Head pain can be a simple ache or a sign of a deeper problem. You need clear facts now. A headache is usually short and mild. A migraine is a brain disorder that causes intense, often one-sided, throbbing pain plus nausea and sensitivity to light or sound. If pain stops your routine, think migraine and get help.
What Is The Difference Between a Headache And Migraine?
You should know the basic difference between the two. A typical headache causes steady, mild to moderate pressure. It often sits on both sides of the head. A migraine causes severe, pulsating pain. It usually hits one side. Migraines bring other problems.
You may feel sick, see flashes, or hate bright light and sound. Migraines last longer than common headaches. They can keep you in bed for hours or days.
Headache: General Pain And Mild Discomfort
A headache feels like steady pressure or a dull ache. It may come from tight muscles, stress, or poor sleep. You can often work through a mild headache. Over-the-counter pain medicine helps. Hydration and rest often stop it. If headaches happen when you move or bend, you should watch them. If they get worse, see a doctor.
Migraine: Neurological Disorder With Severe Symptoms
A migraine is not only head pain. It is a brain condition that makes many body systems work incorrectly for a while. Your stomach may rebel. Your senses may go haywire. You may get an aura, which is a visual or sensory change before pain.
Migraines can start in childhood or later. They often run in families. New medicines target migraine pathways in the brain and cut attacks for many people.
Key Differences In Duration, Pain Location, And Triggers
Headaches usually last minutes to a few hours. Migraines often last four hours to three days without treatment. Headaches tend to sit on both sides. Migraines more often affect one side. Triggers overlap but differ. Stress, lack of sleep, and dehydration cause both. Hormones, certain foods, lights, and weather are classic migraine triggers. Keep a diary to find your triggers.
When A Headache May Actually Be A Migraine
If pain grows strong and steady, check for migraine signs. If lights or sound make the pain worse, think migraine. If you feel sick or throw up, think migraine. If a simple painkiller fails or if the attack lasts many hours, see your clinician.
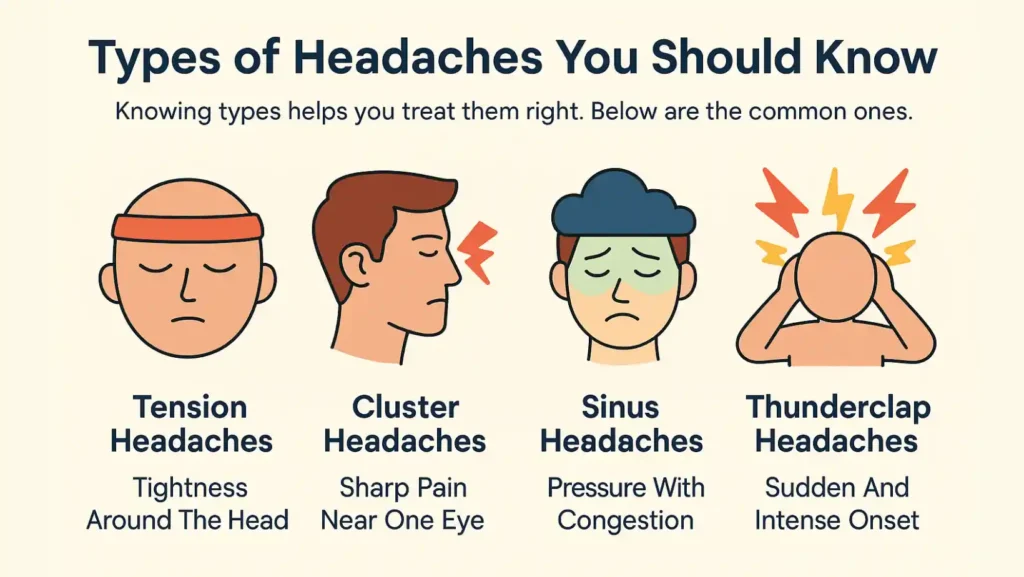
Types Of Headaches You Should Know
Knowing types helps you treat them right. Below are the common ones.
Tension Headaches — Tightness Around The Head
This type feels like a band wrapped around your head. You may feel tight neck muscles. Pain stays steady. It rarely comes with nausea or light sensitivity. Rest, hydration, and simple painkillers help.
Cluster Headaches — Sharp Pain Near One Eye
Cluster attacks are short but very painful. Pain centers around one eye. You may tear or have a red eye. Attacks may come many times a day for weeks. Cluster headaches need urgent care and specialist help.
Sinus Headaches — Pressure With Congestion
Sinus headaches come with facial pressure, a stuffy nose, or a fever. They follow a sinus infection. If you have thick nasal mucus and a fever, treat the infection. If pain remains, see a doctor.
Thunderclap Headaches — Sudden And Intense Onset
Thunderclap pain reaches full intensity in seconds. This is a red flag. You must seek emergency care. It can signal bleeding or other critical brain problems.
Secondary Headaches — Linked To Other Conditions
Secondary headaches occur because of another health issue. Examples include head injury, high blood pressure, infection, or a brain tumor. If your headache follows an injury or comes with fever and stiff neck, seek medical care.
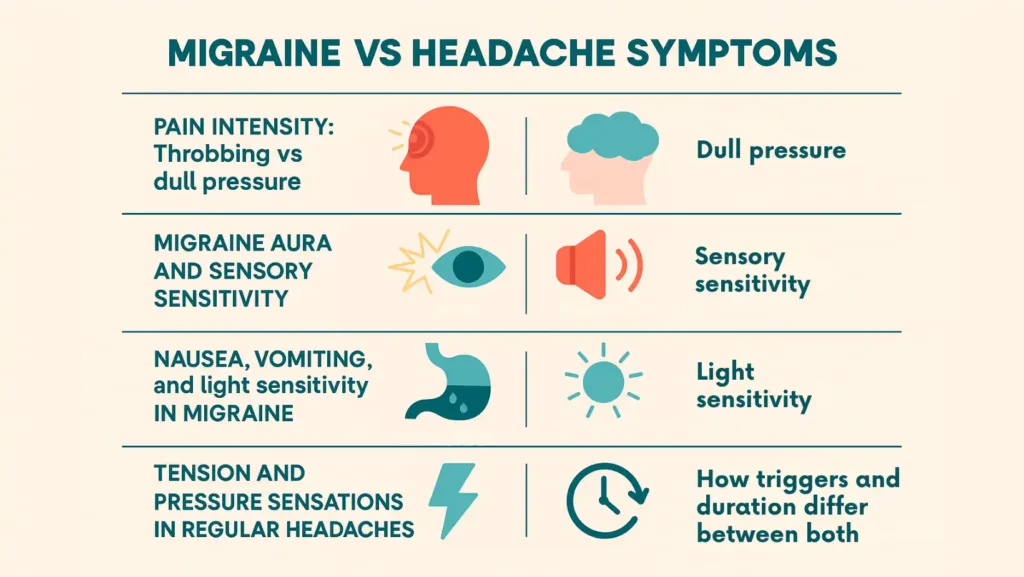
Migraine Vs Headache Symptoms
Compare symptoms so you know what to do.
Pain Intensity: Throbbing Vs Dull Pressure
Headaches feel like steady pressure. Migraines often throb with your pulse. Migraines block tasks. Headaches usually do not.
Migraine Aura And Sensory Sensitivity
An aura is a short, reversible change before the migraine pain. You may see zigzag lights, blind spots, or feel numbness. Auras last from minutes to an hour. Sensitivity to light or sound often follows. If you get an aura, you should record it and tell your doctor.
Nausea, Vomiting, And Light Sensitivity In Migraine
Migraines often bring nausea or vomiting. Light and sound make pain worse. This combination separates migraines from most headaches. These signs matter for treatment choice.
Tension And Pressure Sensations In Regular Headaches
Tension headaches give a steady, bilateral pressure. They do not usually cause vomiting or strong sensitivity to light. Muscle tightness and posture are common causes.
How Triggers And Duration Differ Between Both
Migraines usually follow specific triggers and last longer. Headaches are often linked to stress or a short trigger and end sooner. Track attacks to spot patterns.
Migraine vs Headache Pain Intensity And Location
Pain level and place give big clues.
Headache Pain: Mild To Moderate, Both Sides Of The Head
If pain sits on both sides and does not stop you, it is likely a common headache. You can usually treat it yourself.
Migraine Pain: Severe, One-Sided, Often Pulsating
If pain is strong and one-sided, you likely face a migraine. The pain may pulse and rise with movement. It often forces you to stop and rest.
Associated Neurological Changes In Migraine Attacks
Migraines can change vision, speech, or the sense of touch. You may feel numbness or confusion. These signs need prompt medical review.
Common Triggers: Migraine vs Headache
Find triggers to cut attacks.
Stress, Sleep Deprivation, And Dehydration
You must keep a regular sleep schedule and drink enough fluids. Skipping sleep or water commonly triggers both headaches and migraines.
Hormonal And Dietary Triggers For Migraines
Hormone swings, especially around your period, can start migraines. Certain foods, like aged cheese or processed meats, can trigger attacks. Alcohol can also trigger them.
Weather, Light, And Sensory Overstimulation
Bright lights, strong smells, and loud noise can set off migraines. Sudden weather change can also cause attacks.
When To Track Triggers Using A Headache Diary
Write date, time, food, sleep, weather, and symptoms. Note the medicine taken and result. Over weeks, patterns appear. Bring this diary to your doctor.
Headache Or Migraine: How To Know Which You Have
Ask direct questions and make notes.
Identifying Symptom Patterns And Severity
Note how bad the pain is. Note other symptoms like nausea, aura, or light sensitivity. Severe symptoms point to migraine.
Duration And Recurrence Of Pain Episodes
Short, rare pain favors a headache. Long or frequent attacks suggest migraine. Count how many days per month you have pain.
Physical Vs Neurological Signs
If you have muscle tension and no other signs, think tension headache. If you have vision changes, numbness, or speech trouble, think migraine or other neurological issues.
When To Seek A Medical Diagnosis
See a doctor if attacks limit your work or school. See a doctor if pain lasts over 72 hours or comes with fever, weakness, or a sudden, severe onset. Imaging, like CT or MRI, may be needed if red flags appear.
Migraine Headaches Vs Regular Headaches
Compare to pick the right care.
Migraine Involves More Than Head Pain — It’s Systemic
A migraine affects multiple systems. You may feel tired, sick, and sensitive to your senses. Treatment needs more than a simple painkiller.
Headaches Are Typically Surface-Level And Short-Lived
Most headaches resolve with rest or a simple medicine. They rarely cause long-term disability.
Migraine Phases: Prodrome, Aura, Pain, And Recovery
Migraines often move through stages. Prodrome can start hours or days before. You may yawn or crave food. Aura may follow. Pain comes next. Recovery leaves you tired and slow. Not all people get all stages.
Chronic Headaches Vs Episodic Migraines
Chronic headaches mean many headache days per month. Episodic migraines come in attacks. A clinician helps set prevention and treatment.
Diagnostic Tests For Headaches And Migraines
Doctors use stepwise evaluation.
Physical And Neurological Exams
Your clinician checks reflexes, vision, and coordination. They will ask about triggers and family history.
Imaging Tests (CT Or MRI) When Red Flags Appear
Scans are not routine. Doctors order them if headaches follow injury, have a sudden onset, or come with other worrying signs. Imaging rules out bleeding or structural problems.
Keeping A Pain And Trigger Journal
A clear diary helps diagnosis and treatment choices. It also shows how well medicines work.
Specialist Consultation For Chronic Symptoms
See a neurologist if attacks persist. New options, like CGRP antibodies and gepants, help many people. These options are used when standard treatments fail.
Treatment For Headache And Migraine
Choose treatment by type and severity.
Over-The-Counter Medications For Mild Headaches
Paracetamol or ibuprofen helps with many tension headaches. Read doses and avoid excess use. Overuse can cause rebound headaches.
Prescription Migraine Medicines: Triptans, CGRP Blockers
If you get moderate to severe migraines, doctors may give triptans. New options include CGRP blockers and gepants. These target migraine mechanisms and can prevent or stop attacks. Some work fast and reduce nausea. Your doctor chooses based on your health and other medicines.
Home Remedies: Hydration, Cold Compress, Rest
At the first sign, move to a dark, quiet room. Drink water. Place a cold pack on your forehead. These steps often ease the attack.
Stress Management And Sleep Improvement
Daily exercise and steady sleep reduce attacks. Try short relaxation sessions. Reduce screen time at night.
Lifestyle Changes To Reduce Frequency And Severity
Avoid trigger foods. Keep a steady caffeine level. Limit alcohol. Follow a sleep schedule. These changes lower attack risk.
When To See A Doctor For A Headache Or Migraine
Act on warning signs.
If Pain Lasts More Than 72 Hours
Seek care if pain persists for three days. Prolonged pain is not normal.
When Vision, Speech, Or Balance Issues Occur
These signs need urgent evaluation. Do not wait.
Recurrent Headaches Disrupting Daily Life
If pain stops your work, school, or play, ask for medical help.
Sudden Severe Pain “Worst Headache Ever”
This needs emergency care. Sudden intense pain can signal bleeding or other life-threatening conditions.
Prevention Tips For Migraine And Headache Relief
Small steps bring big gains.
Maintain Consistent Sleep And Hydration
Go to bed and wake up at the same time. Drink water all day.
Eat Balanced Meals And Avoid Skipping Meals
Skipping meals and low blood sugar can trigger attacks. Eat regular, small meals.
Manage Stress Through Exercise And Relaxation
A 20-minute walk helps. Short breathing breaks at work help.
Limit Caffeine And Alcohol
Keep caffeine steady and low. Avoid alcohol before big events.
Track And Avoid Personal Headache Triggers
Your diary shows triggers. Cut them when possible.
FAQs
How can I tell if my headache is actually a migraine?
You look for strong, one-sided throbbing pain, nausea, and light sensitivity. Aura or clear triggers suggest migraine and need specific treatment.
Are migraines more painful than regular headaches?
Yes, migraines usually cause stronger and longer pain. They often bring nausea and sensitivity to light and sound.
What triggers migraine attacks?
Triggers include hormones, certain foods, changes in sleep, bright lights, and weather shifts. Keep a diary to find your personal triggers.
Can stress cause both headaches and migraines?
Yes. Stress triggers both types. Long-term stress often raises migraine risk and frequency for many people.
How long do migraine headaches last?
Migraines typically last four to seventy-two hours without treatment. Some people have shorter attacks and some much longer.
Can a migraine start as a normal headache?
Yes. Mild pain can grow into a full migraine. Watch for nausea and sensitivity to light as signs that it has changed.
Are migraines hereditary?
Yes. Migraines often run in families. If a parent has migraines, you have a higher chance of getting them.
How is a migraine diagnosed by doctors?
A doctor uses your history, exam, and headache diary. They order scans only if red flags or new patterns appear.
Do migraine medications help with other headache types?
Some medications help both, but triptans mainly treat migraines. Over-the-counter painkillers treat many headaches.
When should I see a neurologist for recurring headaches?
See a neurologist if attacks happen often or stop your daily life. Specialists offer preventive care and advanced medicines.
Can dehydration cause migraines or headaches?
Yes. Mild dehydration often triggers headaches. Severe dehydration can also trigger a migraine in those who are prone.
What are natural remedies for migraine prevention?
Regular sleep, hydration, steady meals, exercise, and trigger avoidance lower migraine risk over time.














Leave a Comment