Kidney pain and back pain can feel similar. You must tell them apart to get the right care fast. Kidney pain often sits higher and deeper. Back pain often changes with movement. Look for fever, urine changes, or pain that moves to the groin. These clues point to the difference between kidney pain and back pain.
Table of Contents
ToggleBack Pain vs Kidney Pain Differences
You will learn clear signs that separate the two. Use location, type of pain, and extra symptoms to sort them out. Muscle strain hurts with motion. Kidney problems bring a steady, deep ache and may add fever. Knowing the difference between kidney pain and back pain helps you act right away.
Why It’s Important To Identify The Correct Source Of Pain
If you treat the wrong cause, you delay proper care. An infected kidney can get worse without antibiotics. A strained muscle improves with rest and simple exercises. You must spot whether the problem is kidney pain or a spine issue. Quick correct care lowers the risk of harm.
Key Difference Between Muscle Pain And Kidney-Related Pain
Muscle pain feels like tightness, soreness, or sharp pain when you move. It can ease with rest. Kidney pain feels deeper and steadier. It may not change when you move. If gentle tapping on your flank increases pain, the kidneys might be involved. These tests help show the real source.
When Both Types Of Pain Overlap
Sometimes you have both problems. A kidney stone can cause pain that your brain reads as back pain. A bad back can cause muscle guarding and pain that hides kidney signs. If symptoms do not fit neatly, get a medical test. Urine checks and imaging can find the true cause.
Kidney Pain Location vs Back Pain Location
Where you feel pain is a strong clue. You can use a simple self-check to tell the difference.
Where Kidney Pain Typically Occurs (Flank Area, Under Ribs)
Kidneys sit under your ribs on each side of the spine. Kidney pain usually shows in the flank. That is the side of the back under the rib cage. Pain may spread to the front of the belly or into the groin. If pain stays high and one-sided, think kidney.
Where Back Pain Is Usually Felt (Lower Back Or Spine)
Back pain most often appears lower, in the small of back. It can come from muscles, ligaments, joints, or discs. Pain may move into the buttocks or down a leg. Back pain often worsens with bending, lifting, or sitting.
How To Check If Your Pain Moves — Flank Pain Kidneys Vs Lower Back Pain
Try this at home. Stand up and bend forward slowly. Sit down, then stand. If movement changes your pain a lot, the cause likely comes from your back. If pain remains the same or comes in waves, suspect the kidney. If pain shoots to the groin, a stone might be moving. These simple checks help you decide.
Visual Guide: Identifying Pain Location Correctly
Place your hand under the last rib at your side. Press gently. If pressing the flank is painful, the kidney may be involved. Press along the spine. If the spine or muscles hurt more, the problem is likely a back issue. Use both checks. If unsure, see a clinician for tests.
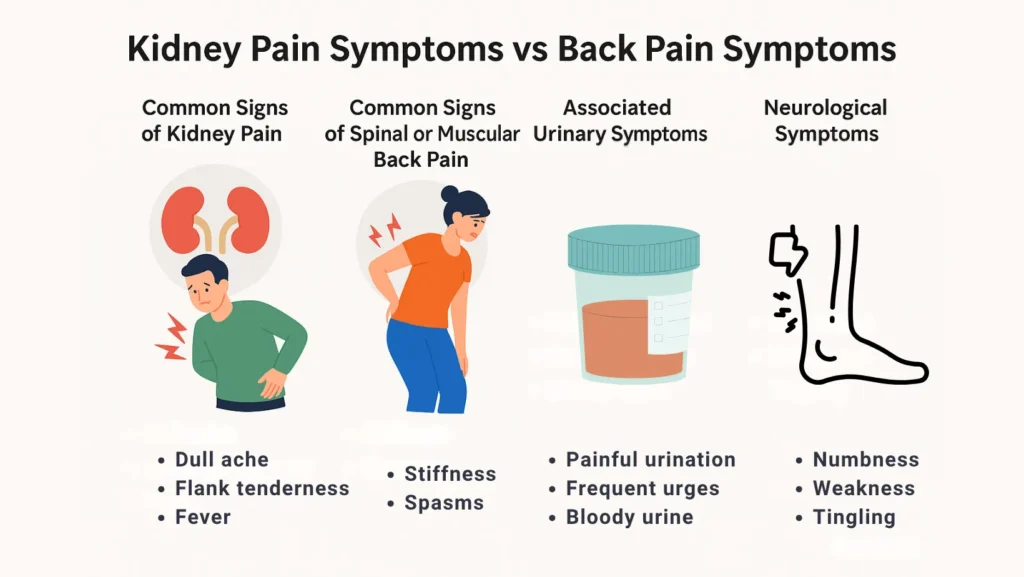
Kidney Pain Symptoms vs Back Pain Symptoms
Nausea and vomiting
Look beyond location. The full list of signs often shows the origin.
Common Signs Of Kidney Pain: Dull Ache, Flank Tenderness, Fever
Kidney pain symptoms often include a dull ache in the flank. You may also have tenderness when the area is tapped. Fever suggests infection. Nausea and vomiting may occur with stones. Blood in the urine or cloudy urine points strongly to a kidney cause.
Common Signs Of Spinal Or Muscular Back Pain: Stiffness, Spasms
Back pain symptoms include stiffness and muscle spasms. You may feel pain that worsens with certain moves. Nerve compression gives shooting pain, tingling, or numbness down the leg. This pattern points to a spine or nerve origin rather than a kidney cause.
Associated Urinary Symptoms That Indicate Kidney Involvement
If you have pain with burning when you pee, frequent urges to urinate, or bloody urine, think kidney or urinary tract problems. Fever with these urine signs is urgent. These kidney pain symptoms are strong clues that you need medical tests.
Neurological Symptoms That Suggest Spinal Or Nerve Back Pain
If you feel numbness, weakness, or tingling in a leg, the problem likely involves a nerve. Loss of bladder or bowel control is a red flag for serious spinal issues. These signs need immediate medical attention. They do not usually come from the kidney.
Flank Pain: Is It Your Kidneys Or Your Lower Back?
Flank pain means pain on the side between your ribs and hips. It has many causes. Use tests and symptom checks to learn what is wrong.
How To Identify Flank Pain From Kidney Issues
Kidney-related flank pain often feels deep and steady. It may spread toward your lower belly or groin. If it comes with fever or changes in urine, think kidney infection or stone. Pain that prevents you from finding a comfortable position can be a sign of stones.
How To Test If It’s Muscle-Related Pain
Move slowly. Twist your trunk. Press along the muscles near the pain. If the pain grows when you use the muscle or change posture, you likely have a muscle problem. Muscle pain usually improves with rest, heat, and gentle stretching. Use these clues to decide.
Kidney Pain vs Spinal Back Pain — Understanding The Root Cause
You can separate kidney pain from spinal pain by looking at how the trouble starts, how the pain spreads, and what signs appear with it. Spinal pain often follows a move, twist, lift, or long hours in one spot. Kidney pain often begins when an infection or a stone builds pressure inside the kidney. These patterns help you tell the difference between kidney pain and back pain in a clear way.
Kidney Pain Caused By Infection, Stones, Or Inflammation
Kidney infections form when bacteria travel up the urinary tract and reach the kidney. This causes swelling, heat, and steady kidney pain in the flank. You may feel fever, chills, or burning when you pass urine.
Kidney stones are tiny, hard crystals. When a stone moves, it blocks the flow of urine. This brings sharp waves of pain that may shoot to your groin. Inflammation inside the kidney, even without infection, can also cause pain that feels deep and constant.
These causes do not change much with posture and often pair with clear kidney pain symptoms.
Spinal Back Pain Caused By Disc Issues Or Muscle Strain
Disc problems happen when the soft cushion between the bones in your spine bulges. This can press on a nerve and cause sharp pain down the leg. Muscle strain shows up when a muscle gets pulled or overused.
The pain may feel like tightness or burning. It often worsens when you bend, lift, or twist. These patterns match back pain symptoms, not kidney issues. If the pain shifts with movement, the spine or muscles are likely the cause.
How Pain Radiates Differently In Each Condition
Pain from a kidney stone may move toward the lower belly or groin as the stone travels. Pain from the spine tends to follow a nerve path down the buttock and leg.
Kidney pain does not follow a nerve line. It stays closer to the flank or moves forward. Spinal pain can run in a straight line down one leg. These differences help you pick between kidney pain and spinal back pain.
Diagnostic Imaging Tests To Confirm The Source
Doctors may order an ultrasound or a CT scan when they suspect kidney pain. These tests can show stones, swelling, or blocked urine flow. When they suspect back pain, they may request X-rays or an MRI.
These tests show discs, nerves, and bones. Urine tests support kidney diagnosis, while nerve tests support spine diagnosis. Imaging confirms whether you face kidney pain or back pain from the spine.
Causes Of Kidney Pain vs Causes Of Back Pain
Common Kidney Related Causes: Stones, Infection, Obstruction
Kidney stones cause sudden, sharp pain. Infection causes fever and a dull ache. Obstruction happens when something blocks urine flow. Any of these can lead to constant or wave-like kidney pain.
Dehydration raises the risk of stones because the urine becomes more concentrated. Poor hygiene or untreated bladder infections raise the risk of kidney infection. These factors help explain why the pain begins and how it behaves.
Common Musculoskeletal Causes: Strain, Posture, Disc Herniation
Strain can come from lifting heavy objects or twisting too fast. Bad posture can stress the muscles over time. A disc herniation means the disc pushes outward and presses on a nerve. These problems lead to back pain that worsens with bending, lifting, or sitting too long. If pain rises with motion, the back is the likely source.
Risk Factors: Dehydration, Poor Posture, Or Existing Conditions
Lack of water raises stone risk. Sitting long hours raises back strain. Diabetes and weak immunity make kidney infections more likely. Weak core muscles also increase spine stress. These risks affect whether you deal with kidney pain or back pain.
How To Identify Kidney Pain At Home
You can use simple tests at home to narrow down the problem. These checks do not replace medical care but help you know when to act fast.
Changes In Urination Patterns
Watch for burning when you pee, cloudy urine, blood in your urine, or a strong smell. These problems match kidney pain symptoms, not muscle strain. If you feel flank pain and notice changes in urination, the kidneys may be the source.
Pain Radiating To the Abdomen Or Groin
If the pain travels toward your belly or groin, a stone may be on the move. This matches kidney pain more than a muscle problem. Stones often send pain in waves. Spine pain does not travel this way.
Fever, Nausea, Or Fatigue With Flank Pain
Fever with flank pain suggests infection. Nausea and tiredness also match kidney trouble. The difference between kidney pain and back pain can be tricky, but a fever is a strong kidney pain. Back issues rarely cause a rise in body temperature.
When To Visit A Doctor Or Get A Urine Test
You should seek care if pain is strong, keeps coming back, or pairs with fever. A urine test can show blood, bacteria, or crystals. These hint at stones or infection. Early tests bring early treatment and prevent damage.
Diagnosing Kidney Pain vs Back Pain
Medical Evaluation: Urine Tests, Imaging, And Blood Work
Doctors often begin with a urine dip test. It checks for blood or infection signs. Blood work checks kidney function. Imaging finds stones or spine issues. These tests help confirm the difference between kidney pain and back pain.
When To Consult A Nephrologist vs An Orthopedist
A nephrologist treats kidney diseases. You should see one if you have repeated infections or stones. An orthopedist treats bones and joints. You should see one if pain shoots down your leg, or if your back pain does not improve. These specialists help with both kidney pain and spinal back pain and spine problems.
What Your Doctor Will Look For In Imaging Scans
In kidney scans, they look for stones, swelling, or blocked flow. In spine scans, they look for disc bulges and nerve compression. These images show where the trouble begins and guide the right treatment path.
Treatment For Kidney Pain And Back Pain
Medical Treatments For Kidney Infections and Stones
Doctors use antibiotics for kidney infections. Stones may pass with water and pain medicine. If stones are too large, they may need a procedure to break them. These steps fall under treatment for kidney pain and back pain, but focus on kidney causes.
Home Remedies For Mild Kidney Discomfort
Water helps flush the kidneys. Warm packs may ease gentle pain. Do not use random herbal items without advice. If fever appears, seek care. Mild discomfort can improve, but strong pain needs medical support.
Physiotherapy And Rest For Spinal Back Pain
Spine pain often improves with rest, heat, gentle stretching, and physical therapy. A therapist can teach safe movements. Strong core muscles support the spine. These steps work well for back pain that comes from muscles and joints.
Preventive Lifestyle Tips For Both Conditions
Drink enough water daily. Sit with your spine straight. Take breaks from sitting. Use safe lifting habits. Exercise often to build core strength. These steps prevent both kidney strain and spine strain.
Prevention: How To Avoid Kidney And Back Pain Confusion
Staying Hydrated To Reduce Kidney Stone Risk
Drink enough water so your urine stays light in color. This lowers stone risk and reduces the chances of kidney pain.
Proper Posture And Spinal Alignment For Back Pain Prevention
Keep your back straight when you sit. Use supportive chairs. Stand up and stretch often. These habits prevent back pain caused by strain.
Regular Exercise And Core Strengthening
Strong muscles support your spine. Regular walking and core routines help prevent strain. Exercise also helps reduce stress that may tighten muscles.
When To Schedule Preventive Health Checkups
If you have repeated infections or serious back pain, schedule regular visits with your doctor. Early checks catch problems before they grow and help you avoid confusion between kidney pain vs back pain.
FAQs
How can I tell if my back pain is actually kidney pain?
You can tell by checking for flank pain, fever, and urine changes. If pain stays steady and sits under the ribs, the cause is more likely kidney pain and not a muscle strain.
What does kidney pain feel like compared to back pain?
Kidney pain feels deep and steady or sharp in waves. Back pain feels tight or sharp with movement. You can sort the difference between kidney pain and back pain by tracking motion and symptoms.
Where is kidney pain located on the body?
Kidney pain sits under the ribs on one or both sides. You may feel it in the flank or see it move toward the groin. This area matches common kidney pain location signs.
Can kidney pain cause back pain?
Kidney pain can feel like back pain because the kidneys sit near the spine. You can tell the cause by checking urine changes and fever. Pain that stays in the flank points to the kidneys.
Does kidney pain get worse when you move or sit?
Kidney pain usually stays the same when you move. Back pain changes with bending or lifting. This helps you judge the cause between kidney pain vs back pain issues.
Can muscle pain mimic kidney pain?
Muscle pain can mimic kidney pain because both occur in the back. Movement tests help you tell them apart. Muscle pain rises with motion, while kidney pain often stays constant.
How long does kidney pain last compared to muscle pain?
Kidney pain lasts until the infection or stone is treated. Muscle pain usually fades with rest and therapy. If pain does not ease, you may need tests to check the kidneys.
What is flank pain and what does it indicate?
Flank pain means pain on the side of your back below the ribs. It can signal kidney problems or muscle strain. Extra signs like fever or burning urine point to a kidney cause.
How do doctors test for kidney pain?
Doctors use urine tests, blood tests, and scans. These tests check for stones, infection, or swelling. They help confirm the difference between kidney pain and back pain clearly.
Is kidney pain always on one side?
Kidney pain can be on one side or both. Stones often hurt on one side. Infection can hurt on one or both. Use urine signs to judge the source.
Can kidney stones cause pain that feels like sciatica?
Kidney stones can cause sharp pain that radiates. Sciatica follows a nerve path down the leg. The two can feel alike but urine changes help you tell them apart.
Can dehydration cause kidney or back pain?
Dehydration can raise kidney stone risk and cause kidney pain. It can also cause muscle cramps that feel like back pain. Drink enough water to avoid both problems.

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, Board-Certified Neurologist, providing expert insights and reliable health information.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained neurologist with over a decade of experience. Known for his compassionate care, he specializes in treating neurological conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Dr. Chugh is highly regarded for his patient-centered approach and dedication to providing personalized care.