Ideal body weight is not just about the number on the scale. It is about health, energy, and lowering risk for diseases. The right balance helps people feel strong, active, and confident. Knowing how to calculate ideal body weight can guide both medical care and personal goals.
Table of Contents
ToggleLet’s look at every angle so you can understand what a healthy body weight really means.
What Is an Ideal Body Weight?
An ideal body weight is not a single number. Doctors look at weight ranges that reduce the chance of illness and improve daily living.
A good target weight supports your metabolic rate, keeps blood sugar stable, reduces pressure on the heart, and lowers risks of diabetes and hypertension. It also means better strength for everyday activities.
Your ideal body weight is a balance. It is not about being “skinny.” Instead, it is about staying in a healthy weight range that supports your organs, joints, and hormones.
How to Calculate Ideal Body Weight
The way you calculate ideal body weight depends on which tool you use. No single formula works for everyone. Doctors often use a combination of formulas, BMI, and waist checks.
Common formulas:
- Devine Formula: Created to calculate drug doses, now used for weight targets.
- Hamwi Method: Uses sex and height to set a basic weight.
- Robinson Formula: Offers slightly lower numbers for shorter people.
Example of Hamwi Formula
- For men: 48 kg + 2.7 kg for each inch over 5 ft.
- For women: 45.5 kg + 2.2 kg for each inch over 5 ft.
This formula is simple but does not account for body composition or bone size. That is why these numbers are guidelines, not strict rules.
Ideal Weight for Men and Women
Ideal weight for men and women hides complexity. Men tend to have more lean body mass and less fat for the same weight. Women carry more fat in hips and thighs for hormonal and reproductive needs.
A healthy range for men often skews higher than for women of the same height. Still, body build and genetics make the biggest difference. For example, two men at 70 kg may look very different if one has more muscle. That is why ideal weight for men and women must be treated as a range, not an exact figure.
Using an Ideal Weight Calculator
An ideal weight calculator makes the math easy. By typing in height, sex, and sometimes age, you get a weight range. Advanced calculators also show BMI, waist to hip ratio, and even waist to height ratio.
A reliable ideal weight calculator does not just give a number but compares several tools. For example, one might show:
- Hamwi result
- BMI result
- Waist-based result
This way, you can see overlap between them and find a realistic target.
Factors Affecting Your Ideal Body Weight
Your healthy body weight is influenced by much more than height and sex.
- Genes: Family history affects where fat is stored.
- Age: With age, muscle mass declines, lowering lean body mass.
- Sex hormones: Menopause, testosterone decline, or PCOS can alter fat storage.
- Medical conditions: Thyroid disorders, diabetes, or heart problems can affect weight.
- Lifestyle: Nutrition and exercise, sleep, and stress play direct roles.
- Medications: Steroids, antidepressants, or insulin may cause weight gain.
These factors explain why people of the same height may have different weight targets.
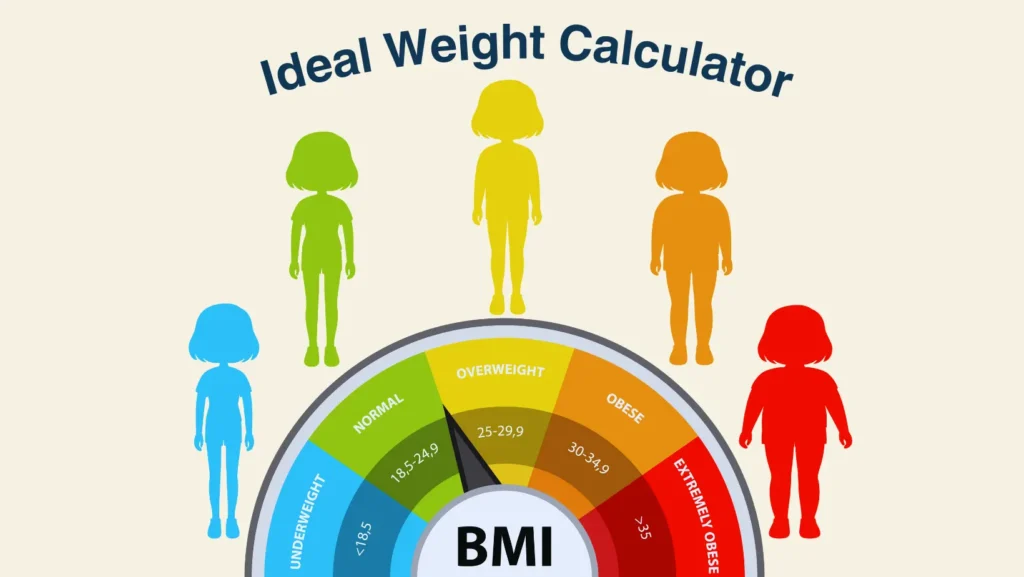
Body Mass Index (BMI) and Its Limitations
The body mass index (BMI) compares weight to height. It is often the first measure doctors check.
- Under 18.5 = underweight
- 18.5–24.9 = healthy
- 25–29.9 = overweight
- 30+ = obese
But BMI has serious limits. It cannot separate fat from muscle. A bodybuilder may have a high BMI but low body fat percentage. BMI also ignores fat location, which is critical. Belly fat carries higher health conditions risk compared to fat in thighs.
Thus, BMI is useful as a quick screen but not a final judgment.
Waist Circumference and Health Risks
Waist size tells us about fat around organs. This fat is linked with diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.
- Men with a waist circumference above 102 cm are at higher risk.
- Women with a waist circumference above 88 cm are at higher risk.
Unlike BMI, this measure directly shows underweight and overweight risks related to belly fat. People with a normal BMI but high waist size are still at risk.
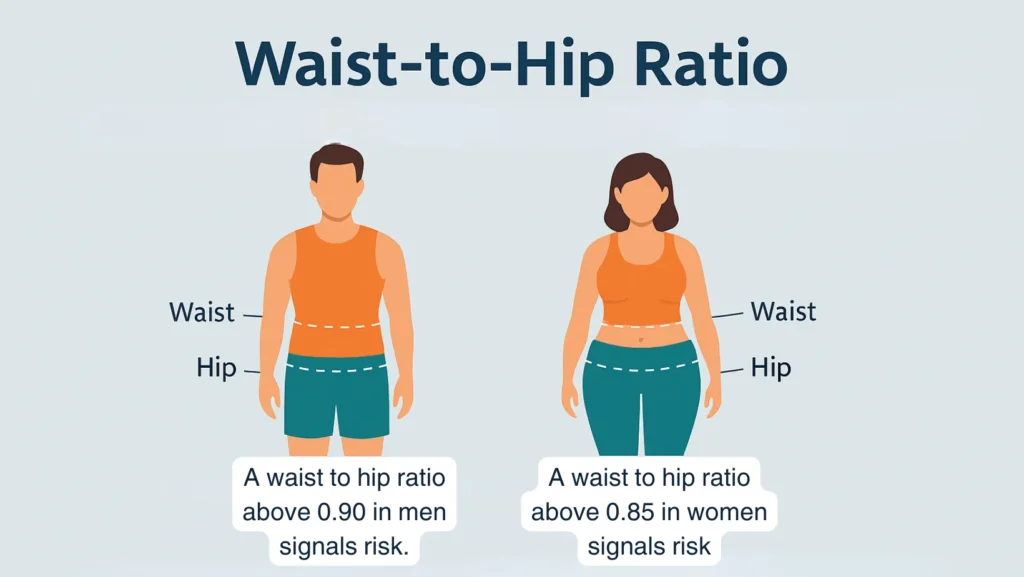
Waist-To-Hip Ratio (WHR)
The waist to hip ratio compares waist size with hip size. It shows fat distribution.
- A waist to hip ratio above 0.90 in men signals risk.
- A waist to hip ratio above 0.85 in women signals risk.
This tool predicts health problems like heart disease more accurately than BMI alone. Fat stored around the belly (apple shape) is more dangerous than fat stored around hips (pear shape).
Waist-To-Height Ratio (WHtR)
The waist to height ratio is even simpler. Keep waist less than half your height.
- Example: If you are 170 cm tall, your waist should stay below 85 cm.
This ratio is valuable across ethnic groups. It predicts risk of diabetes and hypertension earlier than BMI. A waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) above 0.5 is a red flag.
Body Composition and Why It Matters
Body composition tells us what weight is made of. A person may weigh 70 kg but with 15% body fat, while another weighs the same but has 35% body fat. Clearly, health risks differ.
- Muscle burns more calories at rest, making weight control easier.
- High body fat raises obesity and heart disease risk.
- Low muscle weakens mobility and balance in older adults.
Tracking body composition is far better than tracking weight alone.
Best Body Composition Scales
At home, the best body composition scale estimates fat, water, bone, and muscle. A good best body composition scale uses bioelectrical impedance (small safe current). The best body composition scale links to apps, letting users track weekly or monthly changes.
Examples include scales by Withings, Tanita, or Eufy. But results vary by hydration, meals, and time of day. For medical accuracy, DEXA scans or lab tests are better.
How Do I Achieve and Maintain a Healthy Body Weight?
Reaching a healthy body weight is not about quick fixes. It is about long-term weight management.
- Eat balanced meals with protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
- Avoid ultra-processed food and sugar spikes.
- Stay active with daily exercise.
- Track body fat percentage, not just the scale.
- Manage stress to prevent overeating.
When medical conditions interfere, consult doctors for tailored advice.
Focus on Long-Term Lifestyle Changes
Crash diets often fail. The key is to build a healthy lifestyle.
- Sleep 7–9 hours to control hunger hormones.
- Manage stress with yoga or breathing.
- Use small swaps like water instead of soda.
- Increase nutrition and exercise quality instead of cutting food drastically.
Slow, steady progress supports long-term obesity prevention.
Make the Process Fun and Sustainable
If the process feels like punishment, it will not last.
- Join group walks or dance classes.
- Try new recipes that taste good but fit your plan.
- Set small, trackable goals.
- Celebrate progress with non-food rewards like trips or books.
This keeps weight goals sustainable.
The Bottom Line
Your ideal body weight is not one number. It is a mix of BMI, waist measures, waist to height ratio, waist to hip ratio, and body composition. Together, these tools give a full picture.
Reaching a healthy body weight lowers risk of serious disease, keeps energy high, and supports a strong body. Instead of chasing perfection, aim for steady changes. Health comes from balance, not extremes.
FAQs
What is a healthy weight balance?
A healthy body weight balance means enough muscle and moderate fat, keeping energy high and lowering disease risk.
How to find your ideal healthy weight?
Use BMI, waist measures, and ideal weight calculator tools, then compare with your doctor’s advice.
What is meant by ideal body weight?
An ideal body weight means a weight range that supports health, energy, and reduced disease risk.
How do I balance my body weight?
Combine good food, daily activity, sleep, and stress control for lasting weight management.
Why is ideal weight important?
It lowers chances of diabetes, heart disease, and joint strain while supporting longer, healthier living.
What does a healthy balance look like?
Strong muscles, low belly fat, steady weight, and good daily energy are signs of a healthy balance.
When to use ideal body weight?
Doctors use it to guide nutrition and exercise, set medication doses, and plan safe weight loss.

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, Board-Certified Neurologist, providing expert insights and reliable health information.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained neurologist with over a decade of experience. Known for his compassionate care, he specializes in treating neurological conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Dr. Chugh is highly regarded for his patient-centered approach and dedication to providing personalized care.