A high protein diet for weight loss has become one of the most studied and popular strategies for fat reduction. Unlike crash diets, it works by making small but powerful changes to your eating habits. The idea is simple: eat more protein, balance it with the right carbs and fats, and the body will respond with faster fat burning, higher energy, and stronger muscles.
But what exactly makes protein so effective? And how can you use it in real life without ending up with boring meals or unsafe results? Let’s break it down step by step.
Does A High-Protein Diet Help With Weight Loss?
Protein does far more than build muscle. When you eat enough protein, three things happen: your hunger drops, your metabolism rises, and your muscles stay protected during calorie cuts. This is why a high protein diet often outperforms other weight-loss diets.
Protein directly affects appetite through hormones. It raises levels of peptide YY and GLP-1, which signal fullness, and lowers ghrelin, known as the hunger hormone. That is the science behind satiety and protein and protein and appetite control.
Protein also increases calorie burning because it takes more energy to digest. This is called the thermic effect of protein. Compared to fat or carbs, protein burns nearly twice the energy just during digestion. Over time, this becomes one of the easiest metabolism booster foods.
Another hidden benefit is muscle preservation during weight loss. Losing weight without enough protein often means losing muscle mass along with fat. Protein shields muscles, especially when paired with resistance training. That means a leaner body, not just a lighter one.
The Basics: Protein For Weight Loss
So how much protein for weight loss is enough? Nutrition experts suggest around 1.2–1.6 grams per kilogram of body weight daily for active adults. That equals 80–120 grams for someone weighing 70 kilos. For overweight individuals, calculating based on goal body weight gives a more accurate target.
But hitting a number is not enough. Timing and distribution matter. A plate with 60 grams of protein at dinner but only 5 grams at breakfast will not give the same results. Instead, aim for 25–30 grams at each meal. This “spread out” approach maximizes fullness and muscle support. This is why nutritionists stress protein timing (morning, post-workout, evening).
The key is consistency. Daily intake over weeks is what produces steady fat loss.
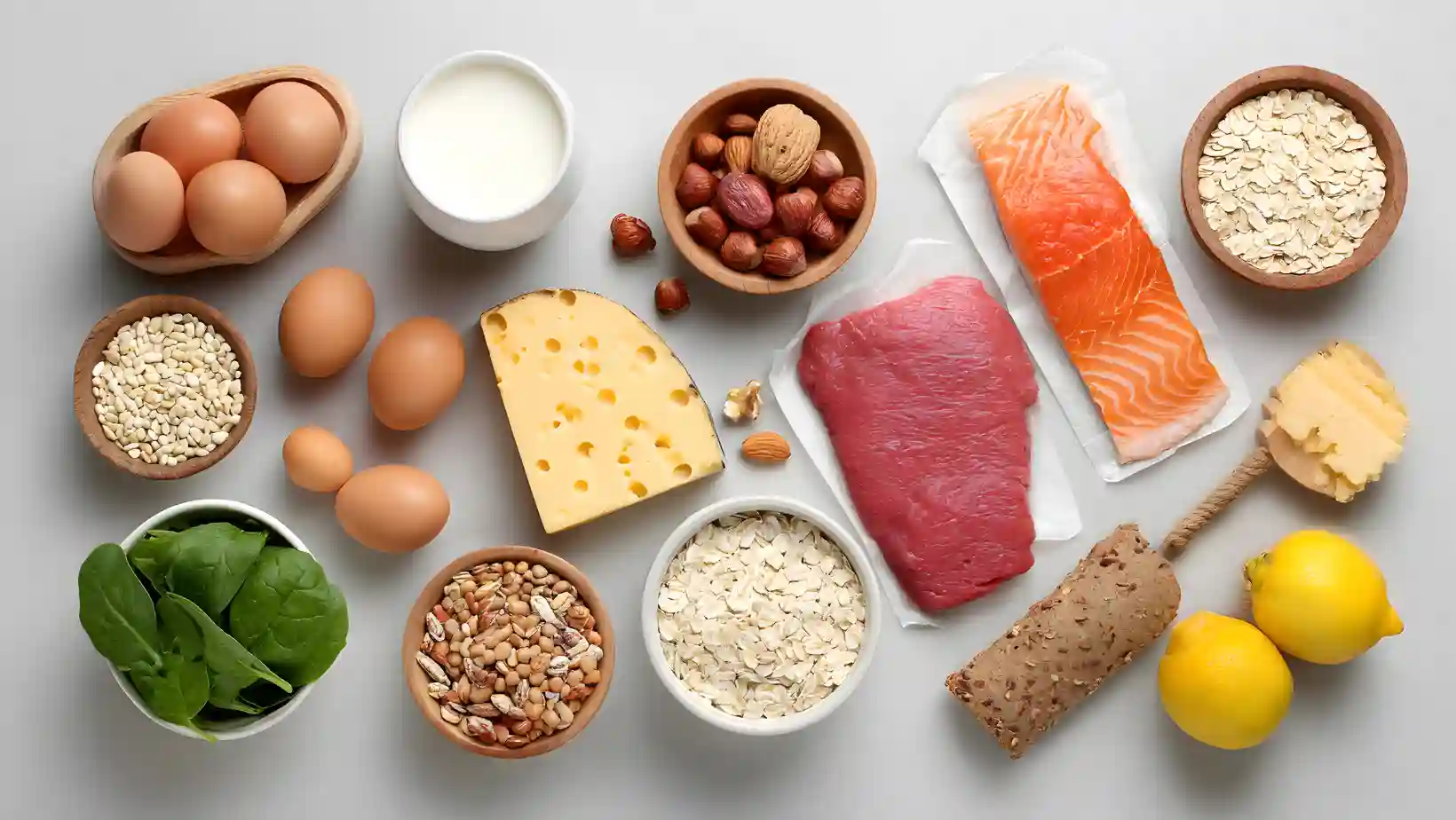
Best Protein Foods And Lean Protein Sources For Weight Loss

Choosing the right foods matters more than simply eating “more protein.” A bag of processed meat sticks will not give the same health outcome as salmon or lentils. Let’s break down the best protein foods for weight loss into animal and plant categories.
Animal-Based Lean Protein Foods
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, lean beef, pork tenderloin): These are classic sources of lean protein foods. A grilled chicken breast offers 25–30 grams of protein per serving with minimal fat.
- Seafood / fish (general): White fish like cod and tilapia are light, while oily fish like salmon provide both protein and healthy omega-3s.
- Eggs: A versatile source. One large egg contains 6 grams of high-quality protein plus vitamins.
- Low-fat dairy (cottage cheese, yogurt, milk, cheese): Cottage cheese stands out with nearly 14 grams of protein per half cup, making it a powerful snack.
Plant-Based Protein-Rich Foods
- Beans / legumes (lentils, kidney beans): A cup of cooked lentils has about 18 grams of protein plus fiber for digestion.
- Soy (tofu, tempeh, soy curls, soy milk): Soy is the only complete plant protein, meaning it has all nine essential amino acids.
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts, peanuts) and seeds: While calorie-dense, nuts and seeds deliver both protein and healthy fats.
- Vegetables: Spinach, broccoli, peas, and Brussels sprouts carry higher protein levels than most vegetables. These are excellent additions to meals.
One caution: limit processed meats like sausages, bacon, and deli slices. They may offer protein but are tied to higher risks of cancer and heart disease. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
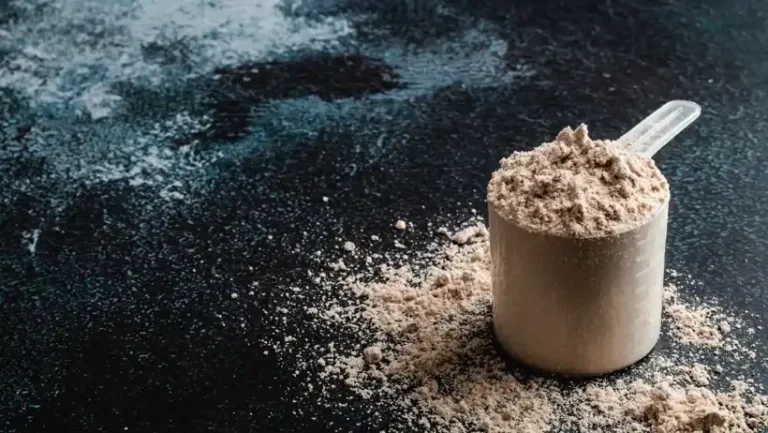
Best Protein Powder For Weight Loss

Not everyone can reach their daily intake through whole food alone. Here is where powders and protein supplements come in. The debate often comes down to: which is the best protein powder for weight loss?
Whey Protein For Weight Loss
Whey protein for weight loss is backed by the most research. Whey digests quickly, supplies all essential amino acids, and supports muscle recovery. People who add whey shakes while dieting often lose more fat while keeping more lean mass.
Plant Protein Options
For those who avoid dairy, pea protein, soy protein, or blends of rice and pea are excellent. While single plant proteins may lack one or two amino acids, blends cover the gaps.
How To Use Protein Powder?
- Post-workout: for recovery and muscle repair.
- Breakfast: to prevent morning hunger and keep energy steady.
- Snacks: as a bridge between meals when hunger strikes.
The trick is not to replace meals with shakes, but to use them as tools. One serving daily is enough for most.
Carbs And Fats In A High-Protein Diet
Protein is the star, but carbs and fats support the plan. Cutting them too low can backfire.
Carbs
Not all carbs are equal. A high-protein low-carb diet works best when carbs come from whole grains, beans, and vegetables. These carbs digest slowly and carry fiber, keeping blood sugar stable. Examples: quinoa, oats, brown rice, lentils, and leafy greens.
Fats
Healthy fats play a role in hormone health and fullness. Use olives / olive oil (extra virgin), canola oil, and avocados. Avoid trans fats and keep fried foods minimal. Balance fat sources with protein-rich meals.
Watch Cholesterol
Too much fatty meat can raise LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol). This risk rises with diets heavy in red and processed meats. To prevent this, replace some meat with fish, soy, or legumes.
Is The Ideal Protein Diet Safe For Weight Loss?
The ideal protein diet is a commercial plan focusing on very low carbs and high protein. It works fast, but questions remain about safety.
For healthy people, higher protein is generally safe. But those with kidney disease should be cautious, as high protein can worsen kidney function. A safe rule: always check with a doctor before starting a strict plan.
Risks include low fiber, constipation, and micronutrient gaps if fruits and vegetables are ignored. To make a high protein diet safe long-term, add fiber-rich carbs, drink enough water, and use a variety of protein sources instead of only red meat.
High-Protein Diet Meal Plan For Weight Loss
Here’s an example of a high protein diet meal plan for one full day. It balances animal and plant sources.
| Meal | Food Example | Protein (grams) |
| Breakfast | 3 boiled eggs, spinach, and 1 slice whole grain toast | 26 |
| Snack | Greek yogurt with nuts and berries | 18 |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken breast, quinoa, mixed vegetables | 32 |
| Snack | Protein shake with whey, soy milk, and banana | 25 |
| Dinner | Baked salmon, lentil salad, broccoli, drizzle of olive oil | 35 |
| Evening | Cottage cheese with sliced apple | 15 |
Total: ~150 grams of protein
This kind of plan gives steady energy, keeps hunger in check, and protects lean muscle.
High-Protein Diet For Weight Loss FAQs
Can you lose weight on a high-protein diet?
Yes. Eating more protein cuts hunger, raises calorie burn, and keeps muscles safe during calorie restriction. This leads to steady fat loss over time.
What is the 3-3-3 rule for weight loss?
The 3-3-3 rule means eating 3 protein-rich meals daily, 3 servings of vegetables, and balancing calories across 3 macronutrients for consistent results.
What is the 90 30 50 method?
This method recommends 90 grams of protein daily, 30 minutes of exercise, and about 50% of calories from healthy carbs and fats for balanced fat reduction.
Which high-protein diet is best for weight loss?
The best is one you can maintain. A balanced plan with whole foods, lean proteins, fiber, and healthy fats works better than strict short-term rules.
Which vegetables are high in protein?
Peas, spinach, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts have higher protein content compared to most vegetables and are excellent to include in a high-protein diet.
What are the disadvantages of a high-protein diet?
Too much red and processed meat may harm the heart, raise LDL cholesterol, and cause constipation if fiber is ignored. Kidney patients must also be cautious.
What is the 30g diet plan?
This plan suggests eating 30 grams of protein at each main meal. It improves fullness, reduces snacking, and supports lean muscle preservation during weight loss.
What are some quick high-protein meals?
Options include cottage cheese with fruit, tuna salad, tofu stir-fry, lentil soup, egg omelet, or a protein shake with soy milk and peanut butter.















Leave a Comment