Antibiotics begin to work usually right after you take the first dose. You often feel clearer in one to three days. Fever and pain drop first. Some infections need longer treatment. Keep taking your medicine until the doctor tells you to stop.
How Long Does It Take for Antibiotics to Start Working?
You often notice a change in 24 to 72 hours. This is the most common window. Some drugs reduce bacteria fast. Others slow bacteria growth so your body can finish the job. If you have a deep infection, you may wait longer. If symptoms worsen, call your doctor right away.
Typical Antibiotic Response Time: When Improvement Begins
Most people see the first signs of healing in two to three days. Pain eases. Fever falls. Drainage and swelling shrink. This shows that antibiotics immediately start working for many common infections. If you see no change after three days, you should contact your provider.
Time To Effect Antibiotics: How Different Types Work
Some antibiotics kill bacteria quickly. Others stop bacteria from growing. Bactericidal drugs reduce bacterial count fast. Bacteriostatic drugs let your immune system finish the job. How fast you improve depends on the drug, the bug, and where the infection is. This matters for the time taken for antibiotics to work.
Why Some Antibiotics Take Longer To Show Results
The medicine must reach the infected tissue. Bone or lung tissue may need higher levels. Some bacteria are harder to kill. Your immune system must help. If you miss doses, drug levels drop and healing slows. These reasons explain why antibiotics may take longer.
When Will I Feel Better After Antibiotics? Common Timelines
For many simple infections, you feel better in a few days. For complex infections, expect more time. Below are common ranges you can expect. These ranges explain typical antibiotic start relief times.
- Ear, throat, sinus: 24 to 72 hours for many cases. If it lasts beyond 10 days, see your doctor.
- Urinary tract: 24 to 48 hours for simple UTI. Severe cases take longer.
- Skin and wounds: 3 to 5 days to see a clear change. Deeper infections take longer.
- Chest infections and pneumonia: up to one week or more for major improvement. A cough can last weeks.
These times show the likely time taken for antibiotics to work for common problems. If you do not see steady improvement, your doctor may change treatment.
Factors That Affect How Soon Antibiotics Give Relief
Several factors change when you get relief. Knowing them helps you set the right expectations.
Infection Location and Severity
Shallow infections clear faster. Lung, bone, or joint infections need longer treatment. Deeper infections may need IV antibiotics and hospital care. This is why the time taken for antibiotics to start working varies widely.
Antibiotic Type and Dosage Schedule
Some drugs reach high levels quickly. Others need consistent dosing to build levels. If you skip doses, the medicine may not stay strong enough. Take doses exactly as prescribed. This helps antibiotics work better.
Your Immune System’s Role in Symptom Improvement
Antibiotics help the body fight infection. Your immune system finishes the job. If your immunity is low, you may heal more slowly. Age, nutrition, and chronic disease affect recovery. You will see improvement in symptoms with antibiotics.
Age, Metabolism, and Coexisting Health Conditions
Young, healthy people often recover faster. Older adults and people with diabetes or kidney disease may need more time. Liver and kidney function change drug levels and dosing. Tell your doctor about all your health issues. This affects antibiotics start relief and how the drug acts in your body.
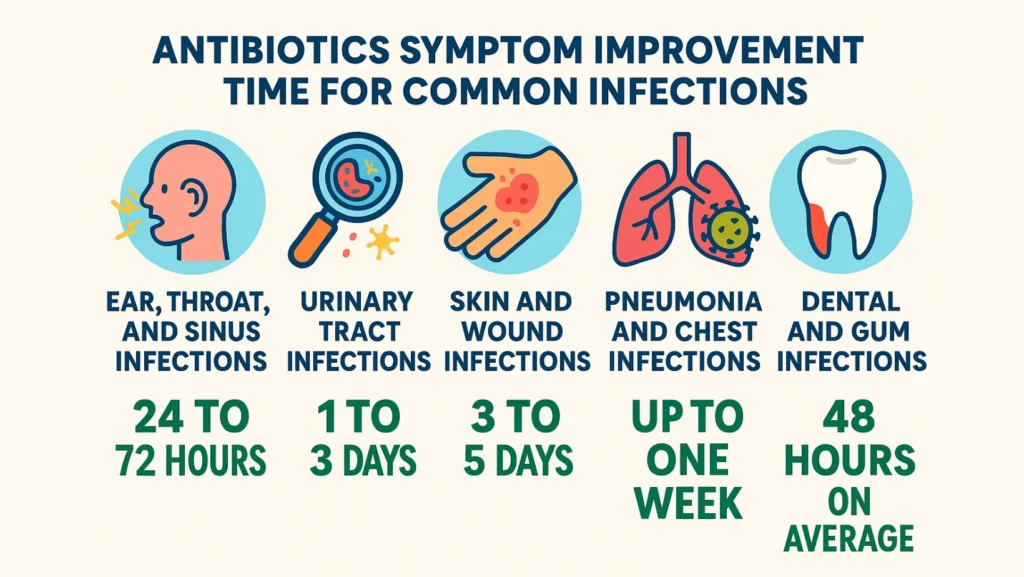
Antibiotics Symptom Improvement Time For Common Infections
Here are typical timelines for common infections. These times show how fast people often get relief.
Ear, Throat, and Sinus Infections — 24 to 72 Hours
You often notice easing of pain and fever within one to three days. Some sinus infections get better without antibiotics. If symptoms last more than ten days, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. This shows how quickly antibiotics start working for ENT infections.
Urinary Tract Infections — 1 to 3 Days For Relief
Simple UTIs often respond quickly. You may feel less burning in 24 to 48 hours. If the infection reaches the kidney, expect a longer course and slower relief. Correct drug choice matters for the time taken for antibiotics to work.
Skin and Wound Infections — 3 to 5 Days To Respond
Small sores and cellulitis often show clear improvement in three to five days. Watch for spreading redness or fever. If infection spreads, seek urgent care. Early action speeds the improvement of symptoms with antibiotics.
Skin And Wound Infections — 3 to 5 Days To Respond
Deep wounds or slow-healing cuts can take longer to clear because the medicine needs time to reach the infected area. If the skin grows warm or streaks spread outward, you need urgent care.
This can mean the bacteria are growing fast and the current drug is not strong enough. When this happens, the antibiotics to work may need to be changed or given through a vein.
Pneumonia And Chest Infections — Up To One Week
Chest infections need more time because the lungs fill with mucus. The medicine must pass through thick lung tissue. You may feel a slight change in two to four days, but clear relief often shows up near day seven.
Cough and tiredness can stay for weeks even after the germs are gone. This does not mean the drug failed. It means your lungs are healing at a slow pace. These cases show why the time taken for antibiotics to work can be longer for chest issues.
Dental And Gum Infections — 48 Hours On Average
Dental infections react fast to treatment. Pain and swelling often drop within two days. But the tooth or gum problem may need a dentist to clean or drain the area. Antibiotics help control germs, but they do not fix the source of the infection. This is why dentists mix medicine with a follow-up procedure. When managed well, you will see a clear improvement in symptoms with antibiotics in the first two days.
How To Tell If Your Antibiotics Are Working
You should watch your symptoms each day. Your body sends clear signs when things move in the right direction.
Signs Of Recovery: Reduced Pain, Swelling, And Fever
Good signs include less heat in the area, easier movement, fewer chills, and more energy. These changes show that antibiotics are hitting the bacteria. Fever dropping by even one degree can show solid progress. Less swelling means the body is clearing waste from the infected space.
When Antibiotics Start Relief? How Soon Is Normal?
Most mild infections calm down within one to three days. This range matches what doctors expect. Some infections may need up to five days before a clear change. If the infection is deep or severe, you may need more time. The common window helps explain how long it takes for antibiotics to start working for most people.
What To Do If Symptoms Don’t Improve After 3 Days
If nothing changes after three days, reach out to your provider. You may need a drug change or dose change. Do not double your dose. Do not stop early. Your doctor might ask for more details or may want to test a sample of the infected area.
When To Contact Your Doctor For A New Prescription
Seek new help if the swelling spreads, fever rises, or you feel weaker. If you cannot keep the pills down due to vomiting, call your provider at once. If you take the full dose schedule but feel worse, the bacteria may resist the drug. You need a new plan so that the antibiotics work can match the type of bacteria present.
When Antibiotics Don’t Work: Causes And Next Steps
When symptoms don’t change, you must act early to keep the infection from spreading.
Antibiotic Resistance And Incomplete Courses
If bacteria resist a drug, the medicine cannot stop them. Stopping early also exposes the bacteria to low levels of the drug. This helps the germs grow stronger. This is a common reason antibiotics fail to work. Always complete your course unless your provider tells you to stop.
Viral Infections That Don’t Respond To Antibiotics
Viruses cannot be killed by antibiotics. Flu, colds, and many ear infections are viral. If a doctor says you have a viral illness, you must rest and manage your symptoms. Antibiotics will not speed healing. When people expect antibiotics to start relief, but no relief comes, a viral cause may be the reason.
Dosage Errors And Timing Inconsistencies
Missing pills lowers drug levels in the blood. Levels must stay steady for the medicine to work. If doses are too far apart, bacteria may grow again. If this happens often, the full course may not clear the infection. This slows the time taken for antibiotics to work and can cause treatment failure.
When To Request A Culture Or Sensitivity Test
If a drug no longer helps, ask your doctor about testing the infected sample. A lab test can find the exact germ and list the best drugs to use. This saves time and prevents guesswork. It helps find a drug that lets your antibiotics work the right way for your case.
How To Take Antibiotics Effectively For Faster Results
You can help your medicine act at full strength by following a few simple habits.
Follow The Full Course, Even After Feeling Better
Even if pain drops early, bacteria may still be present. Stopping too soon lets them grow again. Completing the full course gives the drug enough time to kill the remaining germs. This step gives antibiotics a start relief and keeps it steady.
Timing Doses Evenly For Consistent Blood Levels
Your doctor sets a time gap for a reason. It keeps the drug level strong. If you take a pill too early, the next dose may overlap too much. If you take it too late, the level drops and germs get a chance to grow. A timer or phone alarm can help.
Avoid Alcohol And Antacids That Slow Absorption
Some drugs react with alcohol. Some drugs stick to antacids and form clumps in the stomach. This slows absorption and reduces strength. Always read the label and ask your pharmacist if you have doubts.
Pair Antibiotics With Probiotics To Support Recovery
Some antibiotics upset the stomach. A probiotic taken a few hours later can protect good bacteria in your gut. It will not make antibiotics work faster, but it helps you stay comfortable during treatment.
When Will I Feel Better After Antibiotics? Realistic Expectations
Healing is not the same for everyone. But you can look for certain patterns to understand what is normal.
Day By Day Symptom Timeline And Improvement Markers
- Day 1: The medicine enters your bloodstream. Fever may not change yet.
- Days 2 to 3: Most people feel steady relief. This is when improvement of symptom with antibiotics becomes clear.
- Days 4 to 7: Symptoms should fade. If nothing changes by day 7, you need medical advice.
- After Day 7: Some deeper infections still heal slowly. Your doctor may extend the course if needed.
How Long To Wait Before Contacting Your Doctor
If you feel worse at any time, call right away. If you feel the same by day three, you need to reach out. These patterns help match how long antibiotics take to start working in your case.
Managing Fatigue And Mild Side Effects During Treatment
Fatigue, loose stools, and mild stomach upset can show up with some drugs. Drink water, rest more, and eat simple foods. If you get a rash, swelling, or trouble breathing, get urgent help.
What To Do If You Feel Worse After Starting Antibiotics
If symptoms grow stronger after starting the drug, stop the pills and talk to a doctor at once. You may have an allergy or may be taking the wrong drug for the germ. Your provider may switch you to a different antibiotic so the new antibiotics to work safely.
FAQ
How long does it take for antibiotics to start working?
Most people feel a change in one to three days. The drug acts sooner, but the body needs time to show results. This explains how long it takes for antibiotics to start working in common cases.
What if I miss a dose? Does it delay recovery?
Missing a pill can slow healing because the drug level drops. Take the dose when you remember, unless it is near the next dose time. Always keep a steady timing to help the medicine work well.
Can I stop antibiotics once I feel better?
Stopping early can leave strong bacteria alive. These germs can return and cause a tougher infection later. You should finish your full course unless your doctor gives new guidance.
Do stronger antibiotics work faster?
Stronger does not always mean faster. The right drug matters more than the strength. Your doctor picks the best drug based on the germ, age, and health details.
What if I do not feel any improvement after 5 days?
If your symptoms stay the same after five days, talk with your provider about switching drugs. You may need a test to find the exact cause before choosing the next treatment.
How can I tell if my infection is viral not bacterial?
Viral cases often come with a runny nose, cough, and body aches. Bacterial cases show more swelling, fever, or pus. Only a doctor can confirm which kind you have through symptoms and tests.
Should I still take antibiotics if my fever is gone?
Yes, you must finish the course. Fever dropping does not mean all germs are gone. Stopping early can help prevent the infection from returning and becoming harder to treat.
How do I know if the infection is fully cleared?
Your symptoms should fade steadily. Your doctor may suggest a follow-up if the infection was deep. If pain or fever returns, you should get checked again.
Are there natural remedies that speed up antibiotic effects?
Natural options cannot replace medicine. Rest, fluids, and warm compresses help comfort, but antibiotics remain the main treatment for bacterial infections.
Can probiotics make antibiotics work faster?
Probiotics help with stomach comfort, not speed. They protect good gut bacteria but do not boost the strength of the antibiotic itself.
Is it safe to take painkillers while on antibiotics?
Most painkillers are safe with common antibiotics. Some mixes may cause stomach upset, so it is best to ask your doctor or pharmacist before combining them.
How long after finishing antibiotics will I feel normal again?
Most people feel normal within days. Some infections may leave tiredness or cough longer. Give your body time to rebuild strength after the illness.
Why do antibiotics work faster for some people than others?
Your health, age, immune system, and the type of germ all affect healing speed. Some people respond fast while others need more days for clear improvement.












Leave a Comment