A stroke happens when blood flow to part of the brain suddenly drops or stops, causing brain cells to lose oxygen and begin to die within minutes. Stress is the body’s natural response to pressure or threat, releasing hormones that change heart rate, blood pressure, and blood clotting to help you cope.
Yes, stress can cause a stroke , but not simply or directly for most people. Intense or long-lasting stress can raise blood pressure, disturb heart rhythm, increase inflammation, and make blood more likely to clot. These changes can damage blood vessels over time and, in high-risk situations, stress can trigger a stroke by pushing an already strained system beyond its limit.
Chronic stress also worsens key stroke risks like hypertension, diabetes, poor sleep and unhealthy coping habits. Because of these combined effects, doctors recognize stress as a serious contributor to stroke risk rather than a harmless emotional state.
Stress And Stroke Risk
Your brain needs steady blood flow. A stroke happens when blood cannot reach part of your brain. A clot can block an artery (blood tube). A vessel can also break and bleed.
Stress affects your body in ways that raise stroke risk. High psychosocial stress leads to higher stroke odds. One major study found high stress tied to about double the odds of stroke. It also suggested a meaningful share of strokes could relate to psychosocial factors.
This does not prove stress “alone” causes stroke. It shows that the risk of stress-induced stroke is possible.
Acute Stress Vs Chronic Stress
Acute stress means short-term stress. It can come from a sudden fight, fear, or shock. Your body reacts fast, your heart beats harder, and your blood vessels tighten.
Chronic stress means stress that lasts weeks or years. This kind matters more. Your body stays on alert. You may keep cortisol high. Cortisol is a stress hormone.
Chronic stress also changes habits. You may crave salty foods. You may move less. You may drink more alcohol. Those habits can raise blood pressure and clot risk.
Over time, stress can cause a stroke because your body never gets a true reset.
Stress Hormones And Blood Vessel Damage
Stress hormones help you react to danger. Adrenaline can narrow blood vessels. Cortisol can change how your body handles sugar and fat.
Over time, this can harm the endothelium (the inner lining of blood vessels). A damaged lining lets plaque grow faster. Plaque is a fatty buildup. It can narrow arteries and raise clot risk. This pathway helps explain chronic stress-induced stroke risk .
Can Stress Trigger A Stroke Suddenly?
Sometimes a stroke happens right after intense emotion. People often say, “It happened after a big shock.” That timing can be real. Stress can trigger a stroke in the short term, mainly in people with weak points already.
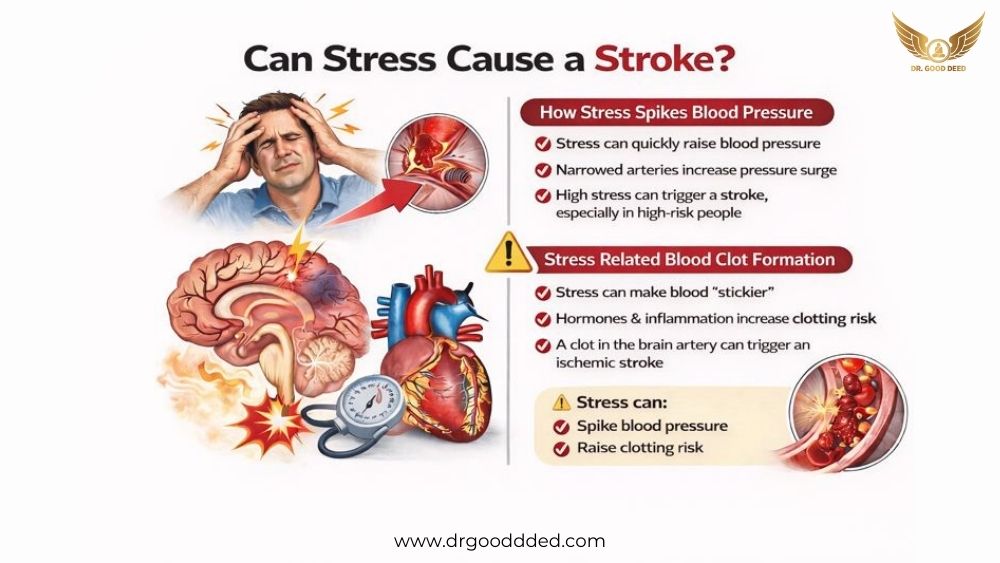
How Stress Spikes Blood Pressure
Stress can raise blood pressure in minutes. Your heart pumps faster. Your vessels narrow. This creates a pressure surge.
Stress causes a hormone surge that raises blood pressure for a time. Stress may raise stroke risk through unhealthy stress responses.
A fast pressure surge can raise the chance of a high stress blood pressure stroke . This risk rises even more if you already have hypertension (long-term high blood pressure).
In some people, stress can also raise blood pressure swings. Big swings are linked with heart and brain events. In this way, stress can cause a stroke through pressure spikes.
Stress Related Blood Clot Formation
Stress can affect clotting. It can raise inflammation. It can also activate platelets. Platelets help blood clot when you bleed. Too much activation can support unwanted clots.
A clot that forms or grows can block a brain artery. That can cause an ischemic stroke (stroke from a blockage).
Some research on stroke “triggers” discusses emotional upset and anger as short-term triggers in some people. This is one reason people use the phrase stress induced stroke .
Can Emotional Shock Cause A Stroke?
A severe shock can strain your heart and vessels. Your blood pressure may jump. Your heart rhythm can also change. Acute psychological stress is linked to higher odds of stroke within a short window after the stress event.
This does not mean every shock causes a stroke. It means a shock can trigger a stroke in a high-risk body. In that setting, stress can cause a stroke because it pushes the system past its limit.
High Stress Blood Pressure Stroke
High blood pressure is the top stroke risk factor. When stress worsens blood pressure, stroke risk rise.
Stress-Induced Hypertension Explained
Hypertension means blood pressure stays too high over time. Stress alone does not prove it causes long-term hypertension in everyone. Still, stress can help it develop and persist.
Stress can drive weight gain. It can worsen sleep. It can increase alcohol use. It can also make you skip exercise. Each of these raises blood pressure.
So stress enables your pressure to stay high, and high pressure helps cause the stroke. In this way, stress can cause a stroke by supporting hypertension.
Long-Term Blood Pressure Damage
Long-term high blood pressure stiffens arteries. It can weaken small brain vessels. Those vessels can leak or break. That can cause hemorrhagic stroke (stroke from bleeding).
High pressure also damages artery walls. It helps plaque grow. Plaque can break and form a clot. So, repeated stress spikes matter, which increases the risk of stress-induced stroke .
Chronic Stress Stroke Risk Over Time
Chronic stress does not just feel bad. It can change biology.
Chronic Stress And Inflammation
Inflammation means your body stays in “fight mode.” Chronic stress can keep inflammatory signals high. Inflammation harms vessel lining. It can also make plaques less stable.
Less stable plaques can crack. Cracks can form clots. Clots can block brain arteries. This is a key part of chronic stress-induced stroke risk .
Stress, Cholesterol, And Arterial Damage
Stress can alter how your body handles fats and sugar. Some people see higher LDL (bad cholesterol). Some people gain belly fat. That combo supports plaque growth.
Over the years, plaque buildup narrows arteries. This can raise stroke risk. Again, stress can cause a stroke by feeding artery damage.
Chronic Stress And Heart–Brain Connection
Your heart can form clots that travel to the brain. This can happen with atrial fibrillation (a fast, uneven rhythm). Stress can worsen rhythm problems in some people. It can also worsen blood pressure control.
So stress can raise stroke risk even when the brain vessels look fine. The clot can start in the heart. This link supports the concern that stress can trigger a stroke in some people.
Stress-Induced Stroke
Medicine usually sees stress as a contributor more than a single cause.
Scientific Evidence Linking Stress To Stroke
Large studies link psychosocial stress to higher stroke odds. A 2022 study in JAMA Network Open found self-reported stress in the prior year linked with higher risk of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
The American Heart Association also notes links between negative mental health and higher heart disease and stroke risk. It also says research still grows on how stress contributes. This means evidence supports the link. It also means some details remain uncertain.
Stress As A Contributing Vs Direct Cause
Most of the time, stress works as a multiplier. It raises pressure. It worsens sleep. It drives smoking and drinking. It makes diabetes control harder.
In fewer cases, stress may act like a direct trigger. This tends to happen with a pressure surge or a clot-friendly moment. Research on acute triggers supports that idea, but it does not cover every person. So yes, stress can cause a stroke , but it often does it by teaming up with other risks.
Stress And Stroke Risk Factors You Should Know
Stress rarely travels alone. When life stays tense, your choices change. Your body also changes. This mix raises the risk of stress-induced stroke far more than stress by itself.
Stress, Smoking, And Alcohol Use
When stress stays high, you may reach for quick relief. Smoking feels calming for a minute. It also tightens blood vessels. It raises blood pressure. It damages the vessel lining. It makes blood more likely to clot. That is a direct path toward stroke.
Alcohol can look like “switching off your brain.” Heavy drinking can raise blood pressure over time. It can also cause heart rhythm problems in some people. An uneven rhythm can form clots in the heart. Those clots can travel to the brain.
Stress can push you into habits that raise stroke risk fast. In that way, stress can cause a stroke by shaping what you do daily.
Stress, Diabetes, And Obesity
Stress can raise blood sugar. It does this through stress hormones. High blood sugar harms blood vessels. It also makes plaques grow faster. Plaques are fatty patches inside arteries.
Stress can also increase belly fat. Belly fat links with insulin resistance (your body struggles to use insulin). Insulin helps move sugar from blood into cells. When insulin resistance rises, diabetes risk rises too.
If you have diabetes already, stress can make control harder. You may miss meals. You may overeat. You may skip medicine. This is not about blame. It is about seeing the pattern so you can break it. It also explains why stress can cause a stroke through indirect damage.
Poor Sleep And Stress-Related Stroke Risk
Stress can ruin sleep. Sleep loss raises blood pressure. It also increases hunger. It can push you toward salty snacks and sugar. It can make you less active.
Some people also get sleep apnea (breathing pauses during sleep). You may snore loudly and still wake up tired. Sleep apnea can raise blood pressure and stroke risk. If stress also harms your sleep, the risk stacks up.
This is why people with poor sleep often show higher chronic stress-induced stroke risk .
Warning Signs Of A Stress-Related Stroke
A stroke is an emergency. The cause does not matter. Stress does not “explain it away.” If anything feels sudden and wrong, act.
FAST Signs Of Stroke
FAST is a simple check. Face droops on one side. Arm weakness shows on one side. Speech becomes slurred or odd. Time means get help right now.
Stress can make you second-guess symptoms. You may think, “I am just anxious.” Do not guess. Stress can cause a stroke in some settings, but you cannot tell at home. You need urgent care.
Early Neurological Symptoms
Some stroke signs look less obvious than FAST. You may feel sudden numbness or tingling on one side. You may get sudden vision loss or double vision. You may feel sudden dizziness with trouble walking. You may get a sudden, severe headache.
If you feel “off” in a new way, treat it seriously. If symptoms start and then fade, that can be a TIA (mini-stroke). A TIA is a warning.
Medical Treatment For Stress And Stroke Prevention
Treatment focuses on two things. Doctors treat your stroke risks. You also work on stress, so it stops feeding those risks.
Managing High Blood Pressure
Blood pressure control matters the most for prevention. Doctors often ask you to check your blood pressure at home. They may adjust meds. They may look for causes like sleep apnea or kidney issues.
- Lifestyle also matters.
- Regular walking can help relieve pressure.
- Lower salt can help.
- Better sleep can help.
If stress keeps pushing your pressure up, you can still make progress. Calm breathing for a few minutes can lower stress signals. It can help lower short spikes. This can reduce the chance of a high-stress blood pressure stroke .
Mental Health Support And Medications
Mental health support is medical care. Therapy can teach skills that stop stress from running your body. It can help you spot triggers. It can help you set boundaries. It can help you sleep.
Some people also need medicine for anxiety or depression. A clinician decides what fits your history. Dosage varies by age and condition. The goal is not to numb you. The goal is steady function and safer health.
This matters because stress can cause a stroke partly through long strain. Treating mental health can lower that strain.
When To See A Doctor For Stress-Related Stroke Risk
You do not need to wait for a crisis. Early care is prevention.
Emergency Warning Signs
Call emergency services for FAST signs. Also call for sudden vision loss, sudden confusion, sudden severe headache, or sudden weakness. Do not drive yourself if you feel unsafe.
If you feel intense stress and sudden brain symptoms, assume danger. Stress can trigger a stroke in some people. The safe move is urgent care.
Preventive Health Screenings
If stress feels constant, ask for a risk check. A basic plan includes blood pressure checks, cholesterol tests, and blood sugar tests. Your clinician may also check your heart rhythm. They may ask about sleep apnea signs.
These checks find silent risks early. That lowers the risk of stress-induced stroke over time.
FAQs
Can Stress Alone Cause A Stroke?
Stress alone rarely acts as the only cause. Most strokes involve clots, bleeding, or artery disease. Still, stress can cause a stroke by raising blood pressure and clot risk, mainly when other risks exist.
Can Stress Cause A Mini-Stroke (TIA)?
Yes, it can play a role. A TIA often comes from a small clot or a narrow artery. Stress may raise pressure and clotting, so stress-induced stroke warning events can happen in high-risk people.
How Long Does Stress Need To Increase Stroke Risk?
A stress spike can matter in minutes or hours, mainly with high blood pressure. Long-term stress over months raises vessel damage. That is why chronic stress-induced stroke risk grows when stress never drops.
Is Stress-Induced Stroke Reversible?
Some recovery can happen, especially with fast treatment and rehab. Full recovery depends on stroke type and size. A stress-induced stroke still needs urgent care to limit brain damage.
Does Managing Stress Reduce Future Stroke Risk?
It can. Better stress control improves sleep and blood pressure habits. It may lower smoking and heavy drinking. Over time, this can lower the risk of stress-induced stroke in a real, practical way.
Can Anxiety Medication Lower Stroke Risk?
It might help indirectly. If anxiety control improves sleep and lowers pressure spikes, risk may drop. A clinician should guide this. Never stop meds suddenly. Stress can cause a stroke risk when care breaks down.
Can Stress Cause Brain Hemorrhage?
Stress can raise blood pressure quickly. In someone with weak brain vessels, a sharp surge can raise bleed risk. So stress can trigger a stroke that involves bleeding, but it usually needs other risks to be present.
Who Is Most At Risk Of Stress-Induced Stroke?
You face a higher risk if you have high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity and sleep apnea , or heart rhythm problems. In that group, stress can cause a stroke more easily because the system has weak points.
Can Work Stress Increase Stroke Risk?
Yes, especially when stress stays high for years. Long hours and low control can harm sleep and blood pressure. That pattern can raise chronic stress-induced stroke risk over time, even in younger adults.
What Tests Assess Stress-Related Stroke Risk?
Clinicians often check blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol. They may do an ECG (heart rhythm test). They may order a sleep study if sleep apnea seems likely. These tests help catch high stress, blood pressure and stroke risk early.








Leave a Comment