Probiotics are live microorganisms that are good for our health. They help with digestion, fight depression, and keep our hearts healthy. They also boost our immune system.
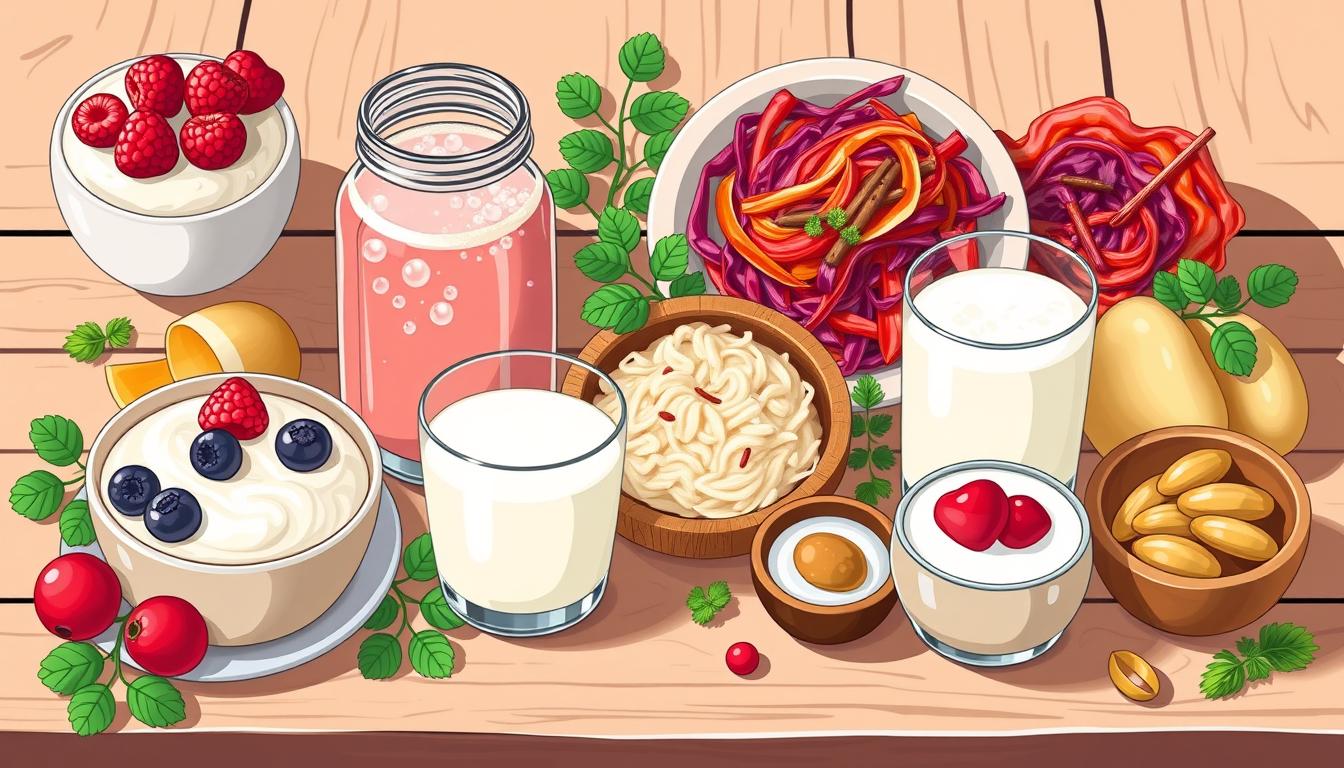
Fermented foods are full of probiotics. Yogurt is a favorite among many. Other foods like kefir, sauerkraut, miso, tempeh, kimchi, and kombucha are also rich in probiotics.
These foods have different types of beneficial bacteria and yeast. They help keep our gut healthy and improve our overall well-being.
Understanding Probiotics and Their Role in Gut Health
Probiotics are key to our gut health. They are part of a group of microorganisms that help us stay healthy. To be called a probiotic, a microorganism must come from humans, survive digestion, and offer health benefits.
What Makes a Microorganism a Probiotic
The Lactobacillus genus is well-studied and often recommended. It includes L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, L. casei, and L. plantarum. The Bifidobacterium genus, with strains like Bifidobacterium longum and Bifidobacterium breve, also has benefits. Acidophilus (L. acidophilus) is known for its wide use and natural presence in our bodies.
Benefits of Probiotics for Digestive Health
Probiotics are vital for a healthy gut microbiome. They help with digestion, reduce inflammation, and ease digestive problems like IBS and IBD. You can get them from fermented foods or supplements.
How Probiotics Support Immune Function
Probiotics also boost our immune system. They help keep our gut healthy, which strengthens our defenses against infections. They may also help with mental health, like reducing depression.
Always talk to a healthcare provider to find the right probiotics for you. Different probiotics work differently in our bodies.
Yogurt: The Most Popular Probiotic Powerhouse
Yogurt is a probiotic-rich food that’s very popular. It’s made by fermenting milk with live cultures. These cultures include lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Yogurt is full of live cultures, lactic acid bacteria, calcium, and protein.
Eating yogurt regularly can help your bones, heart, and gut. It also lowers diabetes risk and helps with weight management.
When picking yogurt, choose ones with live cultures. These are key for getting the probiotic benefits. Watch out for added sugars, as they can lower nutritional value. Yogurt is great in many dishes, from breakfast to savory toppings.

Probiotic yogurt is tasty and full of nutrients. It’s a good source of protein and calcium. These are important for health. The live cultures in yogurt help your gut and immune system.
There are many probiotic yogurts out there. Brands like Dannon’s Activia and Chobani Greek Yogurt are well-known. Artisanal options like Siggi’s Icelandic Style Skyr are also great. Adding probiotic yogurt to your diet can boost your health.
Kefir: A Potent Fermented Dairy Drink
Kefir is a special drink that’s full of good stuff for your health. It’s made by adding kefir grains to milk. These grains are a mix of bacteria and yeast. This makes kefir a stronger probiotic than yogurt.
Different Types of Kefir
There are many kinds of kefir:
- Dairy Kefir: This is the most common type, made from cow, goat, or sheep milk.
- Water Kefir: A dairy-free option, made by fermenting sugar water with kefir grains.
- Coconut Kefir: This one is fermented from coconut water or milk, giving a tropical flavor.
Nutritional Benefits of Kefir
Kefir is very nutritious. A 1 cup of low-fat kefir has:
- Protein: 9 grams
- Calcium: 36% of what adults need daily
- Phosphorus: 20% of what adults need daily
- Vitamin B12: 29% of what adults need daily
- Riboflavin (B2): 25% of what adults need daily
- Magnesium: 7% of what adults need daily
- Vitamin D: 12% of what adults need daily
Kefir has up to 61 strains of good bacteria and yeast. This makes it a great probiotic for your gut health.
How to Include Kefir in Your Diet
You can enjoy kefir on its own or in different ways:
- Drink kefir as a refreshing probiotic drink.
- Add kefir to smoothies, shakes, or overnight oats for extra nutrition.
- Use kefir as a base for dips, dressings, or marinades.
- Replace yogurt with kefir in baking recipes like muffins or cakes.
- Blend kefir with fruit for a tasty and healthy treat.
Adding kefir to your diet can help improve your gut health and overall health.
Foods to Boost Intestinal Health: Traditional Fermented Options
Traditional fermented foods are full of probiotics that help your gut. Buttermilk is one, left over from making butter. It has live probiotic cultures. Sauerkraut, made from fermented cabbage, is also good for your gut. It’s full of fiber, vitamins C and K, and good bacteria.
Pickles made the old way, in brine, are great for your gut too. These foods not only help your gut but also give you vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Choose unpasteurized fermented foods for the best probiotics. Pasteurization kills the live cultures. So, pick products that say they have active, live probiotics.

Eating different fermented foods can help your gut and overall health. By picking unpasteurized ones, you give your body lots of good probiotics.
Exploring Asian Probiotic Foods: Kimchi, Miso, and Tempeh
The Asian culinary world is full of probiotic-rich foods. These foods are not just tasty but also good for your gut. Kimchi from Korea, Miso from Japan, and Tempeh from Indonesia are just a few examples. They are a great way to improve your gut health.
Preparation Methods and Storage Tips
It’s important to prepare and store these foods right to keep their probiotics. Kimchi is made by fermenting veggies in a brine. This process takes days or weeks. Miso is fermented soybeans with a special mold. Tempeh is fermented soybeans with a starter culture.
Keeping the right temperature and conditions is key. This helps the good bacteria grow.
Cultural Significance and Usage
These foods are more than just probiotics. They hold deep cultural value. Kimchi is a big part of Korean meals. Miso soup is a Japanese favorite. Tempeh is a main protein in Indonesian dishes.
Adding these foods to your diet can boost your gut health. It also lets you explore Asian culinary traditions.

Asian probiotic foods open up a world of gut health benefits. They also bring vibrant flavors to your meals. These foods are a tasty and healthy way to improve your diet.
Sauerkraut and Other Fermented Vegetables
Sauerkraut and other fermented veggies are full of probiotics. The fermentation process keeps them fresh and adds good bacteria. Sauerkraut, for example, is packed with fiber, vitamins C and K, and antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin.
Other great fermented veggies include pickled cucumbers, carrots, and beets. They are low in calories but rich in nutrients. This makes them perfect for a healthy diet. Always choose unpasteurized fermented veggies to get live probiotics.
Fermented veggies can be used in many ways. They can be condiments, side dishes, or recipe ingredients. A 2018 study in Foods showed that sauerkraut’s good bacteria grow fast during fermentation. They stay good even when packaged for sale.
Adding sauerkraut and other probiotic veggies to your meals is easy and tasty. These foods are great for your gut health and overall well-being. They are true gut-friendly foods that help nourish your digestive system and support a healthy microbiome.
The Connection Between Probiotics and Mental Health
Research shows a strong link between gut health and mental well-being. This is called the gut-brain connection. Probiotics, found in fermented foods, may help support mental health and brain function.
Research on Gut-Brain Axis
The gut microbiome is a community of microorganisms in our digestive system. It affects the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. These chemicals are key to our mood and thinking.
Studies link gut imbalances to mental health issues like depression and anxiety. This shows how important our gut health is for our mind.
Impact on Mood and Cognitive Function
Eating foods rich in probiotics can help with depression and anxiety. A study found a 40% improvement in mood with probiotics. Symptoms of depression and anxiety also showed positive changes.
Probiotics can help with stress too. They kept cortisol levels stable, unlike the placebo group. This shows how probiotics can help our mental health.
Even though the research is promising, probiotics shouldn’t replace medical treatments. But, a diet rich in probiotics can help our overall health and well-being.
How to Incorporate Probiotic Foods into Your Daily Diet
Adding probiotic-rich foods to your diet is fun and good for your gut. Start with a yogurt parfait or a kefir smoothie for a morning boost. Use miso paste in soups, dressings, or marinades for flavor.
Try fermented veggies like kimchi and sauerkraut as side dishes or condiments. Tempeh, a fermented soy product, is great in stir-fries, salads, and sandwiches. Swap your drinks for kombucha for a probiotic-rich beverage.
Start slow with probiotic foods and mix them up for different bacteria. Add prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, and bananas for extra gut health. Sticking to a probiotic-rich diet helps your gut health and daily nutrition.
FAQ
What are probiotics and how do they benefit gut health?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that help our health. They improve digestion, reduce depression, and boost immunity. They are part of the gut microbiome, helping keep us healthy.
What are the common types of probiotics and their sources?
Common probiotics include Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Saccharomyces boulardii. You can find them in foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, miso, tempeh, kimchi, and kombucha.
What are the health benefits of consuming yogurt?
Yogurt is full of probiotics, offering many benefits. It helps with bone, heart, and digestion health. It also reduces diabetes risk and aids in weight management. Plus, it’s packed with protein, calcium, and more.
What are the unique features and benefits of kefir?
Kefir is a fermented milk drink with many beneficial bacteria and yeast. It’s more diverse than yogurt, improving bone and digestive health. It’s also good for those with lactose intolerance.
What are some traditional fermented foods that are rich in probiotics?
Foods like buttermilk, sauerkraut, and pickles are full of probiotics. They also have vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These foods support gut health and add unique flavors and cultural value.
What are the probiotic-rich foods found in Asian cuisines?
Asian foods like kimchi, miso, and tempeh are rich in probiotics. They support gut health and add unique flavors. It’s important to prepare and store them right to keep their benefits.
How do probiotics influence mental health and the gut-brain axis?
Probiotics link gut health to mental well-being, known as the gut-brain axis. They may help with depression and anxiety symptoms. The gut microbiome affects neurotransmitters like serotonin, impacting mood and thinking.
How can I easily incorporate probiotic-rich foods into my daily diet?
Start with yogurt or kefir in smoothies or oats. Use miso in soups and dressings. Add kimchi or sauerkraut as sides or condiments. Try tempeh as a meat substitute. Introduce these foods slowly and vary them for a wide range of benefits.














Leave a Comment