Medically reviewed by Dr Chandril Chugh,
Renowned Neurologist and American Trained Specialist
Testicular cancer is a rare form of cancer that affects the testicles, the male reproductive organs responsible for producing sperm and testosterone. If you’re experiencing symptoms such as a lump or swelling in either testicle, heaviness in the scrotum, lower belly or groin ache, sudden swelling in the scrotum, pain or discomfort in a testicle or scrotum, enlargement or tenderness of the breast tissue, or back pain, it’s crucial to consult a doctor for further evaluation and diagnosis.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Takeaways:
- Testicular cancer primarily affects men between the ages of 15 and 45.
- Common symptoms include lumps or swelling in the testicles, scrotal heaviness, and pain or discomfort.
- Early detection and prompt medical attention are key to successful treatment.
- Treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
- Regular self-exams and surveillance appointments are important in monitoring for any recurrence or complications.
Understanding Testicular Cancer: Overview of the Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system plays a vital role in the production, storage, and transportation of sperm. Central to this system are the testicles, which are located in a protective pouch called the scrotum. The testicles have two primary functions: producing sperm and synthesizing the hormone testosterone, which is responsible for the development of male characteristics.
Sperm production occurs in the seminiferous tubules within the testicles. These tubules produce immature sperm cells that eventually mature and become capable of fertilizing an egg. The newly formed sperm cells then travel through a network of tubes called the epididymis, where they gain the ability to move.
During sexual stimulation, the sperm cells are expelled from the penis through a process called ejaculation. This process involves the contraction of the muscles surrounding the reproductive structures and the release of seminal fluid. Seminal fluid is a mixture of sperm and secretions from the seminal vesicles and prostate gland. Together, these fluids make up semen, facilitating the transport of sperm during intercourse.
The Structure of the Male Reproductive System:
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Testicles | Produce sperm and testosterone |
| Scrotum | Protective pouch for the testicles |
| Epididymis | Store and mature sperm |
| Semen Vesicles | Produce seminal fluid to nourish and protect sperm |
| Prostate Gland | Produce secretions that enhance sperm function |
| Penis | Expel urine and semen from the body |
Image:
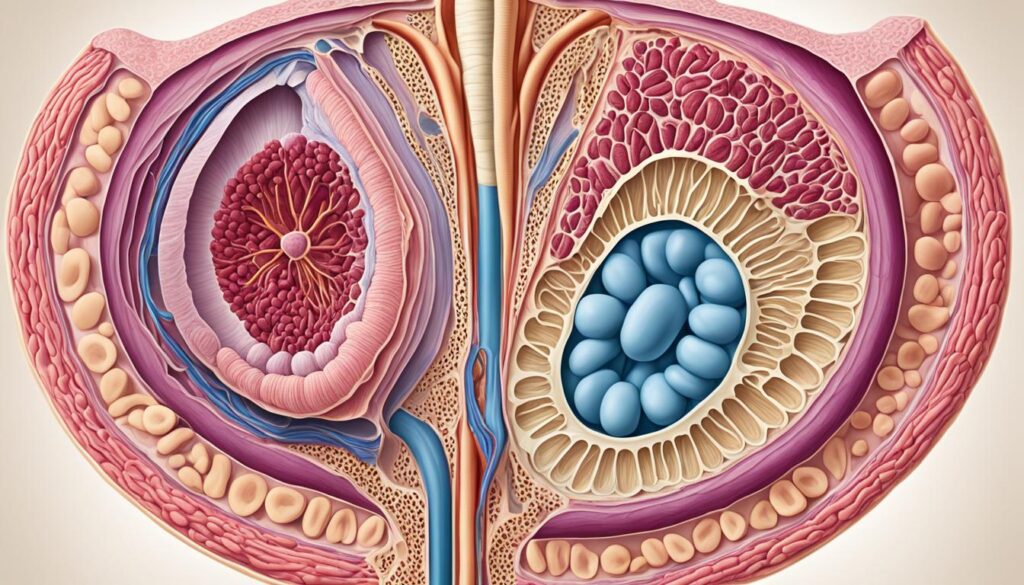
Unfortunately, the male reproductive system is also vulnerable to certain diseases, including testicular cancer. Testicular cancer originates in the testicles and can potentially spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. Understanding the structure and function of the male reproductive system is essential in recognizing the signs and symptoms of testicular cancer and ensuring early detection and prompt treatment.
“The male reproductive system is responsible for producing, storing, and transporting sperm. The testicles, located in the scrotum, produce sperm and the hormone testosterone. The sperm combines with fluids from the seminal vesicles and prostate gland to form semen, which is ejaculated during sexual intercourse. Testicular cancer originates in the testicles and can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. Treatments for testicular cancer may include surgery and chemotherapy.”
Recognizing the Symptoms of Testicular Cancer
If you are concerned about testicular cancer, it is important to be aware of its symptoms. The most common sign is the presence of testicular lumps or swelling. Additionally, you may experience other symptoms including:
- A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- A dull ache in the lower belly or groin
- Sudden swelling in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort in a testicle or scrotum
- Enlargement or tenderness of the breast tissue
- Back pain
It is important to remember that testicular cancer usually only occurs in one testicle. If you notice any of these symptoms persisting for more than two weeks, it is recommended to seek medical attention for further evaluation.
Early detection plays a crucial role in the successful treatment of testicular cancer. Being aware of the symptoms and seeking prompt medical care can lead to better outcomes. Regular self-exams and paying attention to any changes in your testicles can help in the early recognition of potential issues.
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors of Testicular Cancer
The exact cause of testicular cancer is unknown, but certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing the disease. Understanding these causes and risk factors can help individuals identify potential concerns and take necessary precautions.
Undescended Testicle
An undescended testicle, also known as cryptorchidism, is a condition where one or both testicles do not descend into the scrotum during fetal development. This condition increases the risk of testicular cancer. It is important to address undescended testicles early in life through medical intervention to reduce the risk.
Family History
If you have a family history of testicular cancer, particularly among first-degree relatives like your father or brother, you may be at higher risk. However, it is important to note that most cases of testicular cancer occur in individuals without a family history of the disease.
Age
Testicular cancer is more common in young adults, particularly between the ages of 15 and 45. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of testicular cancer during this age range and to seek medical attention if any concerns arise.
Race
White men have a higher risk of developing testicular cancer compared to men of other racial or ethnic backgrounds. The reasons for this racial disparity are not fully understood and require further research.
It is important to note that having these risk factors does not guarantee the development of testicular cancer, and individuals without any risk factors can still be affected by the disease. Regular self-examinations and seeking early medical attention for any concerning symptoms are essential for early detection and improved outcomes.

The Importance of Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection plays a vital role in the successful treatment of testicular cancer. By being proactive and performing regular testicular self-exams, you can help identify any changes or abnormalities in your testicles. While self-exams may not have definitive evidence of reducing the risk of mortality from testicular cancer, they function as a valuable tool for early detection.
To perform a testicular self-exam, follow these simple steps:
- Stand in front of a mirror and examine your scrotum for any swelling.
- Hold one testicle between your thumbs and fingers, gently rolling it to feel for any lumps or hardening.
- Repeat the process with the other testicle.
- Pay attention to any pain, swelling, or irregularities.
If you notice persistent symptoms such as pain, swelling, or lumps in your testicles or groin area, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Only a healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis through a thorough examination and further testing, if necessary.
Remember, early detection empowers you to take control of your health and increase the chances of successful treatment. Don’t ignore any unusual changes and always consult a medical professional for expert guidance and personalized care.
| Benefits of Early Detection | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Early initiation of treatment: | Persistent pain or discomfort in the testicles or scrotum |
| Higher chance of successful outcomes: | Painless lump or swelling in the testicles |
| Reduced risk of complications: | Heaviness in the scrotum |
| Peace of mind: | Enlargement or tenderness of breast tissue |
Treatment Options for Testicular Cancer
When it comes to testicular cancer, the good news is that it is highly treatable, even if it has spread to other parts of the body. The key to successful treatment lies in early detection and a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.
The treatment options for testicular cancer largely depend on factors such as the type and stage of the cancer. Let’s explore some of the most common treatment approaches:
Surgery
Surgery is one of the primary treatment options for testicular cancer. The goal of surgery is to remove the affected testicle, also known as an orchidectomy or radical inguinal orchiectomy. This procedure helps eliminate the source of cancer and may also involve the removal of nearby lymph nodes to prevent the spread of cancer cells.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It may be administered either before or after surgery, depending on the stage and extent of the cancer. Chemotherapy can be given orally or intravenously and is often delivered in cycles to allow the body time to recover between treatments. The type and duration of chemotherapy vary depending on individual factors, such as the size and location of the tumor and your overall health.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It can be used as a primary treatment for early-stage testicular cancer or in combination with surgery and/or chemotherapy. Radiation therapy is typically focused on the area where the tumor was located or on specific sites where the cancer may have spread. The duration and intensity of radiation therapy depend on the size and location of the tumor, as well as individual factors.
Surveillance
After completing the initial treatment, regular check-ups and monitoring are essential to ensure the cancer does not recur. Surveillance involves periodic physical exams, blood tests, and imaging studies such as CT scans and X-rays. This ongoing monitoring helps detect any signs of cancer recurrence at an early stage, allowing for timely intervention if needed.

Remember, the specific treatment plan for testicular cancer will be determined by your healthcare team based on several factors, including the stage and type of cancer, your overall health, and your preferences. It’s important to discuss your treatment options thoroughly with your healthcare provider to make informed decisions and ensure the best possible outcome.
Coping with Testicular Cancer: Fertility Preservation and Emotional Support
Testicular cancer and its treatments can have significant impacts on fertility and emotional well-being. It is imperative to explore options for fertility preservation with your healthcare provider if you desire to have children in the future. Sperm banking is a commonly recommended method to preserve fertility, providing you with the opportunity to conceive after treatment.
Furthermore, the removal of a testicle during treatment may affect the appearance of the scrotum. To restore the natural look, a testicular prosthesis can be considered. This custom-designed prosthesis can help restore confidence and self-esteem following testis removal.
Emotional support plays a crucial role in coping with the diagnosis and treatment of testicular cancer. It is essential to seek support from loved ones, friends, or support groups who can provide understanding, companionship, and encouragement throughout your journey. Counseling services are also available to help manage the emotional challenges associated with testicular cancer.
Fertility Preservation Options
Discussing fertility preservation options with your healthcare provider before treatment is vital. Several methods can help preserve fertility:
- Sperm Banking: This involves collecting and freezing your sperm for future use. It is a simple procedure that can be done before starting cancer treatment. Your stored sperm can be used for assisted reproductive techniques, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), to achieve pregnancy.
Testicular Prosthesis
If you undergo testis removal, a testicular prosthesis can be implanted to restore the natural appearance of the scrotum. The prosthesis is made of silicone or saline and is custom-designed to match the remaining testicle. It is a cosmetic solution that provides physical and psychological comfort.
Emotional Support
Receiving emotional support during your testicular cancer journey is vital. Consider the following sources of emotional support:
- Loved Ones and Support Groups: Reach out to family, friends, or support groups who can offer understanding, empathy, and encouragement. Connecting with others who have had similar experiences can provide a sense of solidarity and shared strength.
- Counseling: Professional counseling can help you navigate the emotional challenges of testicular cancer. A counselor can provide a safe and supportive space to express your feelings, address fears and anxieties, and develop healthy coping strategies.
Remember, seeking emotional support is not a sign of weakness but rather a proactive step toward holistic well-being.

Testicular Cancer and Surveillance: Regular Check-ups and Monitoring
After undergoing treatment for testicular cancer, it is crucial to prioritize regular check-ups and monitoring to detect any signs of recurrence or potential complications. Surveillance plays a vital role in ensuring the cancer does not return, allowing for timely intervention if needed.
Surveillance involves a comprehensive approach, including:
- Physical exams: Your healthcare provider will conduct regular physical examinations to assess the status of your testicles and surrounding areas.
- Tumor marker tests: Blood tests may be performed to measure the levels of specific proteins or substances that can indicate the presence or progression of testicular cancer.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasounds and CT scans are commonly used to visualize the testicles and surrounding tissues, providing detailed insights for monitoring purposes.
The frequency of surveillance appointments may vary depending on the stage and type of testicular cancer. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate schedule for your specific situation based on factors such as treatment response, individual risk factors, and medical history.
Adhering to the recommended surveillance schedule is crucial, as it allows for the early detection of any changes or relapse, increasing the chances of successful treatment and long-term remission. Regular monitoring provides peace of mind and ensures that any potential issues are promptly addressed.
It’s important to prioritize your health and well-being by attending regular check-ups and monitoring appointments. Your healthcare team is here to support you throughout your testicular cancer journey and provide the necessary care and guidance.
| Surveillance Approaches for Testicular Cancer: | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular physical exams | Allows for the assessment of testicular health and identification of any abnormalities or changes |
| Tumor marker tests | Provides insights into the progression of testicular cancer and helps in detecting recurrences at an early stage |
| Imaging tests (ultrasounds and CT scans) | Enables visualization of the testicles and surrounding tissues, aiding in the detection of any potential issues |
Regular check-ups and vigilant monitoring are essential components of post-treatment care for testicular cancer. By staying proactive and committed to surveillance, you can ensure the ongoing health of your testicles and take necessary actions if any concerns arise.
Additional Treatment Options for Testicular Cancer
If you have been diagnosed with testicular cancer, there are additional treatment options that may be recommended based on your individual case. These treatment options aim to further prevent the spread of cancer cells and target the affected areas. Two common additional treatment options include:
Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND)
Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of lymph nodes in the abdomen. This procedure is performed to prevent the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body. By removing the retroperitoneal lymph nodes, the risk of cancer recurrence or metastasis is reduced.
During the RPLND procedure, a surgeon makes an incision in the abdomen and carefully removes the lymph nodes. The extent of lymph node removal may vary depending on the stage and location of the cancer. This surgical intervention is typically recommended for certain types and stages of testicular cancer and is performed under general anesthesia.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a treatment option that involves the use of high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It may be utilized for testicular cancer to target cancer cells in the testis or nearby lymph nodes.
In radiation therapy, a radiation oncologist carefully plans and delivers precise radiation doses to the affected area. The radiation damages the DNA of the cancer cells, preventing them from multiplying and eventually leading to their destruction. Radiation therapy may be administered externally, where a machine directs radiation beams to the target area, or internally, where radioactive materials are placed directly into the body near the cancer cells.
The specific treatment approach, whether it is RPLND, radiation therapy, or a combination of both, depends on various factors, including the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the individual’s overall health status. Your healthcare provider will determine the most suitable treatment option for your specific case.
It is crucial to discuss the potential benefits, risks, and side effects of these treatment options with your healthcare provider. They will provide you with detailed information and guide you through the decision-making process based on your unique circumstances and preferences.
Testicular Cancer Prevention and Research
While there are currently no known ways to prevent testicular cancer, ongoing research aims to better understand its causes and develop strategies for prevention. Staying informed about the latest research findings is vital in the quest to reduce the risk of this disease. Additionally, following recommendations for risk reduction can make a significant difference in early detection and successful treatment.
Research for Testicular Cancer Prevention
Researchers worldwide are actively investigating various factors associated with testicular cancer and its prevention. Some ongoing studies focus on:
- Understanding the genetic and environmental factors contributing to testicular cancer development
- Identifying potential biomarkers and genetic markers for early detection
- Exploring the impact of lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise on risk reduction
By furthering our understanding of these aspects, researchers hope to develop effective prevention strategies that can help reduce the incidence of testicular cancer.
Risk Reduction and Early Detection
While prevention measures are not yet available, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of testicular cancer. Regular self-exams play an essential role in early detection. By performing self-exams, you can familiarize yourself with the normal size, shape, and consistency of your testicles, making it easier to identify any changes that may occur.
If you notice any abnormalities during a self-exam or experience symptoms such as lumps, pain, or swelling in your testicles, it is crucial to seek early medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and timely treatment greatly increase the chances of successful outcomes.
“Early detection is key in the fight against testicular cancer. By being proactive in monitoring your health and seeking medical help when needed, you can take control of your well-being and improve your chances of a positive prognosis.” – Dr. Rajesh Gupta, Oncologist
Risk Reduction Strategies
| Risk Factor | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|
| Undescended Testicles | Early treatment and monitoring for undescended testicles in infancy and childhood |
| Family History | Regular self-exams and increased vigilance if there is a family history of testicular cancer |
| Age | Regular self-exams starting from adolescence and continuing into adulthood |
| Race | Regular self-exams for all racial groups, as testicular cancer can occur in individuals of any race |
While these risk reduction strategies do not guarantee prevention, they serve as proactive measures to enhance early detection and improve outcomes.

Testicular cancer prevention is an active area of research, and through ongoing studies and individual efforts, we can strive to reduce the impact of this disease on future generations. By staying informed, taking proactive steps to reduce risk, and seeking early medical attention, you can contribute to the prevention of testicular cancer and the overall improvement of men’s health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, testicular cancer is a relatively rare form of cancer that primarily affects young men. It is crucial to be aware of the signs and symptoms associated with testicular cancer, such as testicular lumps, swelling, and pain. Regular check-ups and prompt medical attention are essential for early detection and appropriate treatment.
Fortunately, testicular cancer has a high cure rate when diagnosed and treated early. This highlights the importance of proactive self-exams and open communication with your healthcare provider. Remember, a timely diagnosis can significantly increase your chances of a successful recovery.
Dealing with testicular cancer can be emotionally and physically challenging. It is important to seek support from your loved ones or support groups to navigate the journey. Stay informed about the latest research and prevention strategies, and remember that you are not alone in this fight against testicular cancer.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of testicular cancer?
Symptoms of testicular cancer include a lump or swelling in either testicle, a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, a dull ache in the lower belly or groin, sudden swelling in the scrotum, pain or discomfort in a testicle or scrotum, enlargement or tenderness of the breast tissue, and back pain.
What are the causes and risk factors of testicular cancer?
The exact cause of testicular cancer is unknown, but risk factors include having an undescended testicle, a family history of testicular cancer, being a young adult (particularly between the ages of 15 and 45), and being of white race.
How can testicular cancer be detected early?
Early detection of testicular cancer is crucial for successful treatment. Regular testicular self-exams can help in identifying any changes or abnormalities in the testicles. It is also important to seek medical attention for further evaluation if you experience persistent symptoms such as pain, swelling, or lumps in your testicles or groin area.
What are the treatment options for testicular cancer?
Treatment options for testicular cancer may include surgery to remove the affected testicle and chemotherapy to kill cancer cells. Other treatments such as radiation therapy and surveillance may also be used depending on the individual’s diagnosis and the extent of the cancer.
How does testicular cancer affect fertility and emotional well-being?
Testicular cancer and its treatments can impact fertility. It is important to discuss fertility preservation options with your healthcare provider before undergoing treatment if you wish to have children in the future. Emotional support, including counseling and support groups, can also be beneficial in coping with the diagnosis and treatment of testicular cancer.
How often should I have check-ups and monitoring after treatment?
Regular check-ups and monitoring are essential after treatment to detect any recurrence or complications. The frequency of surveillance appointments may vary depending on the stage and type of testicular cancer.
What are the additional treatment options for testicular cancer?
Additional treatment options for testicular cancer may include retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND), a surgical procedure to remove lymph nodes in the abdomen, and radiation therapy to kill cancer cells in the testis or nearby lymph nodes.
Can testicular cancer be prevented?
Currently, there are no known ways to prevent testicular cancer. However, ongoing research aims to better understand the causes and develop strategies for prevention. It is important to stay informed about the latest research findings and follow recommendations for risk reduction.
How can I cope with testicular cancer?
Coping with testicular cancer involves discussing fertility preservation options with your healthcare provider, considering emotional support such as counseling and support groups, and maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider and loved ones.
