Testicle pain combined with left abdominal pain can be alarming. This type of pain often confuses men because it can come from different sources: the testicles themselves, surrounding structures, or even conditions outside the scrotum.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding what causes this pain, how it feels, and when to seek urgent care is important for protecting both health and fertility.
What is Testicular Pain?
Testicular pain refers to any aching, throbbing, or sharp discomfort in one or both testicles. It may present as mild and persistent or as abrupt and intense. The scrotum contains delicate structures like the testes, epididymis, blood vessels, and nerves.
Pain from one area often radiates into the abdomen or groin because these structures share nerve pathways. This is why men with testicle pain may also feel it in the left lower abdomen, hip, or back.
Pain can develop gradually from conditions like varicocele or suddenly from emergencies like testicular torsion. Even mild pain should not be ignored because testicles play a vital role in fertility and hormone production.
What Does Testicular Pain Feel Like?
The way testicular pain feels can provide clues about its cause.
- A dull ache may suggest swelling, infection, or varicocele.
- Sharp, stabbing pain could mean trauma or kidney stones radiating pain.
- Heavy, dragging discomfort is often linked to fluid build-up like hydrocele.
- Pain that worsens when standing or lifting may be caused by inguinal hernia.
For example, a young man with a varicocele may complain that his left scrotum feels heavy after sports practice. Another with orchitis might describe pain that comes with fever and difficulty walking.
What is Testicular Torsion Pain Like?
Many patients ask, what is testicular torsion pain like.
The explanation is straightforward: it ranks among the most excruciating pains a man can experience. Unlike dull aches, this pain strikes suddenly, feels severe and unrelenting, and does not improve with rest. It is often accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
A person might wake up at night with sharp scrotal pain and notice that one testicle looks swollen and higher than the other. This is a red-flag sign. Without surgery within six hours, blood flow may be lost permanently, and the testicle could die.
When is Testicular Pain Serious?
Not all scrotal pain is urgent, but knowing the warning signs can save a testicle.
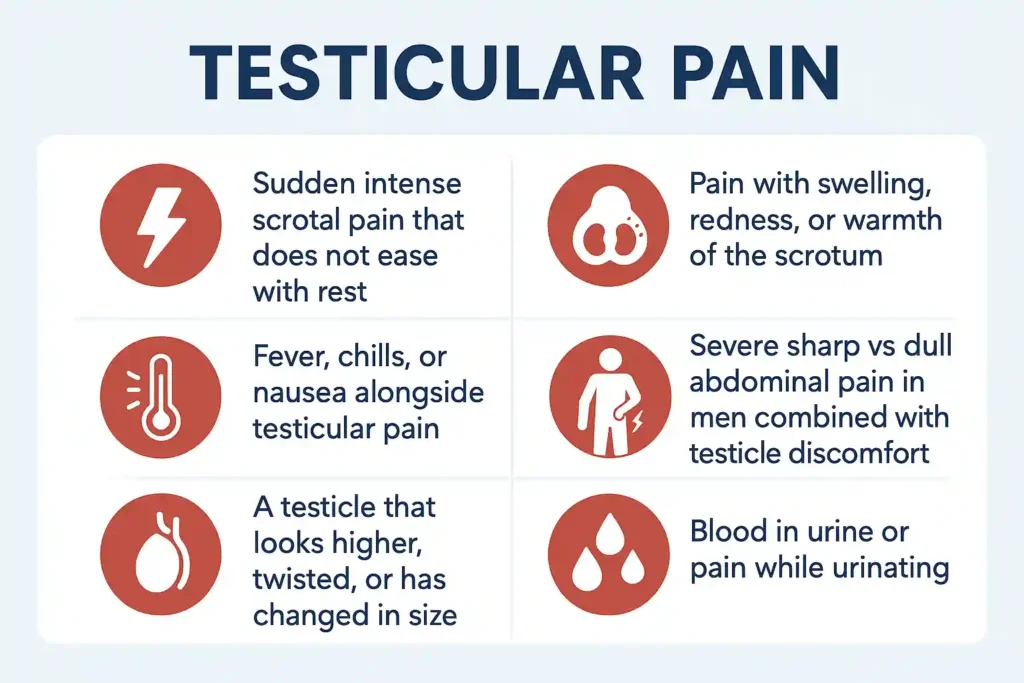
Signs You Should Seek Medical Attention Immediately
- Sudden intense scrotal pain that does not ease with rest
- Pain with swelling, redness, or warmth of the scrotum
- Severe sharp vs dull abdominal pain in men combined with testicle discomfort
- Fever, chills, or nausea alongside testicular pain
- A testicle that looks higher, twisted, or has changed in size
- Blood in urine or pain while urinating
Ignoring these symptoms can risk infertility, infection spreading to other organs, or permanent testicular loss.
Common Causes of Testicle Pain
Understanding the causes of testicular pain helps in recognizing what might be happening in the body.
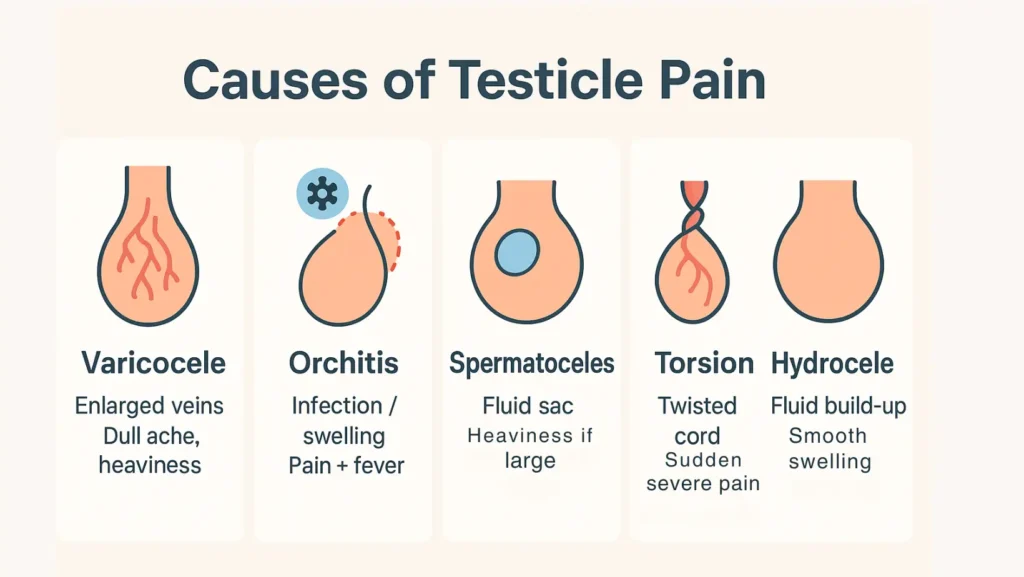
Varicocele: Enlarged Veins in the Scrotum
A varicocele is when veins inside the scrotum enlarge, similar to varicose veins in the legs. It is more common on the left side because of how the testicular vein connects to the kidney vein.
Men often describe a dull ache or heaviness, worse after standing long or during hot weather. Fertility problems can occur because the increased blood flow raises testicular temperature, which affects sperm quality.
Treatment ranges from supportive underwear for mild discomfort to surgical ligation or embolization in severe cases.
Orchitis: Inflammation of the Testicles
Orchitis is painful swelling of the testicles, often caused by bacterial infection, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs), or viruses like mumps.
Symptoms include fever, scrotal swelling, pain radiating into the groin, and sometimes burning urination. It may occur with epididymitis, which is inflammation of the epididymis.
Treatment usually involves antibiotics, pain relief, and rest. If caused by mumps, supportive care is given since it is viral.
Spermatoceles: Fluid-Filled Sac in the Testicle
Spermatoceles are fluid-filled sacs that develop near the epididymis. They often feel like small lumps and may not hurt, but larger ones can cause scrotal heaviness.
Most require no treatment unless they enlarge. In that case, surgery can be done to remove them.
Testicular Torsion: Twisting of the Testicle
Testicular torsion is one of the most dangerous causes of testicular pain. The spermatic cord becomes twisted, obstructing blood flow. Symptoms include sudden severe pain, swelling, nausea, and an abnormal testicle position.
Immediate surgery is needed. Without it, the testicle can be lost within hours.
Hydrocele: Fluid Build-Up in the Scrotum
A hydrocele occurs when fluid collects around the testicle. It usually appears as painless scrotal swelling but can sometimes cause scrotal swelling with abdominal discomfort.
Symptoms of Hydroceles
- Smooth swelling around one or both testicles
- Heaviness in the scrotum
- Usually painless but may ache when large
Treatment Options
In infants, hydroceles often disappear naturally. In adults, surgery or aspiration may be needed if they grow large or painful.
Testicular Injury and Trauma
Testicular pain can result from sports injuries, accidents, or direct impacts to the groin. Symptoms include swelling, bruising, and sometimes blood inside the scrotum. If the pain does not settle or swelling increases, an ultrasound is necessary to rule out rupture.
Wearing protective cups during sports helps prevent serious injuries.
Testicular Cancer: Potential Cause of Testicle Lump
Not all lumps are cancer, but testicular cancer must be considered. It often feels like a firm, painless lump, though some men notice dull aching in the groin or abdomen.
Treatment Options for Testicular Cancer
- Surgical removal of the affected testicle
- Chemotherapy or radiation depending on stage
- Regular follow-up scans to monitor for spread
The likelihood of survival is significantly high if identified promptly. Monthly self-examination is the best preventive measure.
The Bottom Line
Testicular pain and left abdominal pain can come from mild conditions like spermatoceles or serious emergencies like testicular torsion. Pain in this region may also be due to urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones radiating pain, or even chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Never ignore pain in the testicles, especially when combined with swelling, fever, or abdominal discomfort. Early medical attention prevents complications and preserves fertility.
FAQs
Why is my left testicle and abdomen hurting?
Pain may come from testicle swelling, infections, hernia, or kidney stones. Only an examination and ultrasound can confirm the exact cause and rule out emergencies.
When to worry about testicle pain?
Worry if the pain starts suddenly, is severe, or comes with swelling, fever, or nausea. Seek urgent care if the testicle looks twisted or unusually high.
How do I check myself for testicular torsion?
Check for sudden pain, swelling, and a testicle that feels higher than the other. If present, do not wait. Go to the hospital immediately for evaluation.
What are red flags for testicular pain?
Sudden sharp pain, swelling, fever, blood in urine, or abdominal pain with scrotal discomfort are red flags. These signs suggest urgent conditions needing immediate treatment.
Can a hernia cause testicle pain?
Yes, an inguinal hernia can push into the scrotum, causing heaviness, pain, and discomfort in both the abdomen and testicles. Surgery is often needed if the hernia worsens.
Can ejaculating help with testicle pain?
Sometimes, mild pain from congestion improves after ejaculation. However, this does not help with serious causes like infection or torsion, which require medical treatment.
Can kidney issues cause testicle pain?
Yes, kidney stones radiating pain often spread to the groin or testicles. Other kidney or prostate issues and pelvic pain may also present as discomfort in this area.

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, Board-Certified Neurologist, providing expert insights and reliable health information.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained neurologist with over a decade of experience. Known for his compassionate care, he specializes in treating neurological conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Dr. Chugh is highly regarded for his patient-centered approach and dedication to providing personalized care.