Neuroimmunology studies the link between the nervous system (your brain and nerves) and the immune system (your body’s defenders). It asks how they talk and help each other stay healthy. This field also looks at inflammation in the brain and how that can hurt thinking or feeling. Scientists study these neuroimmune communication links to learn why some brain problems begin.
What are neuroimmune diseases (neuroimmunological disorders)?
Neuroimmune diseases refer to conditions in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the brain, nerves, or spinal cord. They are part of a big group called autoimmune neurological disorders. These conditions come when messages between brain and immune system get mixed up.
Types of neuroimmune diseases

Here are a few key examples in the neuroimmunological disorders list:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Immune cells strip away myelin, the nerve’s protective coat, slowing or blocking brain-to-body messages.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS): A sudden immune attack on peripheral nerves, causing weakness that can spread quickly.
- Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Immune damage to the optic nerves and spinal cord, often leading to vision loss or paralysis.
- Myasthenia Gravis: Immune antibodies interfere with the communication between nerves and muscles, resulting in muscle weakness.
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis (ADEM): Often post-infection, immune cells inflame brain and spinal cord tissues.
These are just some from the neuroimmunological disorders list you can find in the journal of neuroimmunology.
What are the symptoms of neuroimmune diseases?
Symptoms depend on the condition, but often include:
- Numbness or tingling in arms or legs.
- Sudden muscle weakness or fatigue.
- Vision loss, double vision, or eye pain.
- Trouble with coordination or balance.
- Cognitive changes like memory lapses.
- Chronic pain or muscle stiffness.
Because they involve the nervous system, symptoms can appear in different combinations and often worsen over time.
How rare are neuroimmunological conditions?
Many of these are rare. Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is more prevalent, affecting approximately 2.8 million individuals globally. In contrast, conditions such as ADEM or NMO are significantly rarer, with some impacting fewer than 1 in 100,000 individuals.
What does a neuroimmunologist treat?
A neuroimmunologist is a highly trained doctor who works at the intersection of neurology and immunology. Their focus is diagnosing, managing, and researching illnesses from the neuroimmunological disorders list, conditions where the immune system mistakenly attacks the brain, spinal cord, or nerves.
They treat a wide range of issues, such as:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and related demyelinating disorders.
- Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD) and optic neuritis.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) are also included in this category.
- Myasthenia Gravis and other nerve-muscle signal disorders.
- Post-viral inflammatory syndromes affecting the nervous system.
Their role goes beyond prescribing medicine. They also monitor disease progression, manage relapses, and coordinate with rehab specialists. A big part of their work involves controlling neuroinflammation and using advanced neuroimmunology mechanisms to prevent long-term disability. Many also contribute to research published in the journal of neuroimmunology, helping develop new diagnostics and therapies.
What are the treatment options for neuroimmune diseases?
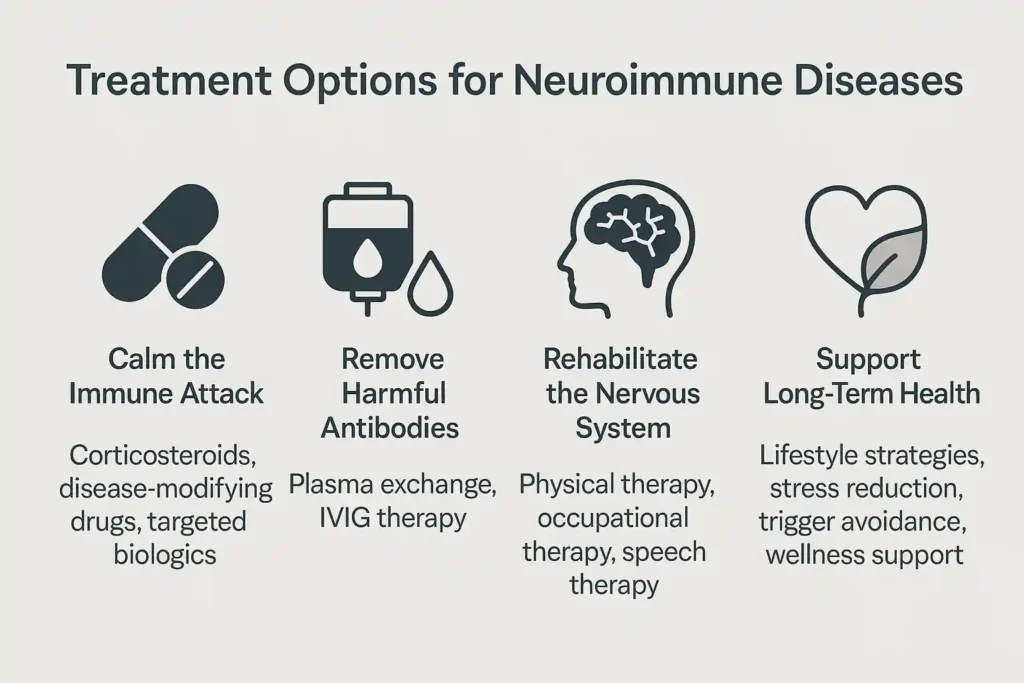
Treatment is never one-size-fits-all. The approach depends on the specific disorder, severity, and how quickly symptoms are progressing. Most plans aim to:
- Calm the immune attack: using medications like corticosteroids for flare-ups, disease-modifying drugs, or targeted biologics to stop further damage.
- Remove harmful antibodies: through plasma exchange or intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), which replaces faulty immune proteins with healthy ones.
- Rehabilitate the nervous system: neuroimmunology therapy includes physical therapy to rebuild strength, occupational therapy to improve daily function, and speech therapy if swallowing or speech muscles are affected.
- Support long-term health: lifestyle strategies to reduce stress, avoid triggers, and support overall wellness.
The ultimate goal is restoring balance in the neuroimmune axis, protecting nerve cells, and improving quality of life. Some patients need ongoing treatment, while others experience remission.
Advances in neurology, neuroimmunology & neuroinflammation research mean new drugs and therapies are regularly emerging, offering hope for better outcomes.
The Bottom Line
Neuroimmunology helps us understand how our brain and immune system work together. It also guides how we fix problems when they don’t. When the immune system attacks shy parts like the brain or nerves, it causes neuroimmune diseases. These conditions can bring hard symptoms, and each needs care from a smart doctor like a neuroimmunologist.
The good news is we have ways to help; drugs, therapy, and research from the journal of neuroimmunology keep making progress. Know that your brain and defenders usually work as one. When they slip, experts can step in. That is why learning what neuroimmunology is matters.
FAQs
What is the meaning of neuroimmunology?
It’s the study of how the nervous and immune systems interact, influence disease, and protect the body. Knowing what neuroimmunology is helps researchers develop better prevention and treatment strategies.
What do neuroimmunologists do?
They diagnose, treat, and research conditions from the neuroimmunological disorders list, using advances in the journal of neuroimmunology studies to improve care and limit nerve damage caused by immune system malfunction.
What are neuroimmune disorders?
These conditions involve the immune system damaging the nervous system, which leads to various neurological symptoms. Common examples include MS, NMOSD, and GBS, all featured in the neuroimmunological disorders list.
When to see a neuroimmunologist?
Seek help if you have sudden vision changes, unexplained weakness, or nerve pain. Early specialist care for neuroimmunological conditions can prevent long-term disability and improve recovery outcomes.
What are famous neuro diseases?
MS is the most widely known. Others like GBS, NMOSD, and myasthenia gravis also receive global research attention in neurology neuroimmunology & neuroinflammation journals.
What are examples of neuroimmunological disorders?
The neuroimmunological disorders list includes MS, GBS, NMOSD, ADEM, and myasthenia gravis. These vary in symptoms but share immune system attacks on the nervous system.
How does neuroimmunology relate to mental health?
Some mental health issues are linked to inflammation in the brain. Neuroimmunology research explores how immune changes may influence mood, cognition, and psychiatric conditions, improving understanding and treatment.














Leave a Comment