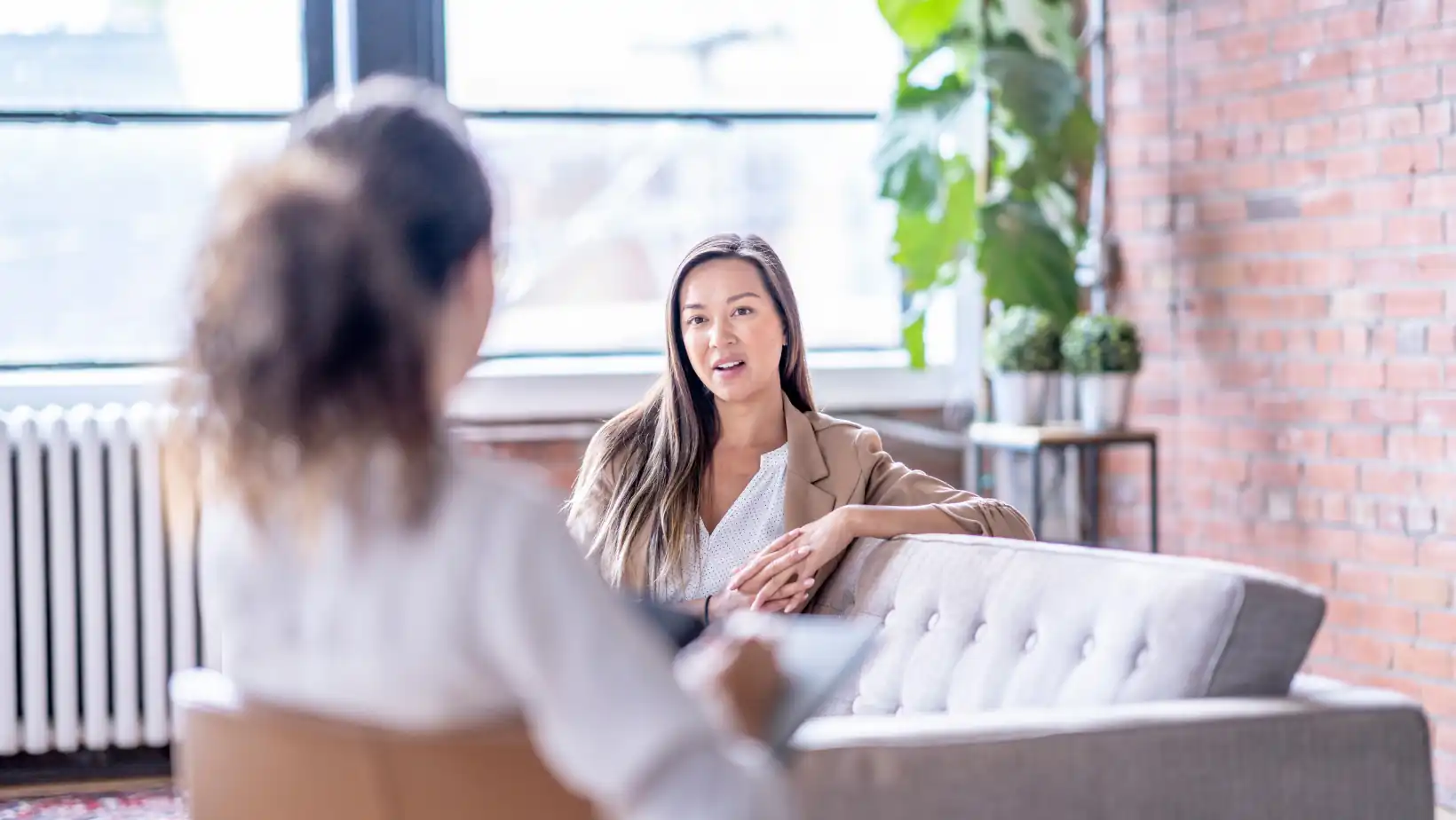
Cognitive behavioral therapy is one of the most widely used and well-researched forms of modern psychotherapy. It helps people change unhelpful thoughts and behaviors that cause or worsen problems.
By focusing on the link between mind and action, CBT teaches practical ways to manage conditions like depression, anxiety, and stress. Unlike vague talk therapy, it offers structure, clear steps, and long-term coping tools that can be used well beyond the therapy room.
Overview of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
What Is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?

Cognitive behavioral therapy is a cycle where thoughts affect feelings, and feelings influence actions. For example, if someone thinks “I will fail at work,” they may feel anxious. That anxiety may lead to avoidance, which then reinforces the original thought. CBT helps break this cycle.
It is a short-term, goal-focused psychological treatment plan designed to address specific problems. Therapists work with clients to identify patterns, challenge distorted beliefs, and replace them with positive thought patterns. Unlike open-ended therapy, CBT often lasts for weeks or months, not years, making it a practical form of mental health therapy.
Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
The benefits of cognitive behavioral therapy are broad. It is proven to help with mental health conditions like depression, social anxiety, panic attacks, OCD, PTSD, eating disorders, and substance misuse. People often notice:
- Improved self-esteem and confidence
- Better sleep and relaxation
- Stronger ability for emotional regulation
- Reduction in physical symptoms of stress such as headaches or fatigue
- Lasting coping tools that can be used independently
Unlike medication, CBT does not mask symptoms; it teaches skills to manage them. Research consistently shows that CBT works as an evidence-based therapy, sometimes even as well as medication for mild to moderate depression or anxiety.
How CBT Helps With Anxiety, Depression, And Other Conditions
For anxiety, CBT identifies false alarms in the brain. For example, if you fear flying, your thought might be “The plane will crash.” CBT helps test that thought and replace it with facts. For depression, the therapy focuses on increasing activities that bring small rewards, breaking the cycle of withdrawal.
CBT also helps with anger, chronic pain, and even medical conditions like irritable bowel syndrome. Therapists tailor the psychological approach so that each client has a customized set of psychotherapy methods to practice.
CBT Techniques For Anxiety And Depression
CBT Therapy Techniques For Anxiety
CBT therapy techniques for anxiety focus on reducing avoidance and fear. Common ones include:
- Exposure therapy: Facing fears gradually. Someone scared of dogs might start by looking at dog pictures, then watching videos, and finally meeting a calm dog.
- Cognitive restructuring: Writing down fears and checking facts. For example, replacing “I will faint in public” with “I have handled stress before and can manage this too.”
- Relaxation and breathing skills for calming the nervous system.
These techniques are paired with homework so patients practice outside CBT sessions.
CBT Techniques For Depression
CBT techniques for depression target negative thinking and inactivity. Helpful tools include:
- Behavioral activation: Scheduling small activities that lift mood, like walking or calling a friend.
- Thought records: Catching automatic negative thoughts such as “I am worthless” and writing balanced responses.
- Graded task assignments: Breaking big tasks into smaller steps so they feel less overwhelming.
By focusing on small actions, depression symptoms start to lift, giving room for mood improvement.
Practical CBT Exercises To Try At Home
CBT exercises can be practiced daily. A few simple but effective ones are:
- Daily thought check: Write down one upsetting thought. Ask, “Is this 100% true?” Then write a realistic replacement thought.
- Mood diary: Note emotions during the day. Add triggers and coping steps. Over time, patterns become clear.
- Problem-solving worksheet: Define the problem, brainstorm three solutions, test one, and review results.
- Relaxation training: Use slow breathing or progressive muscle relaxation when stress rises.
Using CBT Therapy Exercises For Daily Stress Management
CBT therapy exercises are not just for clinical depression or anxiety. They are effective stress reduction techniques for everyday challenges:
- Before a big meeting, practice a quick thought record. Replace “I will mess up” with “I am prepared, and mistakes are normal.”
- Use exposure for social fears by starting small, such as greeting one new person daily.
- Keep a gratitude journal to shift attention from negatives to positives.
These small steps act as daily behavioral modification strategies.
CBT Sessions: What To Expect
How CBT Sessions Are Structured
A typical session lasts 45–60 minutes. The structure usually includes:
- Reviewing homework and progress
- Setting a clear agenda
- Learning and practicing one new technique
- Assigning homework for the week
CBT sessions are highly interactive. Unlike passive listening, therapists encourage clients to practice skills and track changes.
Tips For Maximizing The Benefits Of CBT Sessions
- Take homework seriously; practice is the real treatment.
- Write down questions between sessions.
- Set realistic therapy goals and measure progress weekly.
- Be honest about setbacks so the therapist can adjust the plan.
Risks, Considerations, And Effectiveness
Pros And Cons Of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Pros:
- Short-term, focused, and cost-effective
- Proven effective for many mental health issues
- Builds lasting coping skills
Cons:
- Requires effort and homework
- Can feel uncomfortable when facing painful memories
- May not work well for people unwilling to engage in structured tasks
When CBT May Not Be Suitable
CBT may not suit people in crisis who need immediate safety interventions. It can be difficult for individuals with severe memory or attention problems. Some people may prefer other psychotherapy forms if they want more emotional exploration rather than skills training.
Recovery And Outlook
How Long CBT Therapy Typically Lasts?
Most CBT courses last 12 to 20 sessions. Some specific problems like phobias can improve in as few as 6 sessions, while more complex conditions may need longer. Unlike open-ended therapy, CBT is designed to be time-limited with measurable progress.
Maintaining Long-Term Benefits From CBT
The goal of CBT is independence. Once skills are learned, clients can apply them long-term. Relapse prevention includes:
- Continued use of thought records
- Recognizing early warning symptoms of depression or anxiety
- Scheduling booster sessions if needed
- Practicing positive thought patterns during stress
The Bottom Line
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a structured, effective, and practical approach for many conditions. It empowers people to change their thoughts and behaviors while giving long-term skills. From tackling anxiety and depression to daily stress, the therapy is one of the best-proven methods available today. With consistent practice, the gains of CBT can last a lifetime.
FAQs
What is CBT and its benefits?
CBT is a structured therapy that teaches coping tools. Benefits of cognitive behavioral therapy include better mood, stronger resilience, improved mental health, and long-term management of conditions.
What are cognitive behavioral therapy CBT techniques?
Common CBT techniques include exposure, thought records, and behavioral activation. These CBT therapy techniques reshape thinking and actions, giving practical ways to reduce distress and boost coping.
What are cognitive behavioral therapy exercises?
CBT exercises are small daily practices like journaling, thought checks, and relaxation drills. These CBT therapy exercises help manage stress and build healthy mental habits outside sessions.
What are the 7 principles of CBT?
The seven principles are: goal setting, focusing on the present, structured sessions, evidence testing, skill-building, tracking progress, and continued practice for long-term improvement in mental health.
Does CBT have side effects?
Side effects are minimal. At times, facing fears can raise distress temporarily. But over time, symptoms reduce as coping skills strengthen and confidence improves through continued practice.
What is an example of CBT?
Example: A student anxious about exams learns relaxation skills, keeps a thought diary, replaces “I will fail” with facts, and practices small study steps daily for control.
How to apply CBT in daily life?
Apply CBT by spotting negative thoughts, checking facts, and doing small helpful actions daily. Simple tools like mood diaries and thought records keep stress and anxiety under control.















Leave a Comment