Medically reviewed by Dr Chandril Chugh,
Renowned Neurologist and American Trained Specialist
Testicular cancer is a serious condition that affects men of all ages. Being aware of the early signs and symptoms can help in early detection and prompt treatment. It’s essential to pay attention to any changes in the testicles or scrotum, as they can be potential indicators of testicular cancer.
The early signs of testicular cancer may vary from person to person, but there are some common symptoms to look out for. These include an enlarged testicle, a painless lump or area of hardness in the testicle, pain, discomfort, or numbness in the testicle or scrotum, changes in the way a testicle feels, a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, a dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin, sudden buildup of fluid in the scrotum, breast tenderness or growth, lower back pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and swelling of the legs.
It’s important to note that not all individuals with testicular cancer experience these symptoms, and having these symptoms does not definitively indicate the presence of cancer. However, if you notice any of these signs persisting or worsening, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and necessary medical care.
Key Takeaways:
- Early signs of testicular cancer include an enlarged testicle, a painless lump or area of hardness in the testicle, pain or discomfort in the testicle or scrotum, changes in the way a testicle feels, a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, and a dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin.
- Other symptoms may include a sudden buildup of fluid in the scrotum, breast tenderness or growth, lower back pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and swelling of the legs.
- Not all individuals with testicular cancer experience these symptoms, and having these symptoms does not definitively indicate the presence of cancer.
- Seek medical attention if you notice any persistent or worsening signs to receive a proper evaluation and necessary medical care.
- Early detection of testicular cancer can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
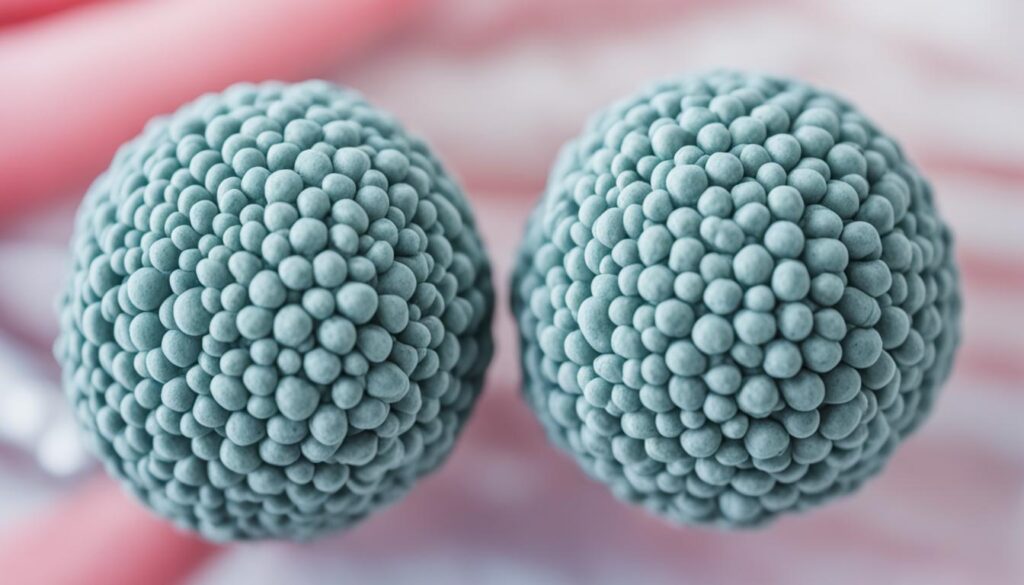
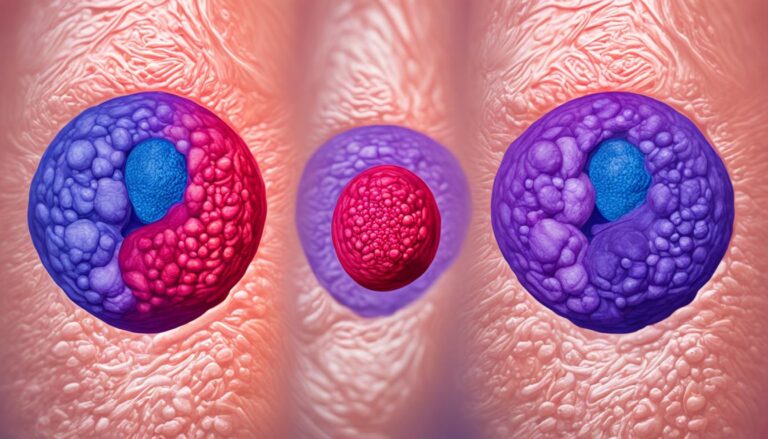
Recognizing Testicular Lumps: A Key Sign of Testicular Cancer.
A painless lump or swelling in either testicle is often the first noticeable sign of testicular cancer. If found early, the lump may be the size of a pea or a marble but can grow larger. Any enlargement, hardness, pain, or tenderness in the testicles should be evaluated by a doctor as soon as possible.
It’s important to note that not all testicular lumps are cancerous, and further medical evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
| Characteristics | Potential Causes |
|---|---|
| Painless lump or swelling in the testicle | Testicular cancer, noncancerous conditions such as cysts or varicoceles |
| Enlargement, hardness, pain, or tenderness in the testicles | Testicular cancer |
Early detection of testicular lumps is crucial for prompt medical intervention. If you notice any abnormal changes in your testicles, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and necessary treatment.
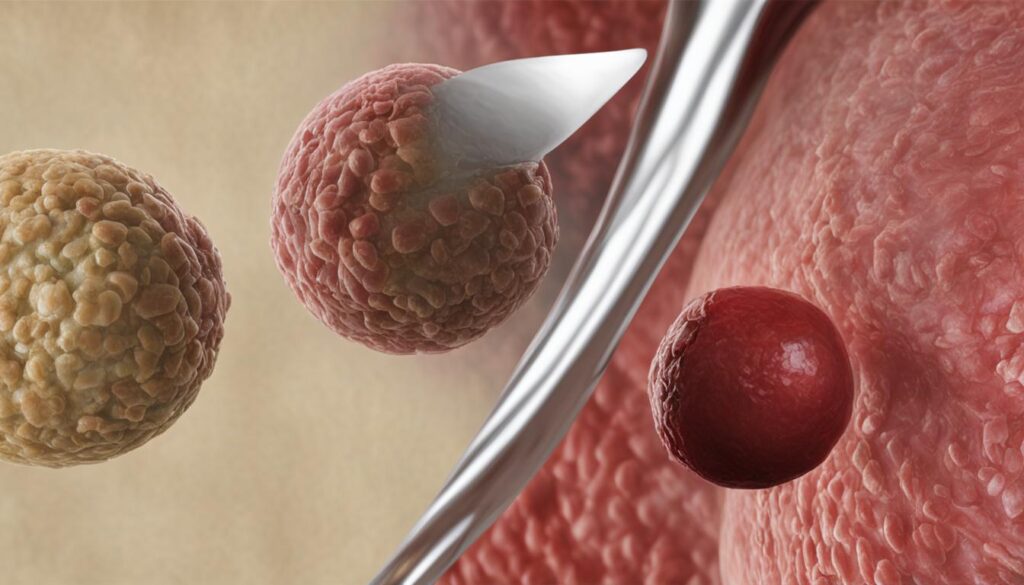
Other Physical Changes Associated with Testicular Cancer.
Testicular cancer can cause various physical changes in addition to testicular lumps. These changes may be a result of the hormonal imbalances caused by the cancer cells and should not be ignored. It is important to discuss any physical changes with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Feeling of Heaviness in the Scrotum
One common physical change associated with testicular cancer is a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum. This sensation can be described as a sense of increased weight or pressure in the scrotal area. It is important to pay attention to this symptom and seek medical advice if you experience it.
Unevenness in the Testicles
In some cases, testicular cancer can cause unevenness between the two testicles. You may notice differences in size, shape, or texture. Any noticeable asymmetry should be checked by a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause.
Changes in the Size or Shape of the Testicles
Testicular cancer may also lead to changes in the size or shape of the testicles. One testicle may appear larger or smaller than the other, or they may change in size over time. These changes can be an indication of a potential issue and should be evaluated by a doctor.
Enlargement or Tenderness of the Breast Tissue
In some cases, testicular cancer can cause hormonal imbalances that result in breast tissue enlargement or tenderness. This change, known as gynecomastia, may affect one or both breasts. If you notice any unusual breast changes, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate assessment and guidance.
These physical changes associated with testicular cancer should not be ignored. If you experience any of these signs, it is crucial to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and diagnosis. Remember, early detection and timely treatment are key to improving outcomes.
| Physical Changes | Potential Signs of Testicular Cancer |
|---|---|
| Feeling of Heaviness in the Scrotum | Increased weight or pressure in the scrotal area |
| Unevenness in the Testicles | Differences in size, shape, or texture between the testicles |
| Changes in the Size or Shape of the Testicles | One testicle appearing larger or smaller, or changes in size over time |
| Enlargement or Tenderness of the Breast Tissue | Breast tissue enlargement or tenderness in males |
Pain and Discomfort: Potential Indicators of Testicular Cancer.
When it comes to testicular cancer, pain, discomfort, or a dull ache in the lower abdomen, groin, testicle, or scrotum can be potential indicators. However, it’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by various other medical conditions, not just cancer. Therefore, a proper evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential to determine the underlying cause.
If you experience persistent or worsening pain or discomfort in any of these areas, it is recommended to seek medical attention. Don’t ignore these symptoms, as early detection is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
Remember, testicular cancer is a relatively rare disease, but it’s important to stay vigilant and listen to your body. If you have any concerns or doubts, it’s always better to consult with a healthcare professional to get the necessary evaluation and peace of mind.
“Persistent pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, groin, testicle, or scrotum should not be ignored. Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and recovery.”
– Testicular Cancer Foundation
Common Causes of Pain and Discomfort in the Testicular Region
While testicular cancer is one possible cause of pain and discomfort in the testicular region, it’s important to consider other potential causes as well. Here are some common conditions that may contribute to these symptoms:
- Testicular injury
- Epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis)
- Orchitis (inflammation of the testicle)
- Testicular torsion (twisting of the spermatic cord)
- Inguinal hernia
- Varicocele (enlargement of the veins inside the scrotum)
If you’re uncertain about the cause of your pain or discomfort, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

Seeking Medical Attention
If you’re experiencing pain, discomfort, or a dull ache in the lower abdomen, groin, testicle, or scrotum, it’s crucial to take action and seek medical attention. A healthcare professional will be able to conduct a thorough evaluation, perform necessary tests, and provide appropriate guidance based on your individual symptoms and medical history.
Remember, early detection and timely intervention can make a significant difference in the successful management of testicular cancer and overall outcomes. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or questions.
About Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the testicles start to divide and multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor. It is relatively rare compared to other forms of cancer but primarily affects young and middle-aged men.
Regular self-examinations and awareness of the common signs and symptoms of testicular cancer are crucial for early detection. By familiarizing yourself with the potential indicators and promptly seeking medical attention when necessary, you can help ensure the best possible outcomes in terms of diagnosis, treatment, and long-term prognosis.
| Potential Indicators of Testicular Cancer | Other Conditions That Can Cause Similar Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Pain, discomfort, or dull ache in the lower abdomen, groin, testicle, or scrotum | Testicular injury, epididymitis, orchitis, testicular torsion, inguinal hernia, varicocele |
| Changes in the size or texture of the testicles | Spermatocele, hydrocele, testicular cysts |
| Enlargement or tenderness of breast tissue | Gynecomastia (hormonal imbalance) |
Unusual Fluid Buildup and Swelling in the Scrotum.
Testicular cancer can lead to a sudden buildup of fluid in the scrotum, causing swelling. This fluid buildup may be related to the spread of cancer to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes. If you notice any unusual swelling in the scrotum, it’s important to consult a doctor for further evaluation.

Less Common Symptoms: Back Pain and Shortness of Breath.
In some cases, testicular cancer can cause symptoms that are not directly related to the testicles. These less common symptoms may include lower back pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and bloody sputum or phlegm. While these symptoms are not exclusive to testicular cancer and can have various causes, they may be indicative of more advanced stages of the disease where the cancer has spread beyond the testicles.
If you experience persistent back pain, especially in the lower back, or if you have difficulty breathing, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. These symptoms could be signs of testicular cancer that has metastasized to other areas of the body, such as the lymph nodes or lungs.
Back pain associated with testicular cancer may be caused by the cancer spreading to the lymph nodes in the back or the nerves in the area. Shortness of breath can occur when the cancer affects the lungs, causing fluid buildup or obstructing the airways. Early detection and treatment are key to improving outcomes, so don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
“It’s important to be aware of these less common symptoms of testicular cancer. Recognizing the signs and seeking medical attention can lead to earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.” – Oncologist
Possible Causes of Back Pain and Shortness of Breath in Testicular Cancer
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Lymph Node Involvement | The cancer cells spread to the lymph nodes in the back, causing inflammation and pressure on surrounding tissues, resulting in back pain. |
| Lung Metastasis | Testicular cancer may spread to the lungs, leading to fluid buildup, tumors, or obstruction of the airways, causing shortness of breath. |
| Tumor Growth | As the cancer grows, it can put pressure on nearby structures, including nerves, causing localized or radiating back pain. |
| Blood Clots | In rare cases, testicular cancer can lead to blood clots that may cause pain and shortness of breath, especially if they travel to the lungs. |
If you are experiencing back pain or shortness of breath along with other symptoms of testicular cancer, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation. They will perform a thorough physical examination and may recommend further tests, such as imaging scans and blood tests, to determine the cause of your symptoms.
Remember, early detection and timely treatment can significantly improve the prognosis and outcomes for individuals with testicular cancer. It’s always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical advice whenever you have concerns about your health.

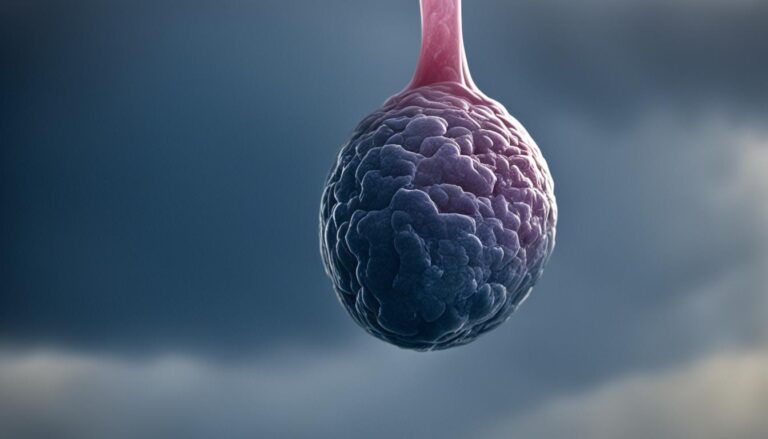
Swelling in the Legs and Blood Clots: Potential Signs of Testicular Cancer.
Testicular cancer can sometimes cause swelling in one or both legs or lead to the formation of blood clots. These symptoms can indicate the spread of testicular cancer to distant parts of the body, and immediate medical evaluation is necessary.
When testicular cancer spreads, it can affect the blood vessels and lymphatic system, resulting in leg swelling known as peripheral edema. This swelling occurs due to the accumulation of fluid in the tissues and can cause discomfort and reduced mobility. It is important to note that leg swelling can also be caused by other factors, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or other medical conditions. Therefore, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Blood clots, specifically deep venous thrombosis (DVT), can also occur as a result of testicular cancer. DVT refers to the formation of blood clots in the deep veins of the legs, which can be life-threatening if a clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Symptoms of DVT include pain, warmth, redness, and swelling in the affected leg. If you experience these symptoms, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention.
Here is an image that demonstrates leg swelling, which can be a potential sign of testicular cancer:

Seek Medical Attention for Leg Swelling and Blood Clots
If you notice swelling in one or both legs or experience symptoms of blood clots, consult a healthcare professional immediately. They will perform a thorough evaluation, which may include physical examinations, imaging tests, and blood work. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help manage these symptoms and prevent further complications.
Non-cancerous Conditions That May Mimic Testicular Cancer Symptoms.
While testicular cancer presents with various symptoms, it’s important to note that many of these symptoms can also occur due to non-cancerous conditions. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and proper management.
Conditions That Mimic Testicular Cancer Symptoms
- Changes in size or a lump in a testicle
- Cyst called a spermatocele
- Enlargement of blood vessels called varicocele
- Fluid buildup in the membrane around the testicle called hydrocele
- An opening in the abdominal muscle called a hernia
- Infection of the testicle or epididymis
- Injury
- Twisting of the testicle
These non-cancerous conditions can manifest similar symptoms to testicular cancer, such as testicular lumps, changes in size or shape of the testicles, and discomfort in the scrotum. However, it’s crucial not to self-diagnose and to seek professional medical advice for an accurate evaluation.
Remember, only a healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and guide you in managing your symptoms effectively.
Conclusion
Detecting the early signs of testicular cancer is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. If you notice an enlarged testicle or a painless lump, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation. However, it’s important to remember that testicular cancer can present with various symptoms, including pain, discomfort, fluid buildup, and physical changes. Don’t ignore these signs; seek medical attention promptly.
Early detection plays a significant role in improving the chances of successful treatment and recovery. By being aware of the early signs and symptoms of testicular cancer, you can take proactive steps to protect your health. Regular self-examinations can also help you identify any potential abnormalities. If you notice any changes or experience any symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
Remember, testicular cancer is highly treatable, especially when detected early. By staying vigilant and proactive about your health, you can take control of your well-being and ensure early intervention if necessary. Your healthcare provider is your partner in maintaining your well-being, so don’t hesitate to reach out if you have any concerns. Together, you can navigate through any challenges and work towards a healthier future.
FAQ
What are the early signs of testicular cancer?
The early signs of testicular cancer can include an enlarged testicle, a painless lump, or an area of hardness in the testicle. Other symptoms may include pain, discomfort, or numbness in the testicle or scrotum, changes in the way a testicle feels, a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, a dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin, sudden fluid buildup in the scrotum, breast tenderness or growth, lower back pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and swelling of the legs.
What should I do if I notice a testicular lump?
If you notice a testicular lump, it is important to have it evaluated by a doctor as soon as possible. While not all testicular lumps are cancerous, further medical evaluation is necessary to determine the cause accurately.
What other physical changes can be associated with testicular cancer?
In addition to testicular lumps, testicular cancer can cause a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, unevenness in the testicles, changes in the size or shape of the testicles, and enlargement or tenderness of the breast tissue. These changes may be a result of hormonal imbalances caused by the cancer cells and should be discussed with a doctor for proper evaluation.
Can testicular cancer cause pain or discomfort?
Yes, testicular cancer can cause pain, discomfort, or a dull ache in the lower abdomen, groin, testicle, or scrotum. However, it is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by various medical conditions other than cancer. If these symptoms persist or worsen, it is recommended to seek medical attention for a proper evaluation.
Can testicular cancer lead to fluid buildup and swelling in the scrotum?
Yes, testicular cancer can lead to a sudden buildup of fluid in the scrotum, causing swelling. This fluid buildup may be related to the spread of cancer to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes. If you notice any unusual swelling in the scrotum, it is important to consult a doctor for further evaluation.
Are there any less common symptoms of testicular cancer?
Yes, in some cases, testicular cancer can cause symptoms that are not directly related to the testicles. These less common symptoms may include lower back pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and bloody sputum or phlegm. These symptoms may be indicative of more advanced stages of testicular cancer where the cancer has spread beyond the testicles. If you experience these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Can testicular cancer cause swelling in the legs or blood clots?
Yes, testicular cancer can sometimes cause swelling in one or both legs or lead to the formation of blood clots. These symptoms can indicate the spread of testicular cancer to distant parts of the body, and immediate medical evaluation is necessary.
What non-cancerous conditions may mimic testicular cancer symptoms?
Many symptoms and signs of testicular cancer can also be caused by noncancerous conditions such as changes in size or a lump in a testicle, spermatocele (a cyst), varicocele (enlargement of blood vessels), hydrocele (fluid buildup in the membrane around the testicle), hernia (an opening in the abdominal muscle), testicle or epididymis infection, testicle injury, and testicle twisting. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and proper management.
Why is it important to detect the early signs of testicular cancer?
Detecting the early signs of testicular cancer is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Early signs can include an enlarged testicle, a painless lump, or physical changes. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of these symptoms to receive a proper evaluation and necessary medical care. Remember, early detection can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and recovery.






Leave a Comment