Signs of an unhealthy gut may manifest in unexpected ways, such as bloating, sudden fatigue, skin breakouts, or even mood swings. Your gut is more than a digestion center; it’s deeply linked to your brain, immune system, and overall health.
When it’s out of balance, your body speaks up. The key is to listen early and take steps before these problems turn into something more serious.
What is the gut microbiome and why is it important?
Your gut microbiome is a collective of trillions of tiny bacteria, viruses, and fungi that inhabit your digestive tract.
While “bacteria” might sound bad, most of these microbes are actually helpful. They help break down food, produce vitamins, and protect you from harmful germs.
A balanced gut microbiome means your digestion runs smoothly, your immune system works well, and your body absorbs the nutrients it needs. When that balance is disturbed, unhealthy gut symptoms start to appear.
How does the gut microbiome affect your health?
The gut is often called the “second brain” because it communicates with your nervous system. This is where gut-brain connection symptoms come in, your gut health can affect your mood, focus, and sleep.
It also plays a huge role in:
- Immune system and gut health: About 70% of your immune cells live in your gut. A damaged gut makes you more prone to infections and allergies.
- Nutrient absorption: A healthy gut absorbs vitamins and minerals properly. But if you have poor nutrient absorption, you might feel tired or weak even if you eat well.
- Skin health: Conditions like acne, eczema, and rashes can be skin problems associated with gut health.
- Weight control: Your gut bacteria help regulate appetite and how your body stores fat.
7 signs of an unhealthy gut
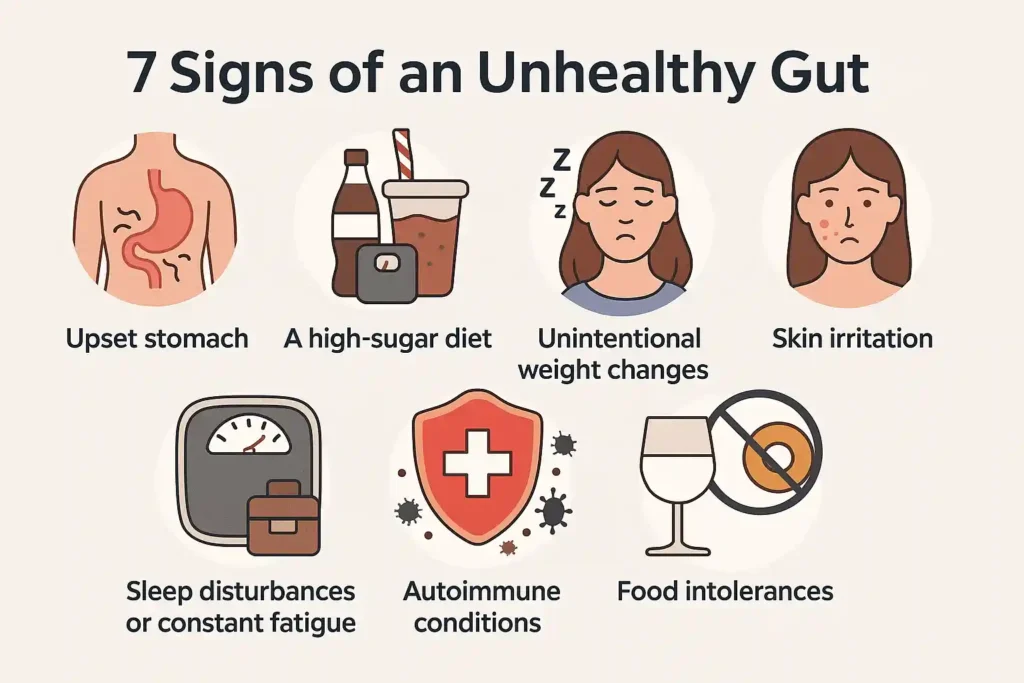
If your gut microbiome is off-balance, your body will send clues. Here are the most common indicators of an unhealthy gut to keep an eye on:
1. Upset stomach
Frequent bloating, gas, heartburn, or irregular bowel movements can point to gut inflammation signs. A healthy gut processes food with minimal discomfort.
2. A high-sugar diet
Eating too much sugar feeds harmful bacteria and yeast in your gut. This imbalance can provoke inflammation and reduce the population of beneficial bacteria.
3. Unintentional weight changes
If you lose or gain weight without changing your diet or activity, it might be due to poor nutrient absorption or bacterial imbalance.
4. Sleep disturbances or constant fatigue
An unhealthy gut can disrupt serotonin production, a hormone that affects sleep. Consequently, this results in fatigue and poor gut health, even if you get sufficient rest.
5. Skin irritation
Conditions like eczema, acne, or rosacea may be skin issues linked to gut health. A leaky gut can trigger inflammation that shows up on your skin.
6. Autoimmune conditions
When your gut is damaged, it can confuse your immune system. This may lead to your body attacking its own tissues.
7. Food intolerances
If you suddenly can’t handle dairy, gluten, or other foods, it may be because your gut bacteria can’t break them down anymore.
7 things you can do for your gut health
When you notice unhealthy gut symptoms, the right changes can help restore balance. These aren’t quick fixes; they’re habits that protect your digestive system for life.
Lower your stress levels
Stress isn’t just in your head, it directly impacts your gut bacteria and can trigger gut inflammation signs. Try short daily breaks for breathing, light stretching, or a walk outdoors. Even 10 minutes can help.
Get enough sleep
Your gut repairs itself while you sleep. Poor sleep disrupts your bacteria’s natural rhythm, which may affect digestion and immunity. Aim for 7–8 hours of quality rest every night.
Eat slowly
Rushed meals make your stomach work harder, leading to discomfort. Eating slowly lets your digestive enzymes do their job, improves poor nutrient absorption, and can reduce bloating.
Stay hydrated
Water keeps food moving smoothly through your intestines and helps maintain the gut’s protective lining. Dehydration can lead to chronic constipation or diarrhea, which disturbs the bacterial balance.
Take a prebiotic or probiotic
Probiotics add good bacteria; prebiotics feed them. Together, they help with unhealthy gut treatment by restoring balance, improving digestion, and supporting immune system and gut health.
Check for food intolerances
If certain foods cause bloating, headaches, or rashes, your gut may struggle to break them down. Keeping a food diary can reveal patterns so you can avoid irritants.
Change your diet
Cut back on processed, high-sugar foods and add more whole, fresh options. Diet is the biggest factor in preventing symptoms of an unhealthy gut and maintaining a balanced microbiome.
4 types of food for gut health
The right foods can act as daily medicine for your digestive system. When you’re focused on unhealthy gut treatment, these choices make the most impact.
High fiber foods
Fiber feeds beneficial bacteria and keeps your digestion regular. Lentils, beans, oats, and fresh fruits also help ease chronic constipation or diarrhea and improve stool consistency.
Garlic
Garlic works like a natural prebiotic, helping healthy bacteria grow while keeping harmful ones in check. It may also lower inflammation and protect against certain infections.
Fermented foods
Yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut provide live probiotics. They can ease fatigue and poor gut health by improving digestion, reducing bloating, and supporting overall bacterial diversity.
Collagen-boosting foods
Bone broth, salmon, and chicken skin help strengthen the gut lining. A stronger lining means fewer skin issues linked to gut health and reduced risk of inflammation.
The Bottom Line
Your gut is the control center for more than just digestion. If you spot signs of an unhealthy gut, act early. Adopting simple habits, a better diet, adequate rest, and managing stress can naturally restore your gut health.
Remember, unhealthy gut treatment doesn’t have to be complicated.It involves making small, consistent adjustments that promote your body’s natural equilibrium.
Frequently asked questions
Why does the gut microbiome vary in individuals?
Each person’s microbiome is shaped by diet, lifestyle, environment, stress, and even birth method, which explains why symptoms of an unhealthy gut differ widely between individuals.
How does the gut microbiome respond to fasting?
Short-term fasting may boost good bacteria diversity, but prolonged fasting can reduce beneficial strains. Always balance fasting with nutrient-rich foods for long-term gut stability.
Does eating probiotics actually change your gut microbiome?
Yes, probiotics can temporarily alter gut bacteria composition. For lasting benefits, combine them with prebiotics and a nutrient-rich diet.
How can I improve my gut health?
Eat fiber-rich foods, stay hydrated, reduce stress, sleep well, and include probiotics or fermented foods daily to promote a balanced microbiome.
What are the signs of an unhealthy gut?
Bloating, irregular stools, skin flare-ups, unexplained fatigue, weight changes, and food intolerances are common unhealthy gut symptoms needing prompt attention.
















Leave a Comment