signal internal imbalance rather than random variation. Medical consensus shows that repeated periods of brown blood across cycles often points to hormonal, structural, or inflammatory causes needing evaluation.
Brown Blood Lasting Multiple Cycles
Repeated period blood brown over several months may signal a hormone imbalance, fibroids, or polyps.
Brown Blood With Severe Pain
Pain that limits movement or sleep needs medical review.
Brown Blood After Menopause
Any bleeding after menopause is abnormal. Brown blood included.
Brown Blood With Pregnancy
Bleeding during pregnancy should always be checked, even if light.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Evaluate Brown Period Blood
Diagnosis focuses on patterns, not single episodes. Imaging, hormone tests, and exams help identify whether period blood brown stems from ovulation changes, uterine growths, or systemic hormone disruption.
Medical History and Cycle Tracking
Doctors ask about cycle length, stress, birth control, and pain. Tracking apps or notes help identify patterns.
Pelvic Examination
A pelvic exam checks the cervix, vagina, and uterus for infection, polyps, or tenderness.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound shows fibroids, adenomyosis, polyps, or pregnancy location. NIH-supported imaging guidelines recommend ultrasound as a first tool.
Hormone Testing
Blood tests may check thyroid levels, estrogen, progesterone, or pregnancy hormones. Doctors usually decide on tests based on symptoms.
FAQs
Is brown period blood normal?
In many cases, yes. Brown period blood is normal often depends on timing, pain, and repeat patterns. Early or late-cycle brown blood without symptoms is usually harmless.
Can stress cause brown period blood?
Yes. Stress changes hormone signals from the brain. Those changes slow uterine shedding. That slow flow causes period blood to be brown , especially after intense stress.
Does brown blood mean pregnancy?
Not always. Implantation or early pregnancy can cause brown spotting, but hormones and stress can too. A pregnancy test confirms the cause.
Is brown blood a sign of infection?
Sometimes. Infection becomes likely when brown bleeding comes with odor, pain, fever, or discharge changes. Color alone does not confirm infection.
Why is my period brown with cramps?
Slow blood flow plus uterine contractions cause this. brown period blood with cramps is common on lighter days. Severe or worsening pain needs evaluation.
Can birth control cause brown periods?
Yes. Hormonal birth control thins the uterine lining. Thin lining sheds slowly, which turns blood brown during adjustment months.
How long should brown period blood last?
One to three days is common. Longer or repeated brown bleeding needs medical review.
Is brown blood instead of red a problem?
Often, no. brown blood instead of red period usually means older blood. Patterns and symptoms matter more than color.
Can PCOS cause brown period blood?
Yes. PCOS disrupts ovulation. Irregular shedding leads to brown menstrual blood patterns, including brown flow or spotting.
When should I worry about brown menstrual blood?
You should worry when pain, fever, pregnancy, foul odor, or repeated changes appear. Persistent period blood brown deserves medical attention.
















Leave a Comment