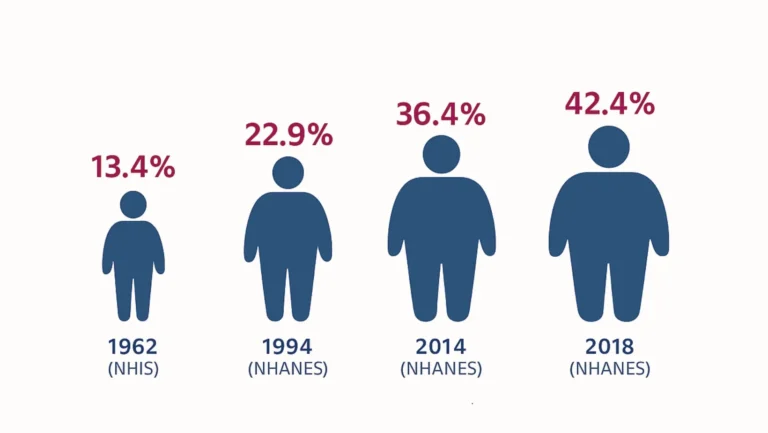
Intermittent fasting is one of the most popular lifestyle changes in health and nutrition today. Instead of focusing on what foods to eat, it emphasizes when you should eat. For many people, this approach is easier to follow compared to strict calorie-counting diets. With research showing multiple intermittent fasting health benefits, this eating style is becoming a common choice for weight management, better metabolism, and even long-term wellness.
This guide gives intermittent fasting explained in detail, covering its benefits, schedules, risks, and safe practices. If you are looking for intermittent fasting for beginners, this will help you start in a safe, informed, and sustainable way.
What Is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is a way of structuring your day around eating and fasting periods. The times when you don’t eat are known as the fasting window, and the hours when you eat are called the eating window.
Unlike traditional diets that tell you what foods to avoid, intermittent fasting works by limiting the time frame during which you consume food. This allows your body to naturally reduce calorie intake, rest the digestive system, and tap into stored energy.
People often confuse it with starvation, but fasting is a controlled, planned eating style. Humans have practiced it throughout history for cultural, spiritual, and survival reasons. Modern science now confirms that it can support weight loss, improve blood sugar control, and help regulate hormones.
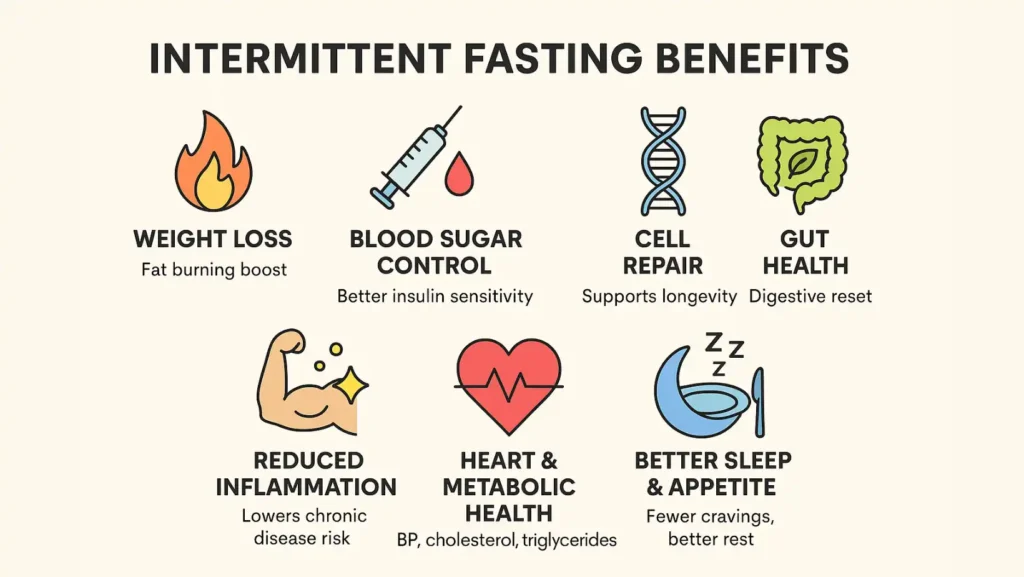
Intermittent Fasting Benefits And Health Effects

The list of intermittent fasting benefits is wide, ranging from weight management to cellular repair. Below are some of the most studied effects:
1. Weight Loss And Fat Burning
When your body goes several hours without food, insulin levels drop. Lower insulin makes it easier to burn fat for energy. Over time, this shift supports fat burning and reduces stored body fat. Unlike diets that cut out entire food groups, fasting works by changing when your body uses energy.
2. Improved Blood Sugar And Insulin Sensitivity
Intermittent fasting may help lower blood sugar spikes after meals. It improves insulin sensitivity, which means your body uses insulin more effectively. This is especially helpful for people with prediabetes or early Diabetes, but medical supervision is essential.
3. Cell Repair And Longevity
Fasting stimulates autophagy, a natural process where cells remove damaged parts and recycle them. This supports cell health and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases linked with aging.
4. Better Gut Health
A rest period from eating can improve gut health by allowing the digestive system to reset. Some studies suggest that fasting can strengthen the gut barrier and reduce bloating.
5. Reduced Inflammation
Many chronic diseases link back to inflammation. Intermittent fasting can reduce inflammatory markers in the body. This may help conditions like arthritis, heart disease, and even some autoimmune issues.
6. Heart And Metabolic Health
Fasting has shown positive effects on blood pressure, high cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Together, these changes support long-term heart health.
7. Better Sleep Quality And Appetite Control
When fasting aligns with your circadian rhythm, sleep often improves. Many people also notice reduced cravings and better control of appetite, especially late at night.
Intermittent Fasting Schedules For Beginners

Choosing a method that fits your life is key. Below are the most common intermittent fasting schedule options, explained in simple terms.
The 16/8 Or 14/10 Method
This is the most popular plan for beginners. You fast for 16 hours and eat during an 8-hour eating window. For example, eat between 12 pm and 8 pm.
- 14/10 is a lighter version, fasting 14 hours and eating within 10 hours.
- It works well for most people since it includes overnight sleep as part of the fast.
The 5:2 Fasting Diet
In this fasting diet, you eat normally five days a week and reduce food intake on two non-consecutive days.
- Women usually aim for 500 calories, men about 600.
- This method allows flexibility but requires discipline on fasting days.
Alternate Day Fasting
This approach involves fasting every other day. On fasting days, you either eat very little (about 500 calories) or nothing at all.
- It can result in faster weight loss, but it is hard to sustain.
- Beginners may find it too restrictive.
Eat: Stop: Eat Method
This plan involves fasting for a full 24 hours once or twice a week. For example, finishing dinner at 7 pm and eating again at 7 pm the next day.
- It is powerful but more challenging.
- Only attempt this after trying shorter fasting periods first.
How Intermittent Fasting Works?
Understanding how intermittent fasting works helps you see why it can be effective.
- Shift in energy use: After several hours without food, your body uses stored glucose. Once those stores run low, it turns to fat. This shift supports steady calorie restriction and fat burning.
- Hormonal changes: Fasting lowers insulin, increases growth hormone, and may regulate appetite hormones like ghrelin and leptin.
- Circadian rhythm alignment: Eating earlier in the day supports metabolism. Late-night eating disrupts sleep and raises the risk of weight gain.
- Cellular repair: Fasting activates autophagy, helping the body remove damaged cell parts and reduce disease risk.
When applied correctly, intermittent fasting explained is not just about skipping meals. It is about syncing your body with natural cycles and supporting health at multiple levels.
Intermittent Fasting Risks And Safety Tips
Fasting is not suitable for everyone. While there are many intermittent fasting health benefits, it can also pose risks.
- People with diabetes or low blood sugar must not fast without medical guidance.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid fasting.
- People with eating disorders or underweight individuals should not use fasting.
Safety Tips For Beginners
- Stay hydrated with water to maintain hydration.
- Include mineral-rich drinks or foods to balance electrolytes.
- Break your fast with balanced meals. Include protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
- Avoid overloading your body with heavy meals after fasting.
- Be mindful of exercise. Gentle workouts are safe, but intense training may need adjustment.
- Limit artificial sweeteners since they may affect appetite.
- Watch how fasting interacts with medical conditions like high cholesterol, blood pressure, or hormonal changes in perimenopause.
The Bottom Line
Intermittent fasting explained simply means changing when you eat instead of what you eat. It offers intermittent fasting benefits like weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and reduced inflammation.
For intermittent fasting for beginners, start with 12–14 hours of fasting and gradually increase. Pick a method that suits your lifestyle, listen to your body, and follow safe fasting practices.
Fasting is not magic. It is a tool. The real results come from consistency, healthy food choices, and respecting your body’s needs.
FAQs
What is the rule of intermittent fasting?
The rule is to alternate eating and fasting times. For instance, follow a 16-hour fast with an 8-hour eating period each day.
What is allowed during intermittent fasting?
You can drink water, black coffee, and unsweetened tea. Avoid sugary drinks and foods, as even small amounts can break your fasting state.
What are the best hours for intermittent fasting?
The best hours are those that fit your lifestyle. Many people prefer 12 pm to 8 pm, while others choose morning to evening schedules.
Does sleeping count as fasting?
Yes, hours spent sleeping count toward your fasting period. Overnight fasting makes it easier to complete longer fasting windows.
Can I drink water during intermittent fasting?
Yes, water is encouraged. It helps maintain hydration, reduces hunger pangs, and supports the body’s natural detoxification process during fasting.
How to start fasting for beginners?
Start small with a 12-hour fast. Gradually increase to 14 or 16 hours. Keep meals balanced and seek medical advice if you have health issues.
Can I drink coffee during intermittent fasting?
Yes, black coffee without cream or sugar is usually fine. It may help control appetite and keep you alert during fasting hours.














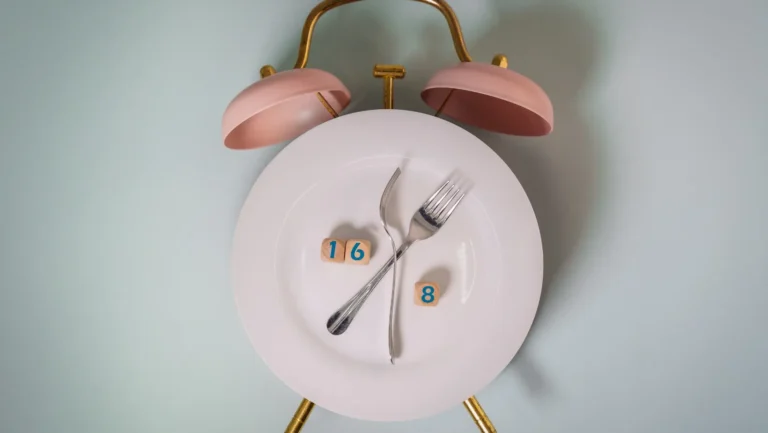

Leave a Comment