Obesity is one of the most common health problems worldwide. It affects both children and adults, but not everyone knows how it is defined, what causes it, or how it can be treated. This article explains the obesity definition, symptoms, causes, complications, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention in simple words.
What Is Obesity? (Obesity Definition)
Obesity is a condition where a person has too much body fat that harms health. Obesity is not the same as being slightly overweight. It is measured with tools like body mass index (BMI) and obesity charts and waist circumference.
Obesity is now seen as a chronic disease because it affects metabolism, hormones, and organs. Doctors rely on clear criteria such as BMI (Body Mass Index) and other tests to decide when a person is considered obese.
Symptoms And Causes
What Are The Symptoms Of Obesity?
Obesity does not always show obvious signs early on. Many people only notice when health problems begin. Common obesity symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath during simple activities.
- Daytime tiredness and poor sleep.
- Joint or back pain due to extra stress on bones.
- Snoring or sleep apnea.
- Low mood or lack of confidence.
Other signs of being overweight are clothes fitting tighter, slower movement, and difficulty doing daily tasks.
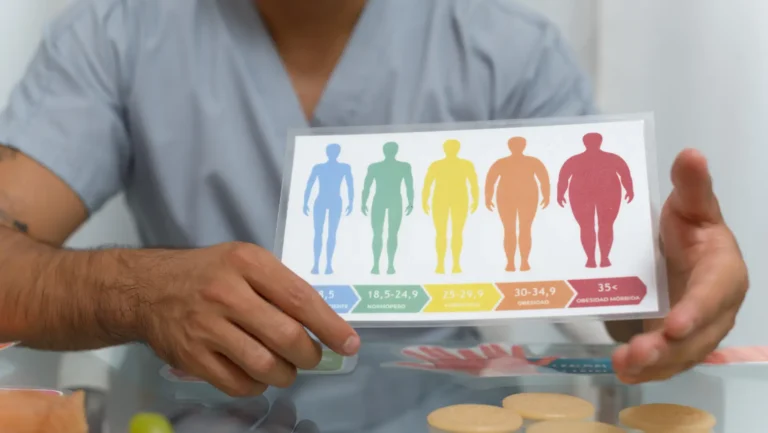
BMI Classifications: What BMI Is Obese?
Doctors often use BMI to check what BMI is obese. The BMI formula is weight (kg) divided by height (m²).
Here is a simple chart:
| BMI Value | Category | Health Status |
| Below 18.5 | Underweight | Possible nutrition issues |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal | Healthy BMI |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight | Higher risk |
| 30 – 34.9 | Obesity Class I | Increased risk |
| 35 – 39.9 | Obesity Class II | High risk |
| 40 and above | Class III obesity | Very high risk |
A BMI of 30 or more answers the question of what is considered obese. Still, BMI alone is not perfect.
Waist Circumference And Signs Of Being Overweight
Waist size is another strong health marker. High waist circumference points to fat around internal organs. For men, 40 inches or more is risky. For women, 35 inches or more shows risk. People with high waist size face more problems like diabetes and heart disease even if their BMI looks normal.
What Causes Obesity?
The causes of obesity are mixed. It is not just about food intake.
- Diet and obesity: Eating more calories than the body uses causes weight gain. Sugary drinks, fried foods, and processed snacks are common triggers.
- Lifestyle and obesity: Sedentary life with little activity is a major factor. Long sitting hours at work increase risk.
- Genetics and obesity: Family genes affect how fat is stored and burned. Some people have genetics / obesity-susceptibility genes that raise risk.
- Stress / cortisol: Long stress raises cortisol hormone, which stores belly fat.
- Lack of sleep, some medicines, and health conditions (like thyroid disorders) also play a role.
What Are The Complications Of Obesity?
Obesity raises the chance of several illnesses. These are linked to metabolic health and obesity.
Metabolic Changes
- Type 2 diabetes from insulin resistance.
- Metabolic syndrome which combines high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol.
- Hormonal imbalance affecting hunger and energy use.
Direct Effects On Health
Obesity causes or worsens many conditions:
- Cardiovascular diseases (heart disease, heart attack, stroke, CHF, CAD).
- Fatty liver disease / cirrhosis / hepatitis.
- Gallstones / gallbladder disease.
- Kidney disease / chronic kidney disease.
- Breathing problems like asthma and sleep apnea / obesity hypoventilation syndrome.
- Joint pain and arthritis.
- Cancers such as esophageal, pancreatic, colorectal, breast, uterine, ovarian.
- Mental health concerns like depression / mood disorders.
- Women may face female infertility / pregnancy complications.
- Older adults risk Alzheimer’s disease / dementia.
Diagnosis And Tests
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Obesity?
Doctors diagnose obesity by:
- Measuring weight and height to calculate BMI.
- Checking waist circumference for belly fat.
- Asking about eating habits, activity, and family history.
- Running blood tests for cholesterol, glucose, and liver function.
The CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) guidelines are often used to standardize checks.
What Is A Healthy BMI?
So, what is a healthy BMI? For most adults, 18.5 to 24.9 is considered healthy. This range shows less risk of chronic illness.
What Is Considered Obese?
The common cut-off for what is considered obese is a BMI of 30 or higher. A waist size above the risk limit can confirm high risk even at lower BMI.
Management And Treatment
How Is Obesity Treated?
There is no single fix. Obesity treatment needs lifestyle changes plus support from doctors.
- Dietary changes: Balanced meals with more vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- Activity: At least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
- Sleep: Regular, good-quality sleep reduces hormonal imbalance.
- Behavior support: Counseling for eating habits and stress management.
Obesity Treatment With Medication For Weight Loss
Some people need medicines to control appetite or slow digestion. Doctors prescribe only when lifestyle steps are not enough. Medicines must be monitored carefully.
Weight Loss Surgery
Surgery, such as gastric bypass or sleeve surgery, is an option for severe obesity. It changes the stomach size or how food is absorbed. This helps major weight loss and reduces risks from obesity-related diseases. Surgery is usually for Class II / III obesity when other treatments fail.
Outlook / Prognosis
What Can I Expect If I Have Obesity?
The outlook depends on health status and treatment. Even 5–10% weight loss improves blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol. Quality of life also improves. Early treatment reduces risk of long-term disease.
Prevention
Can Obesity Be Prevented? (Obesity Prevention)
Yes, obesity prevention is possible. Steps include:
- Eating fewer processed foods and more natural meals.
- Staying active every day.
- Managing stress and getting enough sleep.
- Avoiding excess sugar and alcohol.
- Teaching kids healthy habits early.
Community-level changes, such as safe parks and affordable healthy food, also matter for prevention of obesity.
The Bottom Line
Obesity is not just about weight. It is about health risks that can affect the heart, liver, lungs, and mind. It can be treated with steady changes, medical help, or surgery if needed. Remember that even small steps like reducing sugary drinks or walking daily can bring big health gains.
FAQs
What do you mean by obesity?
Obesity is a disease where excess body fat raises the risk of health problems and shortens life expectancy.
What causes obesity?
Obesity causes include poor diet, low activity, stress, hormones, and family genes. Medicines and sleep also play a role.
What is type 3 obesity?
Type 3 obesity, also called Class III, means a BMI above 40. This stage carries the highest health risks.
How to avoid obesity?
To avoid obesity, eat healthy meals, stay active daily, manage stress, and maintain proper sleep. Small steps matter most.
What are 5 symptoms of obesity?
Obesity symptoms include fatigue, breathlessness, joint pain, snoring, and sleep problems. Each symptom may get worse over time.
Who is at risk of obesity?
Risk is high for those with family history, poor diet, low activity, certain medicines, and stressful lifestyles.














Leave a Comment