Eating too much dietary fiber can upset your gut quickly. If you eat a huge amount at once, you will feel bloated, gassy, and uncomfortable. Over time, very high intake can slow your stools, cause cramps, and even lead to dehydration. You fix most problems by drinking more water, cutting fiber temporarily, and moving gently. See a doctor if pain or inability to pass stool appears.
What Is Considered Too Much Dietary Fiber?
Adults usually need 25 to 38 grams of fiber each day. Eating far above this, especially all at once, is risky. When you take more than about 70 grams a day, your gut can struggle. Supplements, bran, beans, and raw vegetables can push you past this limit fast. You must add fiber slowly. A sudden jump makes too much dietary fiber is more likely to cause trouble.
Recommended Daily Fiber Intake By Age & Gender
Below are clear targets you can use.
- Children 1 to 3 years: 19 grams.
- Children 4 to 8 years: 25 grams.
- Girls 9 to 13 years: 26 grams.
- Boys 9 to 13 years: 31 grams.
- Women under 50: 25 grams.
- Men under 50: 38 grams.
- Older adults: targets drop slightly.
These are general guides. If you have a medical condition, follow your clinician’s advice. If you suddenly exceed these amounts, you risk too much dietary fiber effects.
How Excess Fiber Builds Up In The Digestive Tract
Fiber moves differently depending on type. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and makes a soft gel. Insoluble fiber adds bulk and helps stool move. Both need water to work well. If you do not drink enough, fiber can clump. Clumps sit in the gut and slow movement. Gut bacteria then ferment the fiber. Fermentation makes gas. The result is pressure, bloating, and pain. This is how too much dietary fiber causes symptoms.
Early Fiber Overdose Symptoms
Early signs warn you before a worse problem starts. Watch for these.
Bloating And Abdominal Pressure
You will feel a swollen belly. The pressure comes from the fiber that holds water and from gas. Bloating can start within hours. It may last a day or more. If you feel tightness after meals, you may have fiber overdose symptoms.
Gas Buildup And Digestive Discomfort
Bacteria break down fiber and make gas. A sudden high intake increases gas quickly. You may pass gas often. You may also feel sharp pains when the bowel contracts to move gas. These signs are common when you add a lot of fiber fast.
Feeling Overly Full After Eating
High fiber fills your stomach fast. You may stop eating sooner. Fullness can make it hard to sleep or move. It can also reduce your normal appetite. If fullness lasts, cut back on fiber till you feel normal.
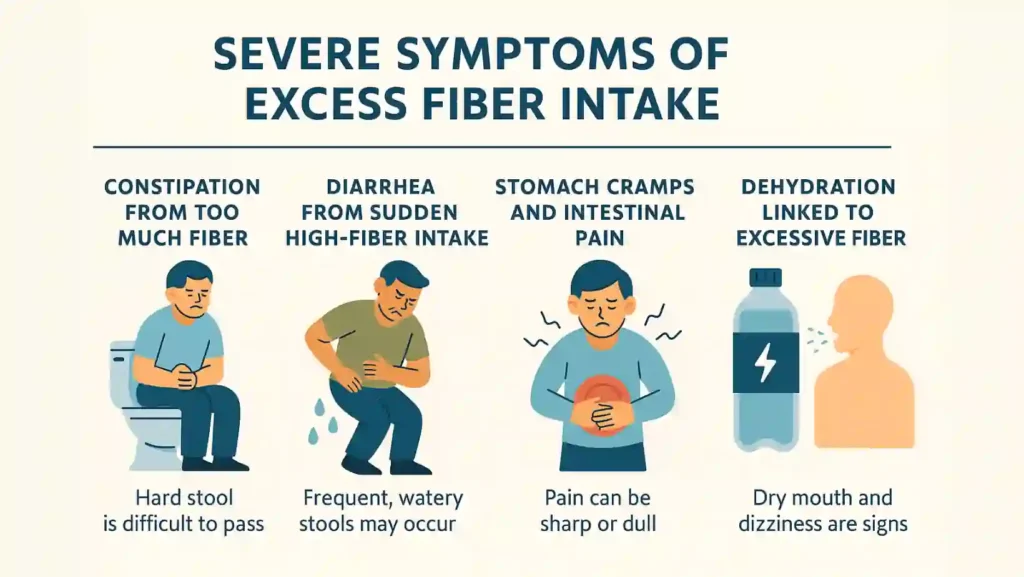
Severe Symptoms Of Excess Fiber Intake
If early symptoms do not improve, severe problems can develop. These signs need faster action.
Constipation From Too Much Fiber
When fiber absorbs water but you do not drink enough, stool can harden. Hard stool is hard to pass. The bowel must push harder. You may strain and have pain. Constipation from too much dietary fiber can last days if you do not increase fluids. This is a major fiber overdose symptom.
Diarrhea From Sudden High-Fiber Intake
Some fiber types draw water into the gut. A sudden surge can make stool loose. You may get frequent, watery stools. This can cause dehydration. Diarrhea can follow a quick change to a high fiber diet side effects list.
Stomach Cramps And Intestinal Pain
Cramps occur when muscles try to move a large fiber load. Pain can be sharp or dull. Cramps often happen after meals. They can wake you at night. If pain becomes severe, seek help.
Dehydration Linked To Excessive Fiber
Fiber pulls fluid into the gut. If you do not replace that fluid, you can become dehydrated. Signs include dry mouth, dark urine, dizziness, and low energy. Dehydration makes constipation worse. Drink more clear fluids if symptoms start.
How Too Much Fiber Affects Digestion
When you eat more fiber than your gut can handle, your digestion slows or speeds up in the wrong way. This shift leads to pressure, gas, cramps, and stool changes. You see Symptoms of Excess Fiber Intake when the load becomes too heavy.
Fiber Slowing Digestion In Low-Hydration States
Fiber needs water so it can move without trouble. If you eat too much dietary fiber but drink very little, the fiber becomes thick. Thick fiber sits in your gut longer. This makes the gut muscles work harder. The slower movement leads to constipation and pain. You may feel trapped gas because the stool moves too slowly.
Impact On Nutrient Absorption And Minerals
Very high fiber intake can affect the absorption of minerals like iron, zinc, and calcium. Fiber can bind these minerals in the gut. When this happens often, your body absorbs less. Kids, older adults, and people with weak digestion are at greater risk. If you rely on supplements and eat too much dietary fiber, check your mineral levels with your doctor.
Why Fiber Fermentation Increases Gas
Gut bacteria eat fiber. This process is called fermentation. Fermentation makes gas. When you add a lot of fiber fast, bacteria get more fuel at once. Gas increases. This can cause sharp pain and a swollen belly. The gas stays until the gut pushes it out. This part of eating too much fiber affects digestion, with a feeling of pressure soon after eating.
Common Causes Of Excessive Fiber Intake
You need to know how people end up with too much dietary fiber so you can avoid it.
Switching To A High-Fiber Diet Too Quickly
A quick jump is the biggest risk. When someone moves from a low-fiber diet to a large amount in one day, their gut reacts. The body cannot adjust that fast. This is one of the most common causes of excessive fiber intake.
Overuse Of Supplements
Fiber powders like psyllium, inulin, and other blends add huge amounts of fiber in one serving. Many people take more than the label says because they want fast results. When this happens, the gut gets overloaded. This is another major entry in causes of excessive fiber intake.
Eating Large Quantities Of Raw Fruits Or Vegetables
Raw produce has more fiber than cooked produce. Eating large bowls of raw greens, raw carrots, beans, lentils, or bran-filled cereal can push your intake too high. Many people do not realize how much fiber they are eating. That is why this fits under causes of excessive fiber intake.
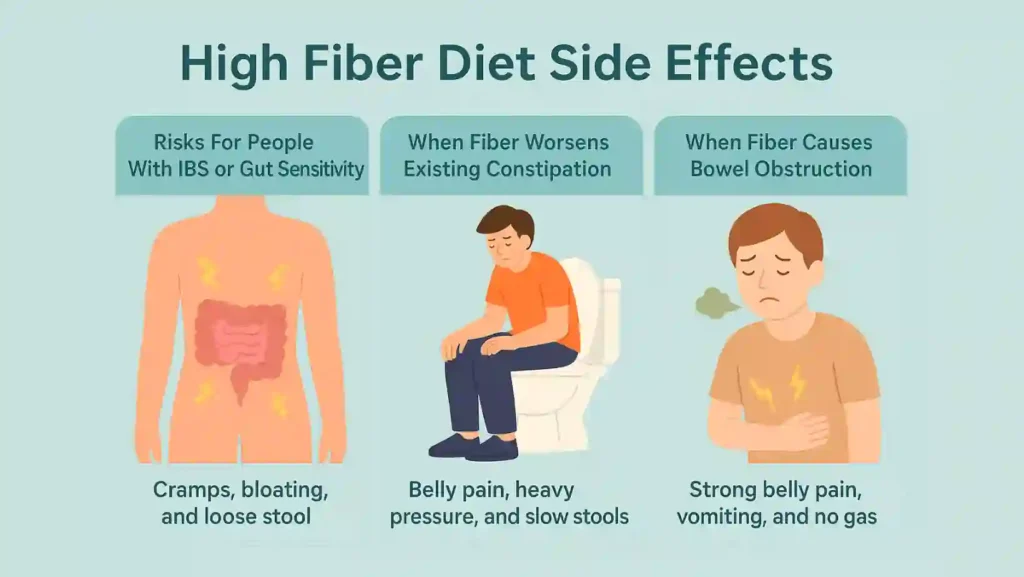
High Fiber Diet Side Effects
A high fiber diet helps most people. But some groups react strongly. When intake rises too fast, you feel high fiber diet side effects that affect your daily life.
Risks For People With IBS Or Gut Sensitivity
People with IBS have sensitive guts. Their bowels react to changes. A high fiber load can trigger cramps, bloating, and loose stool. Insoluble fiber is harder for them to handle. If you have IBS, increase fiber slowly and see which type causes more trouble.
When Fiber Worsens Existing Constipation
Some people think more fiber will fix constipation. But if you drink very little water, more fiber makes the stool harder. The bulk becomes stiff. This can make constipation worse. You see Symptoms of Excess Fiber Intake like belly pain, heavy pressure, and slow stools.
When Fiber Causes Bowel Obstruction
This problem is rare but serious. When someone eats too much dietary fiber and does not drink enough, the bulk can form a tight mass. This mass may block the stool. Signs include strong belly pain, vomiting, and no gas. This is a medical emergency. Do not wait for symptoms to pass.
How To Fix Digestion After Too Much Fiber
Most people recover with simple steps. These steps help your gut clear the extra bulk from too much dietary fiber.
Increase Water Intake To Move Fiber
Water is your first tool. Drink more than usual. Water softens the fiber so it can move. Sip water throughout the day. Clear fluids like broth also help. Once the fiber softens, discomfort drops.
Reduce Fiber Temporarily And Rebalance Diet
Cut back on high-fiber foods for a short time. Choose foods like plain white rice, bananas, eggs, chicken, and cooked vegetables. This break gives your gut space to reset. After symptoms improve, add small amounts of fiber back in.
Gentle Activity To Stimulate Bowel Movement
Light movement helps the gut push stool along. A short walk works well. You do not need intense exercise. Slow, steady movement helps gas and stool pass. This reduces Symptoms of Excess Fiber Intake.
When To Use Stool Softeners Or OTC Remedies
If stools stay hard, a stool softener may help. Some people use an osmotic laxative for a day or two. These keep water in the bowel so the stool stays soft. Follow instructions on the box. If symptoms do not improve, ask a doctor before taking more.
How To Prevent Fiber Overload
You can avoid eating too much dietary fiber by using these simple habits.
Increase Fiber Slowly And Track Tolerance
Add fiber in small steps over weeks. Increase by only a few grams at a time. Pay attention to changes in your gut. If you feel bloating or gas, slow down.
Balance Soluble And Insoluble Fiber Intake
Soluble fiber softens stool. Insoluble fiber adds bulk. A mix helps you get the benefits without trouble. This balance reduces high fiber diet side effects and helps your gut stay steady.
Avoid Supplement Overdose
Supplements add large amounts of fiber quickly. Follow the serving size. Do not take extra scoops. If you already eat a lot of fruits and vegetables, you may not need supplements. This prevents too many dietary fiber episodes.
When To See A Doctor For Fiber-Related Problems
Most cases improve with water and diet changes. But some signs require medical care.
Persistent Constipation Or Severe Abdominal Pain
If constipation lasts more than a week, see a doctor. If pain becomes strong or affects breathing, seek help now. These can be Symptoms of Excess Fiber Intake that turned serious.
Symptoms Of Bowel Blockage Or Dehydration
Hard belly, vomiting, no gas, or fainting are danger signs. Severe dehydration shows as very dark urine or dizziness. If you have these signs, get medical help at once.
FAQs
How Long Do Fiber Overdose Symptoms Last?
Most fiber overdose symptoms last one to three days. Recovery is quicker when you drink more water and cut back on fiber. If symptoms stay longer than a few days, ask a doctor to check for other problems.
Can Too Much Fiber Stop Bowel Movements?
Yes. Eating too much dietary fiber can slow down stool when water is low. Thick stool becomes hard to pass and may stop bowel movement. Drinking water and eating low-fiber foods help restore normal movement.
Does Excess Fiber Cause Weight Gain Or Loss?
Some people lose weight because too much dietary fiber makes them feel full faster. Others may feel bloated and think they gained weight. True fat gain from fiber is unlikely because fiber has almost no calories.
Is High Fiber Dangerous For Kidney Patients?
Kidney patients must watch mineral levels. Very high fiber can bind minerals and reduce absorption. This may affect health. A kidney patient must talk to a doctor before eating a high-fiber diet.
Should Children Eat High-Fiber Diets?
Kids need fiber, but not in high amounts. Symptoms of Excess Fiber Intake can appear quickly in children if they eat too much. Give them age-appropriate servings and plenty of water so their gut stays comfortable.
Can Drinking Water Reverse Fiber Side Effects?
Water helps soften stool and clear excess fiber. Drinking enough water can reduce bloating, gas, and constipation caused by too much dietary fiber. Fluids help the gut return to normal faster.
What Foods Have Extremely High Fiber Levels?
Foods like bran cereal, lentils, black beans, raspberries, chia seeds, and some fiber powders carry very high fiber. If you eat them in large servings, you may feel high-fiber diet side effects soon after.3
















Leave a Comment